文章目录
- 一、RestClient
- 1、什么是RestClient
- 2、导入demo工程
- 3、数据结构分析与索引库创建
- 4、初始化JavaRestClient
- 二、RestClient操作索引库
- 1、创建索引库
- 2、删除索引库
- 3、判断索引库是否存在
- 三、RestClient操作文档
- 1、新增文档
- 2、查询文档
- 3、修改文档
- 4、删除文档
- 5、批量导入文档
一、RestClient
1、什么是RestClient
ES官方提供了各种不同语言的客户端,用来操作ES,即RestClient。这些客户端的本质就是组装DSL语句,通过http请求发送给ES。
官方文档地址:
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/client/index.html
2、导入demo工程
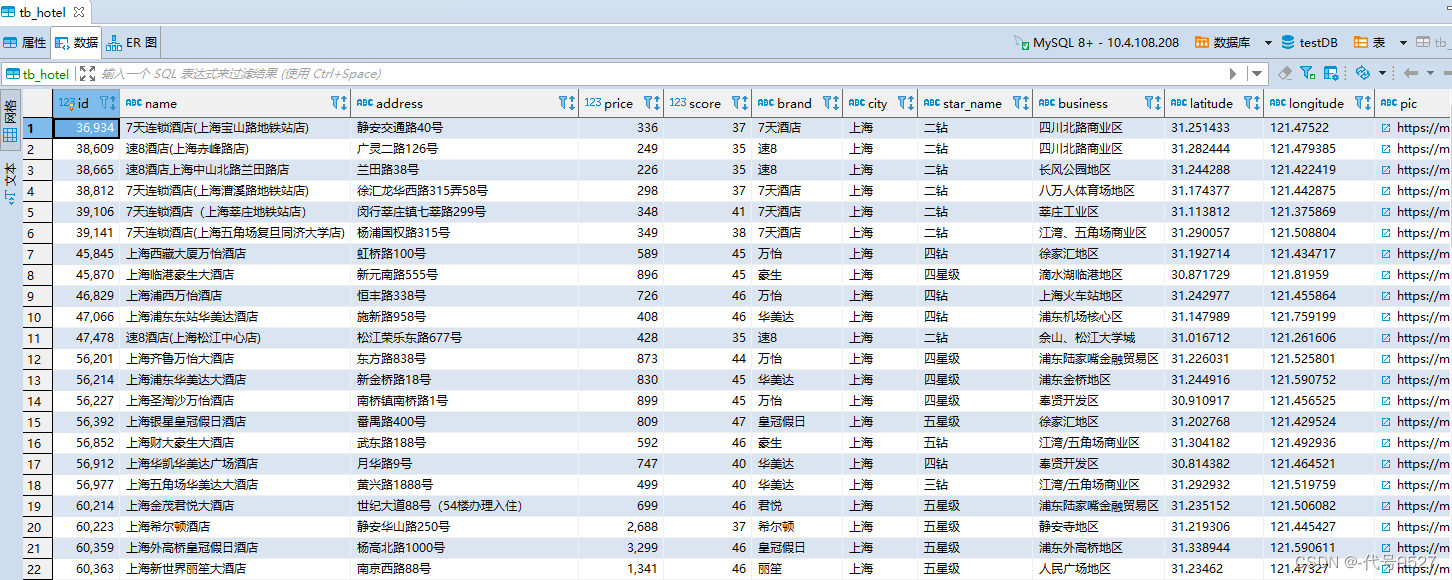
数据库信息如下:
mysql -h localhost -P3306 -uroot -padmian123 testDB < tb_hotel.sql
