之前学习过的SQL语句笔记总结戳这里→【数据库原理与应用 - 第六章】T-SQL 在SQL Server的使用_Roye_ack的博客-CSDN博客
目录
一、DQL 数据查询
1、基本查询
2、条件查询
3、分组查询
(1)聚合函数
① count函数
② max min avg sum函数
(2)分组查询
① where和having的区别
(3)排序查询
(4)分页查询
(5)案例
① if 和 case
二、多表设计
1、一对多 - 外键
① SQL 语句
② IDEA图形化操作
2、一对一
3、多对多
4、案例
一、DQL 数据查询

1、基本查询
*号代表查询所有字段,但不直观,影响效率(开发中尽量少用)
-- 查询name,entrydate
select name,entrydate from tb_emp;-- 查询所有字段
select * from tb_emp;-- 查询所有员工的name,entrydate,并起别名(姓名,入职日期)
select name as 姓名,entrydate as 入职日期 from tb_emp;-- 查询员工所在的职位类型(不重复)
select distinct job from tb_emp;2、条件查询
like 占位符 (_匹配单个字符,%匹配任意字符)
-- 查询name为杨逍的员工
select * from tb_emp where name='杨逍';-- 查询id≤5的员工信息
select * from tb_emp where id<=5;-- 查询没有分配职位的员工信息
select * from tb_emp where job is null;-- 查询有职位的员工信息
select * from tb_emp where job is not null;-- 查询密码不等于123456的员工信息
select * from tb_emp where password<>'123456';-- 查询入职日期在[2000-01-01,2010-01-01]的员工信息
select * from tb_emp where entrydate >= '2000-01-01' and entrydate <= '2010-01-01';select * from tb_emp where entrydate between '2000-01-01' and '2010-01-01';-- 查询入职日期在[2000-01-01,2010-01-01]且性别为女的员工信息
select * from tb_emp where entrydate between '2000-01-01' and '2010-01-01' and gender=2;-- 查询职位是2或3或4的员工信息
select * from tb_emp where job in (2,3,4);-- 查询姓名是两个字的员工信息
select * from tb_emp where name like '__';-- 查询姓张的员工信息
select * from tb_emp where name like '张%';3、分组查询
(1)聚合函数
将一列数据作为一个整体,进行纵向运算
不对null值进行统计
select 聚合函数(字段列表) from 表名
函数 功能
count 统计数量 max 最大值 min 最小值 avg 平均值 sum 求和
① count函数
推荐使用count(*)
-- 1. 统计该企业员工数量
-- A.count(字段)
select count(id) from tb_emp;-- B.count(常量)
select count('A') from tb_emp;-- C.count(*) -- 推荐!
select count(*) from tb_emp;② max min avg sum函数
-- 2. 统计该企业员工 ID 的平均值
select avg(id) from tb_emp;-- 3. 统计该企业最早入职的员工
select min(entrydate) from tb_emp;-- 4. 统计该企业最迟入职的员工
select max(entrydate) from tb_emp;-- 5. 统计该企业员工的 ID 之和
select sum(id) from tb_emp;(2)分组查询
select 字段列表 from 表名 [where 条件] group by 分组字段名 [having 分组过滤后的条件]where > 聚合函数 > having,where不能对聚合函数进行判断,having可以
① where和having的区别
- 执行时机不同:where是分组前过滤,不满足where,不参与分组;having是分组之后对结果进行过滤
- 判断条件不同:having可以对聚合函数进行判断,where不行
分组后,查询字段一般为聚合函数和分组字段,查询其他字段无意义
-- 分组
-- 1. 根据性别分组 , 统计男性和女性员工的数量
select gender,count(*) from tb_emp group by gender;-- 2. 先查询入职时间在 '2015-01-01' (包含) 以前的员工 , 并对结果根据职位分组 , 获取员工数量大于等于2的职位
select job,count(*) from tb_emp where entrydate <= '2015-01-01' group by job having count(*)>=2;(3)排序查询
select 字段列表 from 表名 [where 条件] [group by 分组字段名] order by 字段1 排序方式1,字段2 排序方式2...
