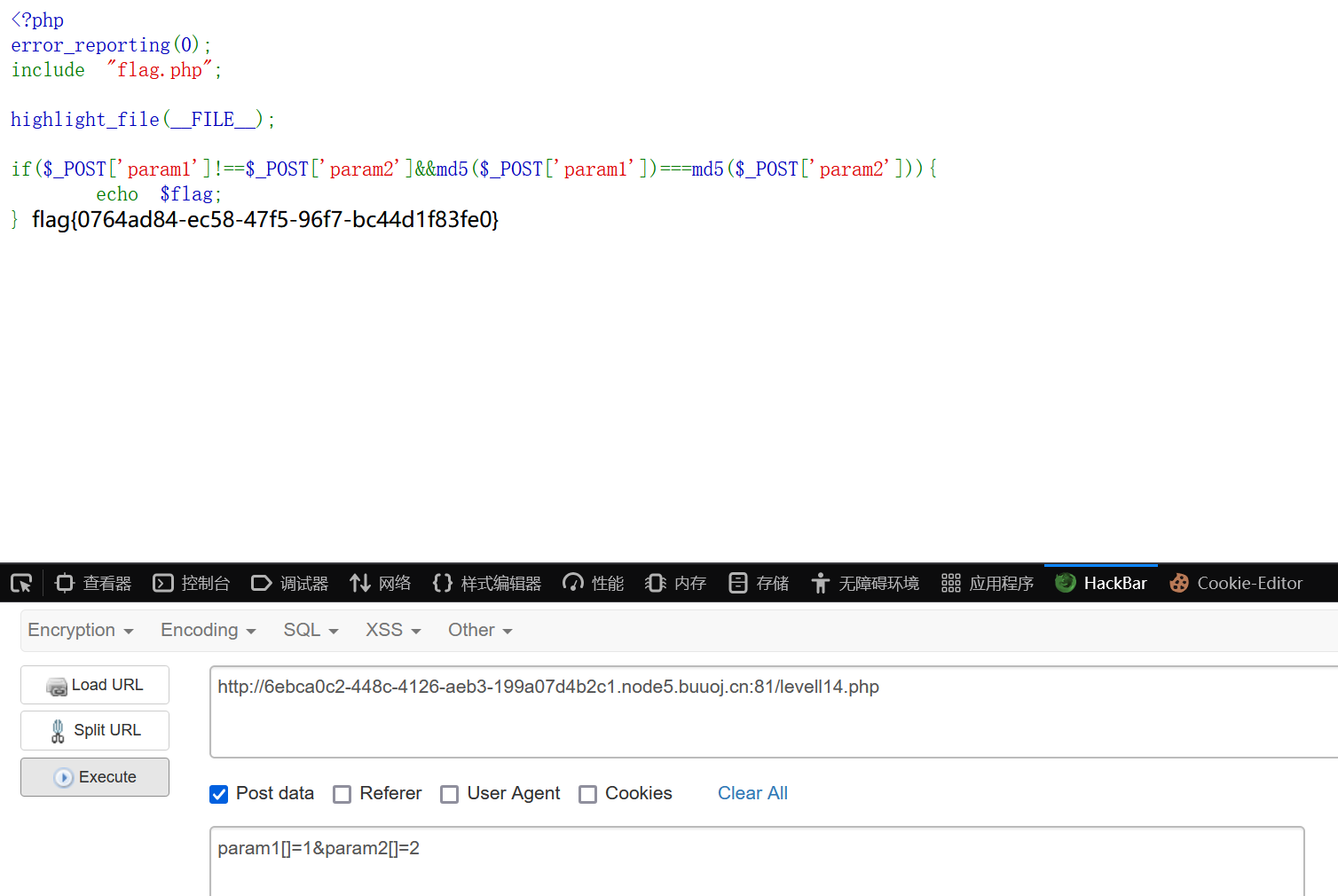
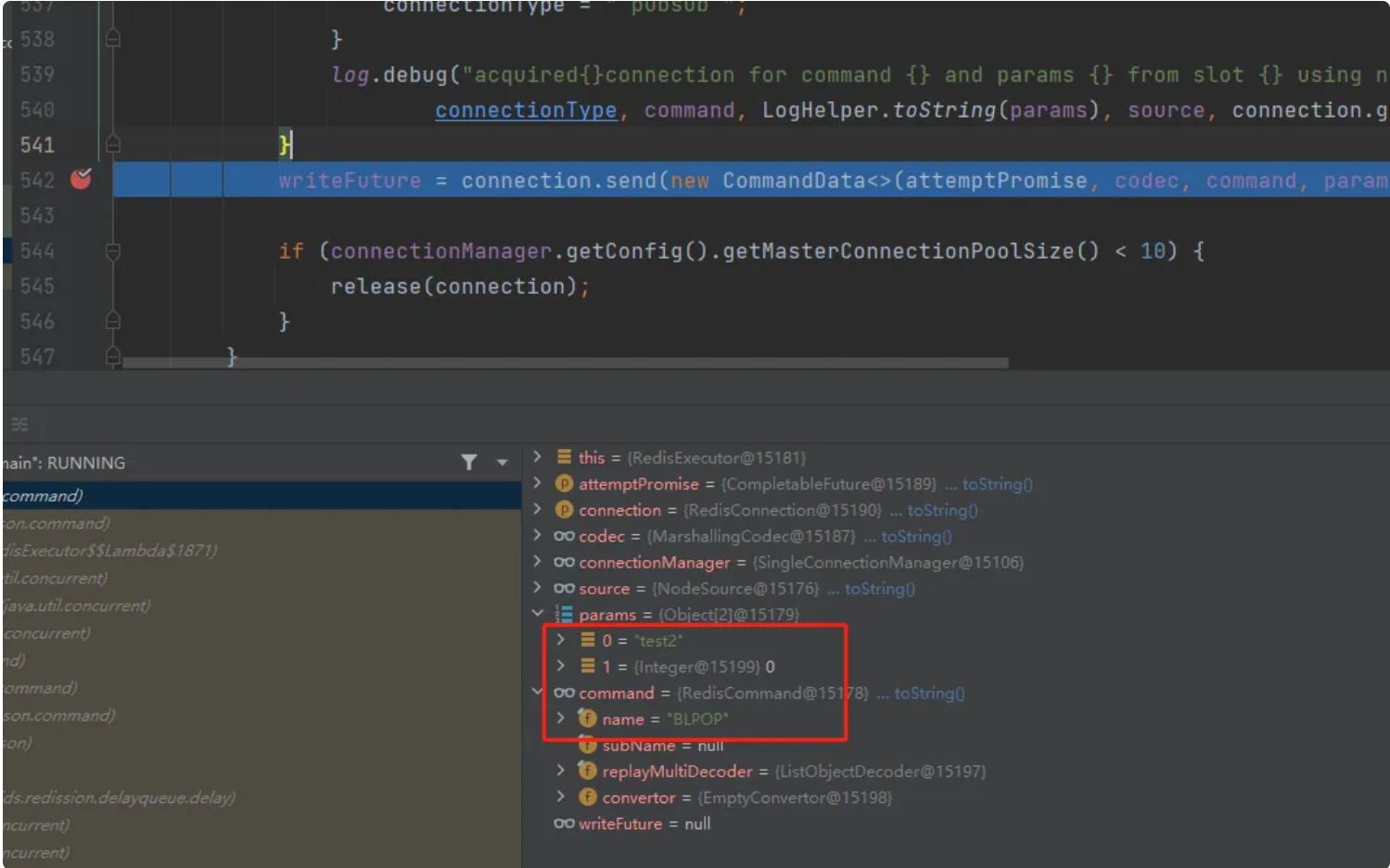
题目
题目链接
解题思路
-
插入操作:
- 创建一个新节点。
- 如果链表为空,直接将新节点作为头节点。
- 遍历链表,找到第一个值为
x的节点,在其前插入新节点。 - 如果没有找到
x,将新节点插入到链表末尾。
-
删除操作:
- 如果链表为空,直接返回。
- 如果头节点的值为
x,直接删除头节点。 - 遍历链表,找到第一个值为
x的节点,删除该节点。
-
输出链表:
- 遍历链表输出每个节点的值。
- 如果链表为空,输出 "NULL"。
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;struct ListNode {int val;ListNode* next;ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
};class LinkedList {
private:ListNode* head;public:LinkedList() : head(nullptr) {}void insert(int x, int y) {ListNode* newNode = new ListNode(y);if (!head) {head = newNode;return;}if (head->val == x) {newNode->next = head;head = newNode;return;}ListNode* prev = nullptr;ListNode* curr = head;while (curr && curr->val != x) {prev = curr;curr = curr->next;}if (prev) {newNode->next = prev->next;prev->next = newNode;} else {newNode->next = head;head = newNode;}}void deleteNode(int x) {if (!head) return;if (head->val == x) {ListNode* temp = head;head = head->next;delete temp;return;}ListNode* prev = nullptr;ListNode* curr = head;while (curr && curr->val != x) {prev = curr;curr = curr->next;}if (curr) {prev->next = curr->next;delete curr;}}void printList() {if (!head) {cout << "NULL" << endl;return;}ListNode* curr = head;while (curr) {cout << curr->val << " ";curr = curr->next;}cout << endl;}
};int main() {int n;cin >> n;LinkedList list;string op;while (n--) {cin >> op;if (op == "insert") {int x, y;cin >> x >> y;list.insert(x, y);} else if (op == "delete") {int x;cin >> x;list.deleteNode(x);}}list.printList();return 0;