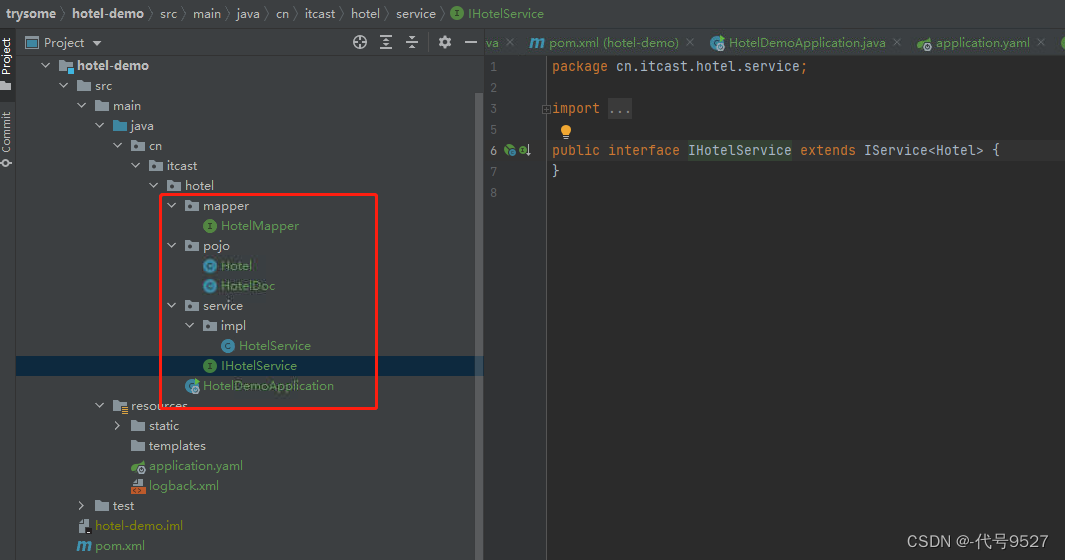
导入demo工程,基本结构如下:
3、数据结构分析与索引库创建
ES的mapping要考虑的点主要有:
- 字段名(name)
- 字段类型(type)
- 是否参与搜索(index)
- 是否分词(type/keyword)
- 分词时,分词器用哪种(analyzer)
接下来,照着表结构,创建ES索引库:
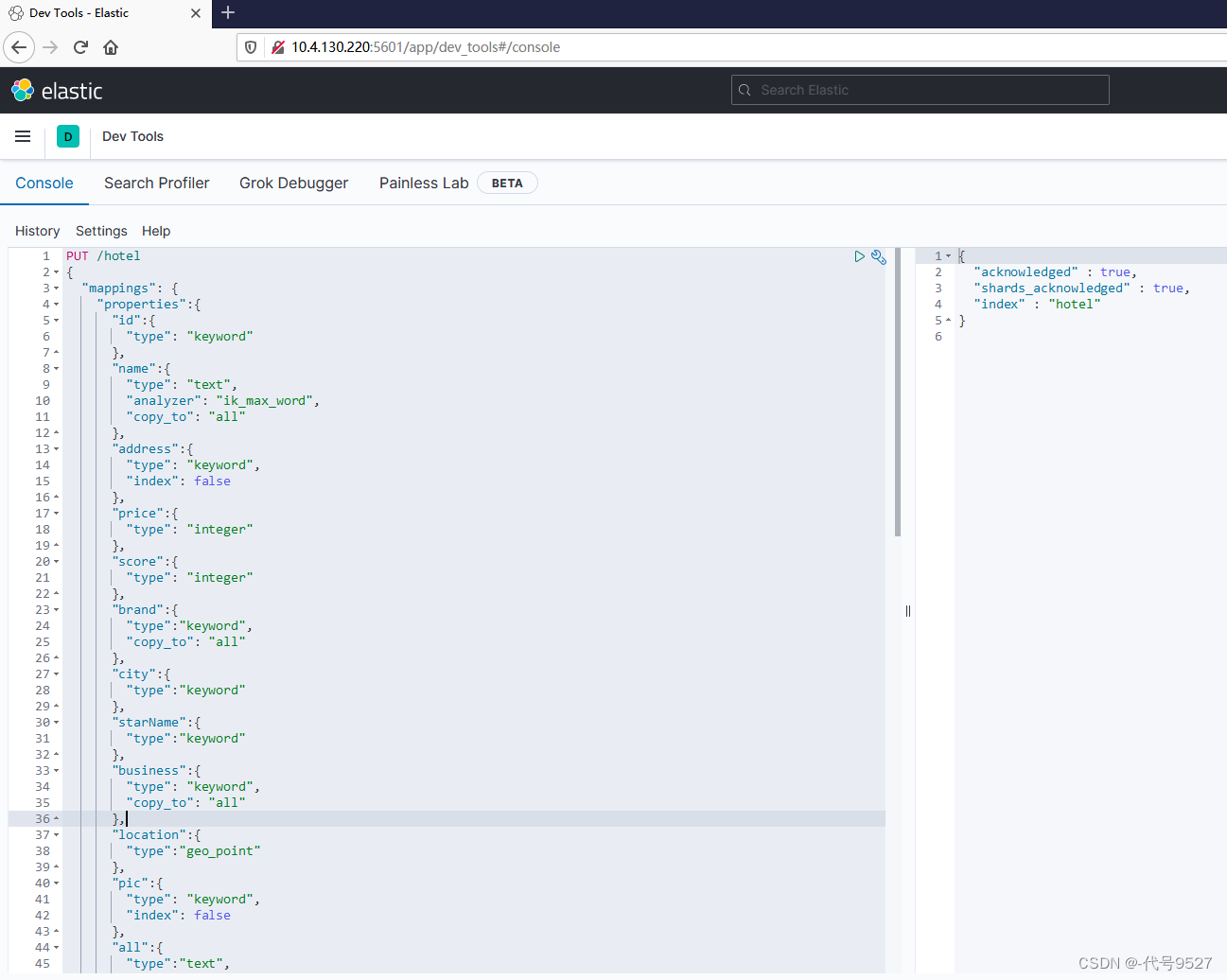
PUT /hotel
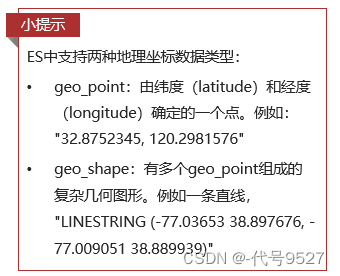
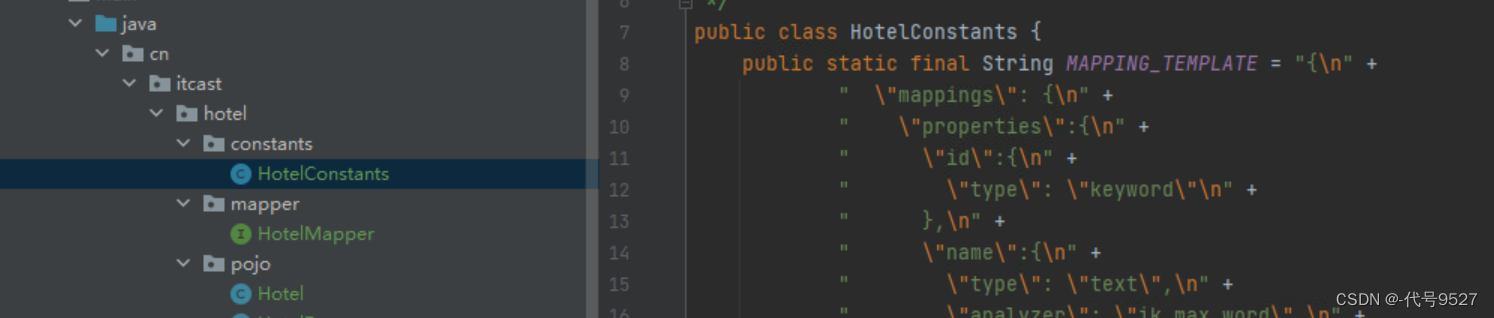
{"mappings": {"properties":{"id":{"type": "keyword" //注意这个类型},"name":{"type": "text","analyzer": "ik_max_word","copy_to": "all"},"address":{"type": "keyword", "index": false //根据业务场景,用户刚来,不会去搜地址address,不参与搜索,index改为false,不再默认,类型选用keyword},"price":{"type": "integer"},"score":{ //price、score等将来要参与过滤和排序,需要index,用默认的true"type": "integer"},"brand":{ //city、brand品牌参与搜索,且不分词"type":"keyword","copy_to": "all"},"city":{"type":"keyword"},"starName":{ //不用下划线"type":"keyword"},"business":{"type": "keyword","copy_to": "all"},"location":{"type":"geo_point" //经纬度两个字段合并为location,用ES的特定类型geo_point},"pic":{"type": "keyword","index": false //pic既不分词,也不搜索},"all":{ //copy_to用的"type":"text","analyzer": "ik_max_word"}}}
}
用户就输入一个虹桥,我既想返回地址带虹桥的,也想返回商圈在虹桥的,还想返回酒店名称带虹桥的,如何实现?
