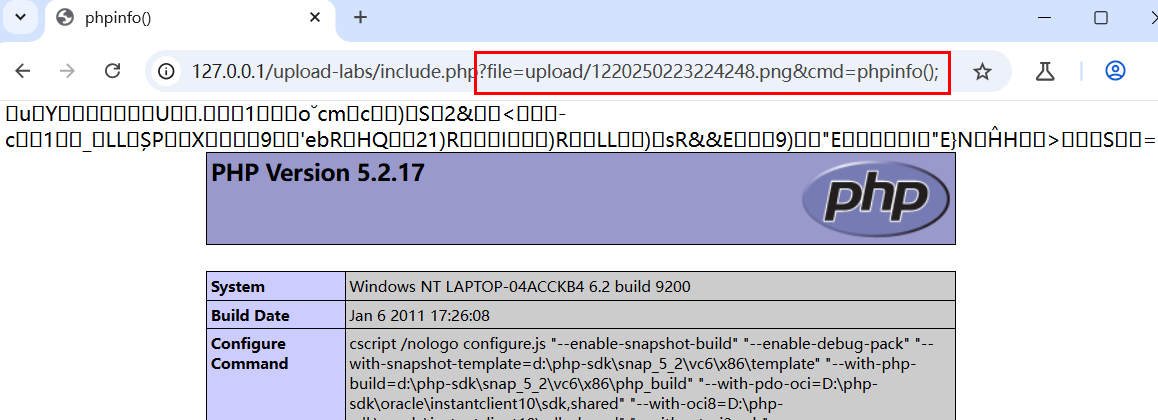
lab1
这次作业主要完成两个类 StreamReassembler 和 ByteStream。我的思路是每读入数据就O(n)扫一遍,用map维护每个index对应的数据,用一个指针指向当前需要写入值的位置,不断向后移动。原本没深刻认识到overleap的含义,记录的是整串string,然而测试数据相当于把一个字符串随机剁碎,字符串反而不好维护。
这是第三个版本,能过94%,15/16。没过的因为lab0的历史遗留问题,连接CS144官网时会connection reset by peer。
stream_reassembler.hh
#ifndef SPONGE_LIBSPONGE_STREAM_REASSEMBLER_HH
#define SPONGE_LIBSPONGE_STREAM_REASSEMBLER_HH#include "byte_stream.hh"#include <cstdint>
#include <climits>
#include <string>
#include <set>
#include <map>using std::string;
using std::map;//! \brief A class that assembles a series of excerpts from a byte stream (possibly out of order,
//! possibly overlapping) into an in-order byte stream.
class StreamReassembler {private:// Your code here -- add private members as necessary.size_t _capacity; //!< The maximum number of bytesmap<size_t,char>store;ByteStream _output; //!< The reassembled in-order byte streamsize_t reassembleByte = 0;size_t unAssemble = 0;int lastIndex = -1;public://! \brief Construct a `StreamReassembler` that will store up to `capacity` bytes.//! \note This capacity limits both the bytes that have been reassembled,//! and those that have not yet been reassembled.StreamReassembler();StreamReassembler(const size_t capacity);//! \brief Receives a substring and writes any newly contiguous bytes into the stream.//!//! If accepting all the data would overflow the `capacity` of this//! `StreamReassembler`, then only the part of the data that fits will be//! accepted. If the substring is only partially accepted, then the `eof`//! will be disregarded.//!//! \param data the string being added//! \param index the index of the first byte in `data`//! \param eof whether or not this segment ends with the end of the streamvoid push_substring(const std::string &data, const uint64_t index, const bool eof);//! \name Access the reassembled byte stream//!@{const ByteStream &stream_out() const { return _output; }ByteStream &stream_out() { return _output; }//!@}//! The number of bytes in the substrings stored but not yet reassembled//!//! \note If the byte at a particular index has been submitted twice, it//! should only be counted once for the purpose of this function.size_t unassembled_bytes() const;//! \brief Is the internal state empty (other than the output stream)?//! \returns `true` if no substrings are waiting to be assembledbool empty() const;
};#endif // SPONGE_LIBSPONGE_STREAM_REASSEMBLER_HHstream_reassembler.cc
#include "stream_reassembler.hh"
#include <iostream>
// Dummy implementation of a stream reassembler.// For Lab 1, please replace with a real implementation that passes the
// automated checks run by `make check_lab1`.// You will need to add private members to the class declaration in `stream_reassembler.hh`template <typename... Targs>
void DUMMY_CODE(Targs &&... /* unused */) {}using namespace std;/*
size_t _capacity; //!< The maximum number of bytesset<dataNode>s;map<size_t,int>submited;ByteStream _output; //!< The reassembled in-order byte streamsize_t reassembleByte = 0;bool isEof = false;
*/
StreamReassembler::StreamReassembler(const size_t capacity) : _capacity(capacity), store(), _output(capacity) {// 构造函数体可以为空,因为成员变量都已在初始化列表中初始化}//! \details This function accepts a substring (aka a segment) of bytes,
//! possibly out-of-order, from the logical stream, and assembles any newly
//! contiguous substrings and writes them into the output stream in order.void StreamReassembler::push_substring(const string &data, const size_t index, const bool eof) {size_t len = data.length();for(size_t i = 0;i < len;i++){if(store.find(index+i) != store.end() ) {}else store[index+i] = data[i],unAssemble++;}if(eof == true) lastIndex = index + len;while(store.find(reassembleByte) != store.end()){_output.write(std::string(1,store[reassembleByte]));unAssemble--;reassembleByte++;}if(lastIndex != -1 && static_cast<int>(reassembleByte) == lastIndex ){_output.end_input();}}size_t StreamReassembler::unassembled_bytes() const { return unAssemble; }// myTodo
bool StreamReassembler::empty() const { return unAssemble == 0; }byte_stream.hh
#ifndef SPONGE_LIBSPONGE_BYTE_STREAM_HH
#define SPONGE_LIBSPONGE_BYTE_STREAM_HH#include <cstddef>
#include <cstdint>
#include <deque>
#include <list>
#include <string>
#include <utility>
#include <deque>
//! \brief An in-order byte stream.//! Bytes are written on the "input" side and read from the "output"
//! side. The byte stream is finite: the writer can end the input,
//! and then no more bytes can be written.