}
import java.util.Scanner;class ListNode {int val;ListNode next;ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
}class LinkedList {private ListNode head;public LinkedList() {head = null;}public void insert(int x, int y) {ListNode newNode = new ListNode(y);if (head == null) {head = newNode;return;}if (head.val == x) {newNode.next = head;head = newNode;return;}ListNode prev = null;ListNode curr = head;while (curr != null && curr.val != x) {prev = curr;curr = curr.next;}if (prev != null) {newNode.next = prev.next;prev.next = newNode;} else {newNode.next = head;head = newNode;}}public void deleteNode(int x) {if (head == null) return;if (head.val == x) {head = head.next;return;}ListNode prev = null;ListNode curr = head;while (curr != null && curr.val != x) {prev = curr;curr = curr.next;}if (curr != null) {prev.next = curr.next;}}public void printList() {if (head == null) {System.out.println("NULL");return;}ListNode curr = head;while (curr != null) {System.out.print(curr.val + " ");curr = curr.next;}System.out.println();}
}public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);int n = sc.nextInt();LinkedList list = new LinkedList();for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {String op = sc.next();if (op.equals("insert")) {int x = sc.nextInt();int y = sc.nextInt();list.insert(x, y);} else if (op.equals("delete")) {int x = sc.nextInt();list.deleteNode(x);}}list.printList();}
}