加all字段,给需要的字段里加上从copy_to,这样all字段就可以代表这些加了copy_to的字段。
实现了在一个字段里搜到多个字段的内容。

4、初始化JavaRestClient
- 引入es的RestHighLevelClient依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId> <artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client</artifactId>
</dependency>- 因为SpringBoot下默认的ES版本是7.6.2,所以我们需要定义properties覆盖默认的ES版本
<properties> <java.version>1.8</java.version> <elasticsearch.version>7.12.1</elasticsearch.version>
</properties>- 初始化RestHighLevelClient
RestHighLevelClient client = new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder( HttpHost.create("http://10.4.130.110:9200"),HttpHost.create("http://10.4.130.111:9200"),HttpHost.create("http://10.4.130.112:9200") //集群模式写多个
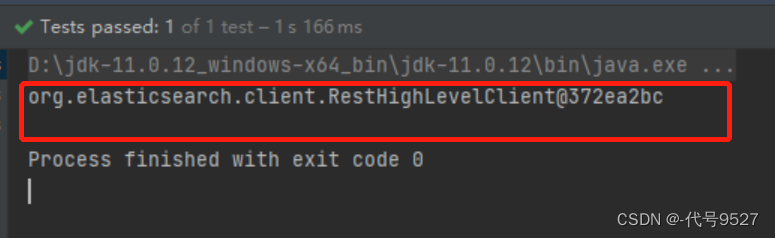
));在单元测试里看下效果,打印restHighLevelClient对象:
二、RestClient操作索引库
1、创建索引库
示例代码:
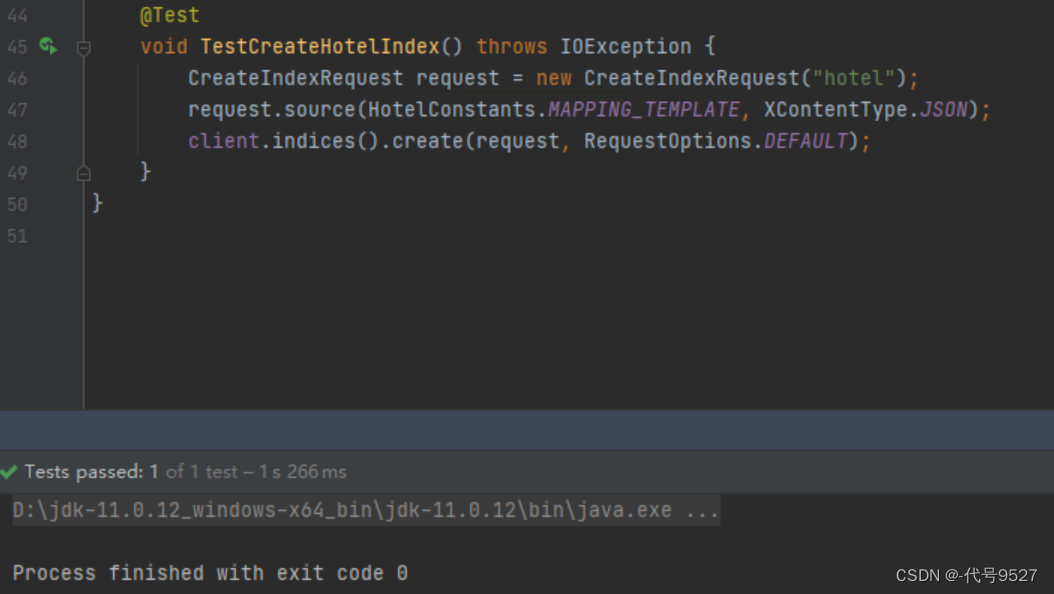
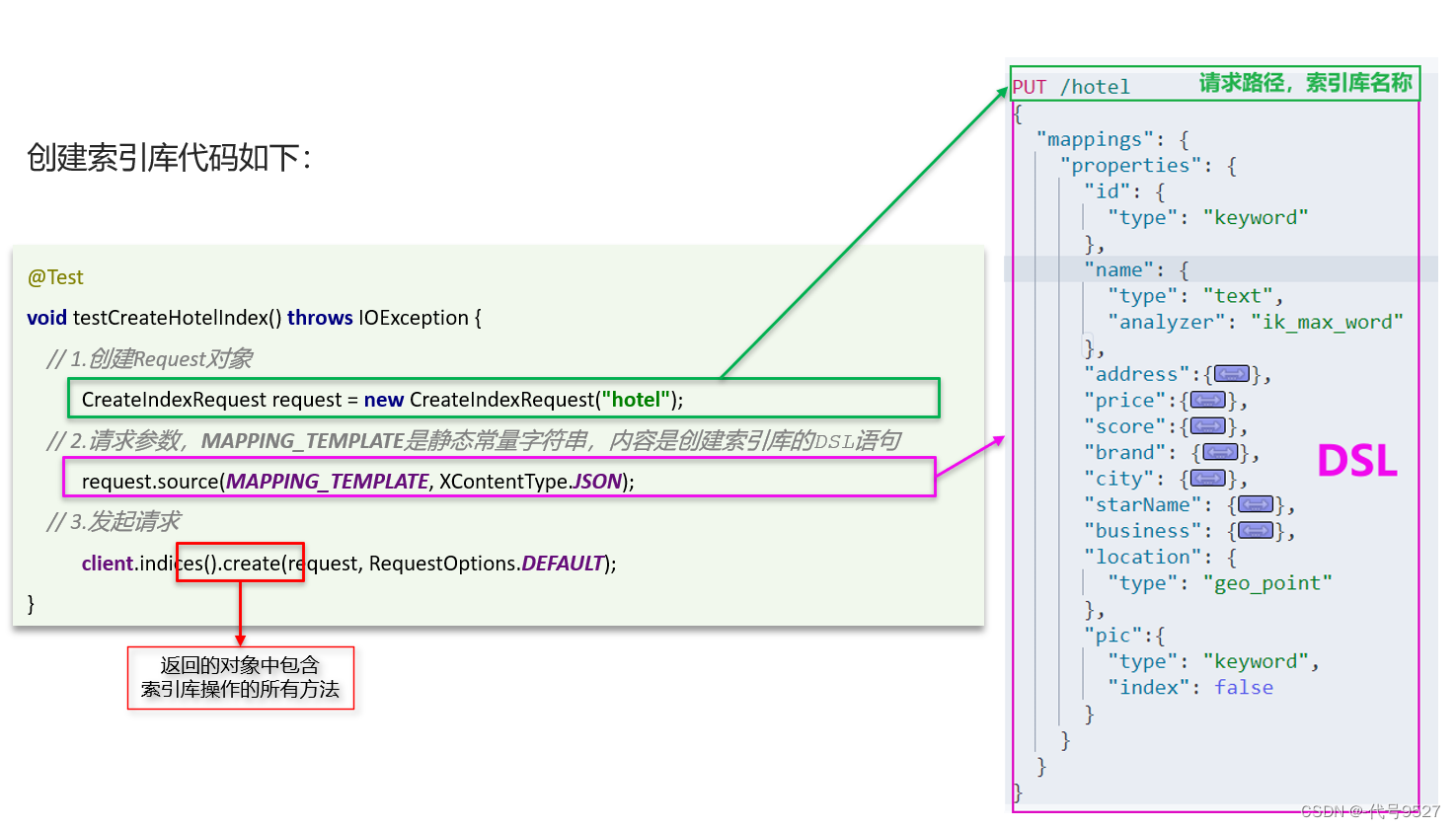
@Test