class ByteStream {private:// Your code here -- add private members as necessary.size_t capacity;std::deque<char> buffer;size_t writtenByte = 0;size_t readByte = 0;bool endInput = false;bool _error{}; //!< Flag indicating that the stream suffered an error.public://! Construct a stream with room for `capacity` bytes.ByteStream(const size_t capacity);//! \name "Input" interface for the writer//!@{//! Write a string of bytes into the stream. Write as many//! as will fit, and return how many were written.//! \returns the number of bytes accepted into the streamsize_t write(const std::string &data);//! \returns the number of additional bytes that the stream has space forsize_t remaining_capacity() const;//! Signal that the byte stream has reached its endingvoid end_input();//! Indicate that the stream suffered an error.void set_error() { _error = true; }//!@}//! \name "Output" interface for the reader//!@{//! Peek at next "len" bytes of the stream//! \returns a stringstd::string peek_output(const size_t len) const;//! Remove bytes from the buffervoid pop_output(const size_t len);//! Read (i.e., copy and then pop) the next "len" bytes of the stream//! \returns a vector of bytes readstd::string read(const size_t len) {const auto ret = peek_output(len);pop_output(len);return ret;}//! \returns `true` if the stream input has endedbool input_ended() const;//! \returns `true` if the stream has suffered an errorbool error() const { return _error; }//! \returns the maximum amount that can currently be read from the streamsize_t buffer_size() const;//! \returns `true` if the buffer is emptybool buffer_empty() const;//! \returns `true` if the output has reached the endingbool eof() const;//!@}//! \name General accounting//!@{//! Total number of bytes writtensize_t bytes_written() const;//! Total number of bytes poppedsize_t bytes_read() const;//!@}
};#endif // SPONGE_LIBSPONGE_BYTE_STREAM_HHbyte_stream.cc
#include "byte_stream.hh"#include <algorithm>
#include <iterator>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <iostream>
// Dummy implementation of a flow-controlled in-memory byte stream.// For Lab 0, please replace with a real implementation that passes the
// automated checks run by `make check_lab0`.// You will need to add private members to the class declaration in `byte_stream.hh`template <typename... Targs>
void DUMMY_CODE(Targs &&... /* unused */) {}using namespace std;ByteStream::ByteStream(const size_t Capacity):capacity(Capacity),buffer(){ }size_t ByteStream::write(const string &data) {size_t len = data.length();size_t bufferLeft = capacity - buffer.size();size_t i;for(i = 0;i < len && bufferLeft;i++,bufferLeft--){writtenByte++;buffer.push_back(data[i]);}return i;
}//! \param[in] len bytes will be copied from the output side of the buffer
string ByteStream::peek_output(const size_t len) const {size_t i;std::string s = "";for(i = 0;i < min(len,buffer.size());i++){s.push_back(buffer[i]);}return s;
}//! \param[in] len bytes will be removed from the output side of the buffer
void ByteStream::pop_output(const size_t len) { size_t i;for(i = 0;i < len;i++){readByte++;buffer.pop_front();}}void ByteStream::end_input() { endInput = true; }bool ByteStream::input_ended() const { return endInput; }size_t ByteStream::buffer_size() const { return buffer.size(); }bool ByteStream::buffer_empty() const { return buffer.empty(); }bool ByteStream::eof() const { return endInput && buffer.empty(); }size_t ByteStream::bytes_written() const { return writtenByte; }size_t ByteStream::bytes_read() const { return readByte; }size_t ByteStream::remaining_capacity() const { return capacity - buffer.size(); }