class ListNode:def __init__(self, x):self.val = xself.next = Noneclass LinkedList:def __init__(self):self.head = Nonedef insert(self, x, y):new_node = ListNode(y)if not self.head:self.head = new_nodereturnif self.head.val == x:new_node.next = self.headself.head = new_nodereturnprev = Nonecurr = self.headwhile curr and curr.val != x:prev = currcurr = curr.nextif prev:new_node.next = prev.nextprev.next = new_nodeelse:new_node.next = self.headself.head = new_nodedef delete(self, x):if not self.head:returnif self.head.val == x:self.head = self.head.nextreturnprev = Nonecurr = self.headwhile curr and curr.val != x:prev = currcurr = curr.nextif curr:prev.next = curr.nextdef print_list(self):if not self.head:print("NULL")returncurr = self.headwhile curr:print(curr.val, end=" ")curr = curr.nextprint()# 读取输入
n = int(input())
linked_list = LinkedList()for _ in range(n):op = input().strip().split()if op[0] == "insert":x, y = int(op[1]), int(op[2])linked_list.insert(x, y)elif op[0] == "delete":x = int(op[1])linked_list.delete(x)linked_list.print_list()
算法及复杂度分析
算法:
- 链表的基本操作
时间复杂度:
-
插入操作(insert):\(\mathcal{O}(n)\)
- 需要遍历链表找到插入位置
- 最坏情况下需要遍历整个链表
-
删除操作(delete):\(\mathcal{O}(n)\)
- 需要遍历链表找到要删除的节点
- 最坏情况下需要遍历整个链表
-
打印操作(print_list):\(\mathcal{O}(n)\)
- 需要遍历整个链表输出所有节点
-
总体时间复杂度:\(\mathcal{O}(qn)\)
- \(q\) 是操作次数
- \(n\) 是链表长度
- 每个操作最坏情况下都需要遍历整个链表
空间复杂度:
-
链表存储:\(\mathcal{O}(n)\)
- \(n\) 是链表的节点数
- 每个节点需要存储值和指针
-
其他变量:\(\mathcal{O}(1)\)
- 只需要少量额外变量来处理操作
-
总体空间复杂度:\(\mathcal{O}(n)\)
- 主要由链表本身的存储空间决定