void testCreateHotelIndex() throws IOException { // 1.创建Request对象 CreateIndexRequest request = new CreateIndexRequest("hotel"); // 2.请求参数,MAPPING_TEMPLATE是静态常量字符串,内容是创建索引库的DSL语句 request.source(MAPPING_TEMPLATE, XContentType.JSON); // 3.发起请求 client.indices().create(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}
将创建索引库的DSL语句以静态字符串常量的形式统一写在常量类里:
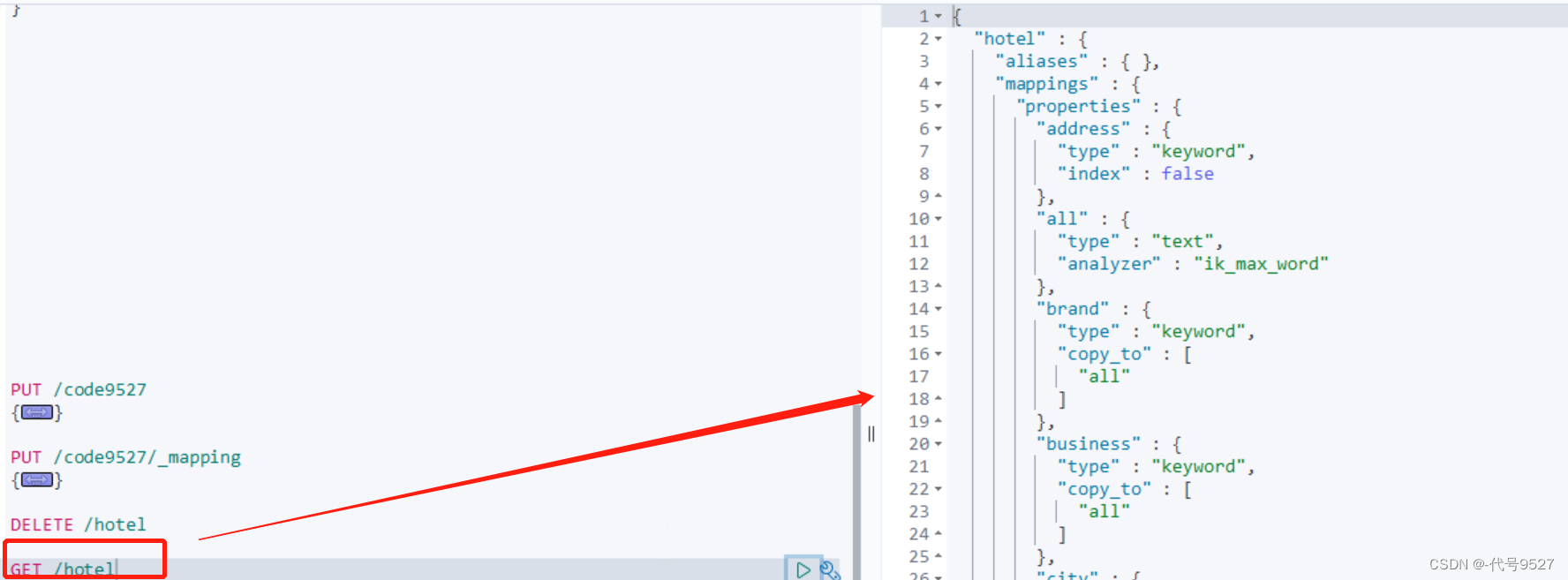
运行完成后,查看ES索引库:
GET /hotel
整个过程,和我们去Kiana手动执行DSL对比:
2、删除索引库
示例代码:
@Test
void testDeleteHotelIndex() throws IOException { // 1.创建Request对象 DeleteIndexRequest request = new DeleteIndexRequest("hotel"); // 2.发起请求 client.indices().delete(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}3、判断索引库是否存在
示例代码:
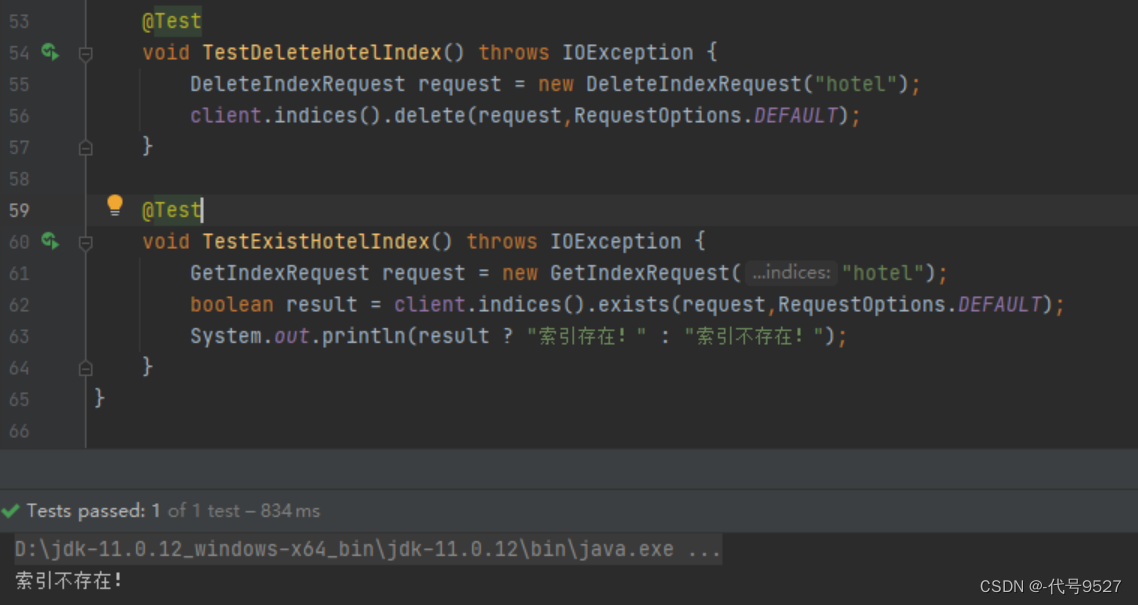
@Test
void testExistsHotelIndex() throws IOException {// 1.创建Request对象 GetIndexRequest request = new GetIndexRequest("hotel"); // 2.发起请求 boolean exists = client.indices().exists(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT); // 3.输出 System.out.println(exists);
}
小结:

三、RestClient操作文档