- ASC 升序(默认值)
- DESC 降序
-- 1. 根据入职时间, 对员工进行升序排序
select * from tb_emp order by entrydate asc;-- 2. 根据入职时间, 对员工进行降序排序
select * from tb_emp order by entrydate desc;-- 3. 根据 入职时间 对公司的员工进行 升序排序 , 入职时间相同 , 再按照 更新时间 进行降序排序
select * from tb_emp order by entrydate, update_time desc;(4)分页查询
select 字段列表 from 表名 limit 起始索引,查询记录数;
- 起始索引 = (页码 - 1)* 每页展示记录数
- 如果查询的是第1页数据,则可以省略索引
- 先查询再排序!
-- 1. 从起始索引0开始查询员工数据, 每页展示5条记录
select * from tb_emp limit 0,5;-- 2. 查询 第1页 员工数据, 每页展示5条记录
select * from tb_emp limit 0,5;-- 3. 查询 第2页 员工数据, 每页展示5条记录
select * from tb_emp limit 5,5;-- 4. 查询 第3页 员工数据, 每页展示5条记录
select * from tb_emp limit 10,5;(5)案例
-- 按需求完成员工管理的条件分页查询 - 根据输入条件,查询第一页数据,每一页展示10条记录
-- 输入条件:
-- 姓名:张
-- 性别:男
-- 入职时间:2000-01-01 2015-12-31
-- 要求查询结果根据最后修改时间进行倒序排序
-- 支持分页查询
select *
from tb_emp
where name like '张%'and gender = 1and entrydate between '2000-01-01' and '2015-12-31'
order by update_time desc
limit 10;① if 和 case