接下来利用JavaRestClient实现文档的CRUD,去数据库查询酒店数据,导入到hotel索引库,实现酒店数据的CRUD。
和操作索引库一样,还是要先完成JavaRestClient的初始化:
public class ElasticsearchDocumentTest { // 客户端 private RestHighLevelClient client; @BeforeEach void setUp() { client = new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder(HttpHost.create("http://192.168.150.101:9200"))); } @AfterEach void tearDown() throws IOException { client.close(); }
}
接下来要在mysql查数据,写下Service层接口,让它继承MyBatisPlus的IService<PO>
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.IService;public interface IHotelService extends IService<Hotel> {
}
1、新增文档
先看下DSL语法和使用JavaRestClient操作代码来实现的对比:
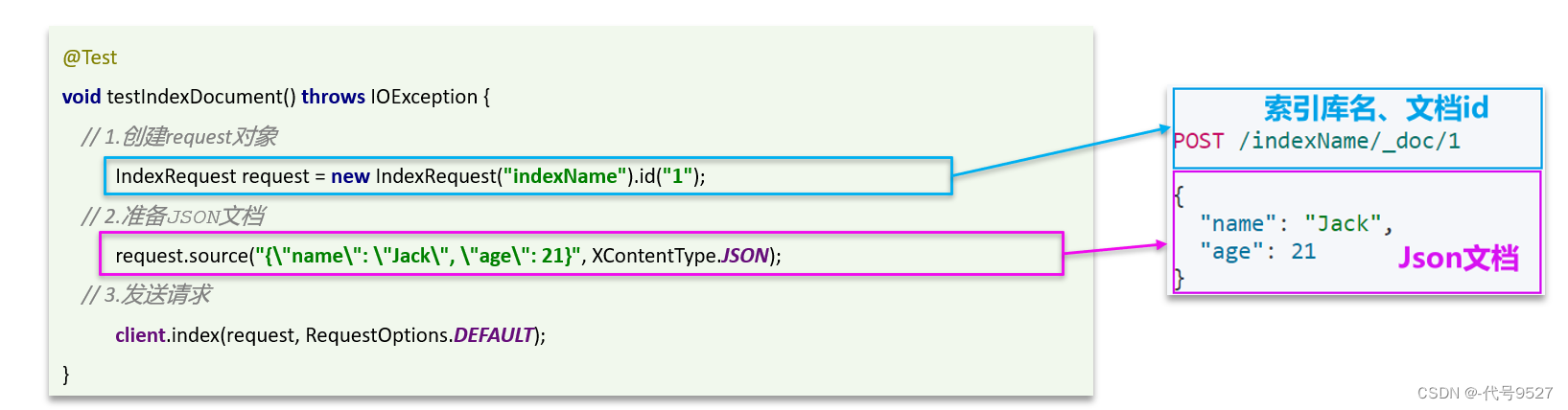
以上是简单逻辑和流程。注意MySQL中查出来的实体类字段和DSL下面的json字段不一样,这是tb_hotel表对应的实体类:
@Data
@TableName("tb_hotel")
public class Hotel {@TableId(type = IdType.INPUT)private Long id;private String name;private String address;private Integer price;private Integer score;private String brand;private String city;private String starName;private String business;private String longitude;private String latitude;private String pic;