- if (条件表达式,true取值,false取值)
- case 表达式 when 值1 then 结果1 when值2 then 结果2 ... else 结果n end
-- 按需求完成员工的性别统计 -- count(*)
-- if(条件表达式,true取值,false取值)
select if(gender = 1, '男', '女') as 性别, count(*) as 人数
from tb_emp
group by gender;-- 按需求完成员工的职位信息统计 -- count(*)
-- case 表达式 when 值1 then 结果1 when值2 then 结果2 ... else 结果n end
select (case jobwhen 1 then '班主任'when 2 then '讲师'when 3 then '学工主管'when 4 then '教研主管'else '未分配职位' end) 职位, count(*)人数
from tb_emp
group by job;
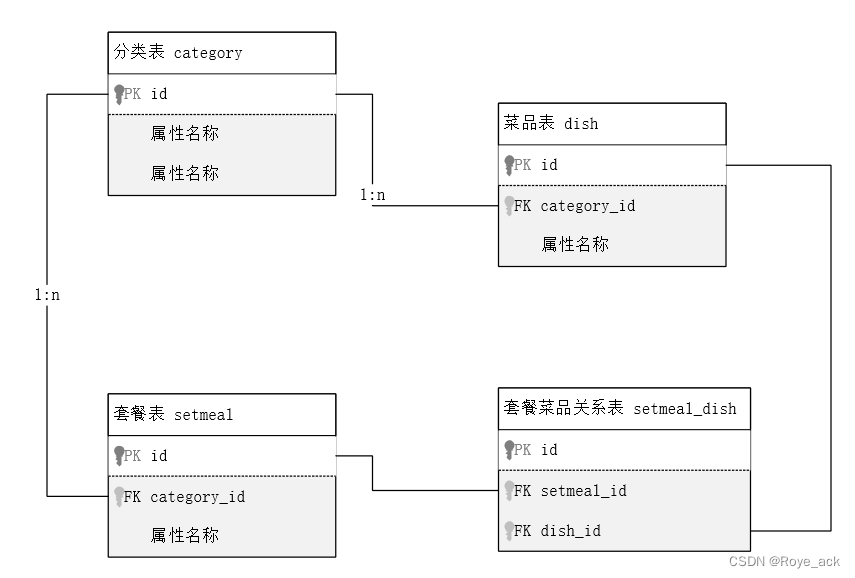
二、多表设计
1、一对多 - 外键
在作为【多】的表中将【一】的主键设置为外键
① SQL 语句
create table 表名(字段名 数据类型,...constraint 外键名称 foreign key (外键字段名) reference 主表(字段名)
);-- 指定完表后添加外键
alter table 表名 add constraint 外键名称 foreign key (外键字段名) reference 主表(字段名)② IDEA图形化操作
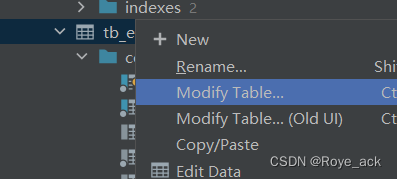



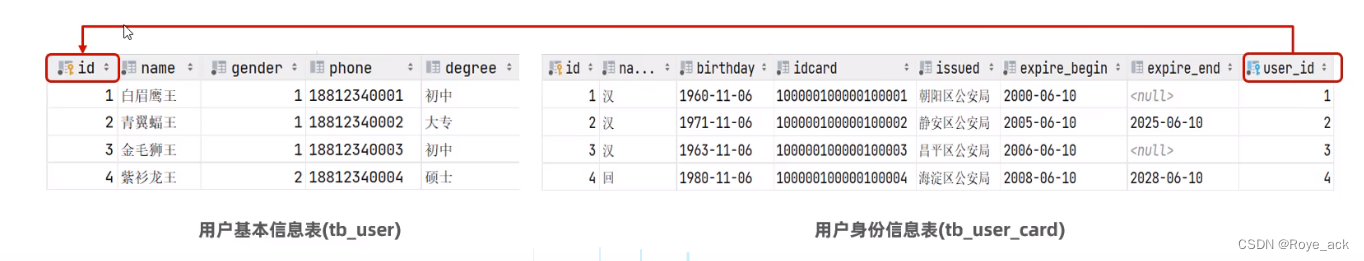
2、一对一
在任意一方加入外键,关联另一方的主键,并设置外键为唯一的unique
3、多对多
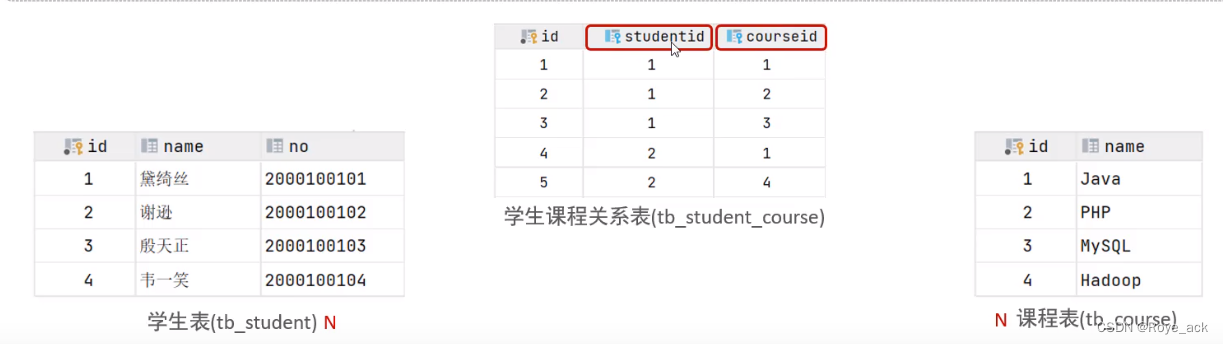
建立一个中间表,该表包含两个外键,分别关联两方主键
4、案例