}这里写个新类HotelDoc,将Hotel类封装成为和ES索引库字段对应的类:
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
public class HotelDoc {private Long id;private String name;private String address;private Integer price;private Integer score;private String brand;private String city;private String starName;private String business;private String location; //!private String pic;public HotelDoc(Hotel hotel) { //有参构造,传入要封装的对象this.id = hotel.getId(); //对于这些不用包装的字段,直接get到后赋值给包装对象的属性就行this.name = hotel.getName();this.address = hotel.getAddress();this.price = hotel.getPrice();this.score = hotel.getScore();this.brand = hotel.getBrand();this.city = hotel.getCity();this.starName = hotel.getStarName();this.business = hotel.getBusiness(); this.location = hotel.getLatitude() + ", " + hotel.getLongitude(); //注意这里this.pic = hotel.getPic();}
}
接下来实现去数据库查询酒店数据,导入到hotel索引库:
@Resource
IHotelService iHotelService;@Test
void testIndexDocument() throws IOException {//从MySQL查Hotel hotel = iHotelService.getById(60359L); //封装HotelDoc hotelDoc = new HotelDoc(hotel);//创建requestIndexRequest request = new IndexRequest("hotel").id(hotelDoc.getId().toString());//放入要新增的json传request.source(JSON.toJSONString(hotelDoc), XContentType.JSON);//发请求client.index(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);}
2、查询文档
根据id查询到的文档数据是json,再反序列化成Java对象。代码和DSL语句的对比:
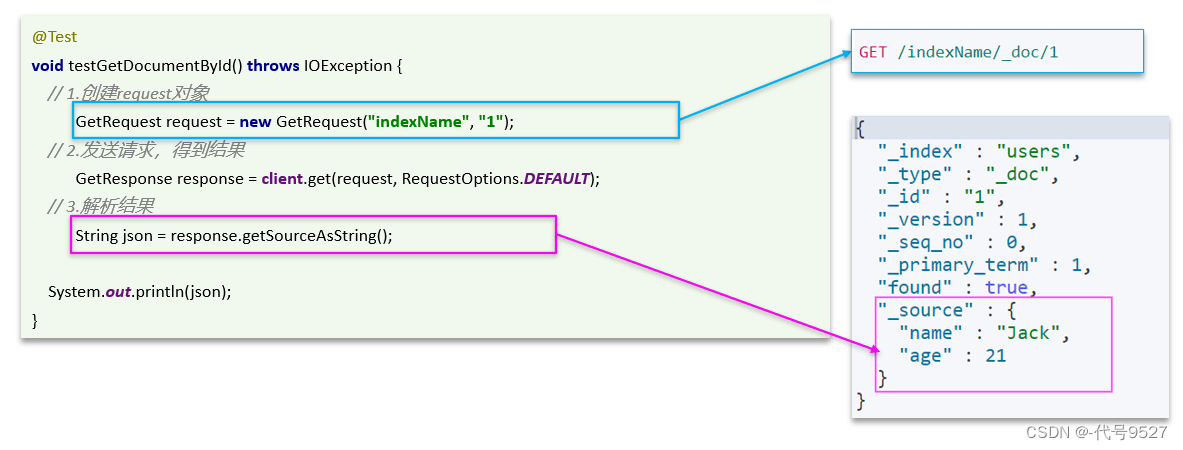
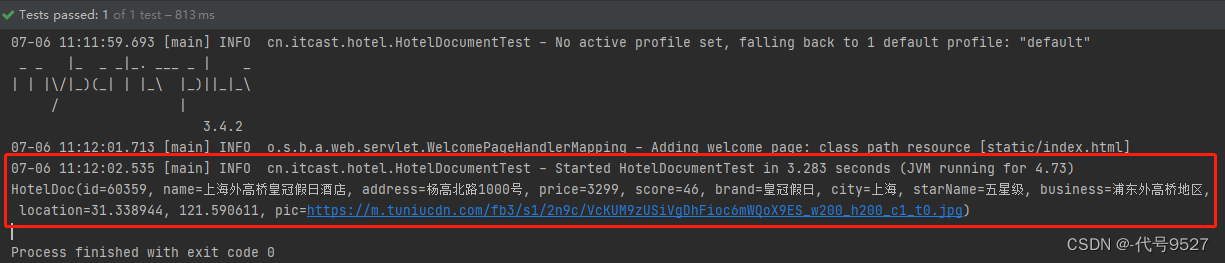
@Test
void testGetDocumentById() throws IOException {GetRequest request = new GetRequest("hotel","60359");GetResponse response = client.get(request,RequestOptions.DEFAULT);//看上图DSL执行返回结果中有个_source,这个getSource方法就是拿这个数据String json = response.getSourceAsString();//解析HotelDoc hotelDoc = JSON.parseObject(json,HotelDoc.class);System.out.println(hotelDoc);
}
3、修改文档
接下来根据id去修改ES文档的酒店数据。修改文档数据有两种方式:
方式一:全量更新。再次写入id一样的文档,就会删除旧文档,添加新文档
方式二:局部更新。只更新部分字段
实现下方式二:
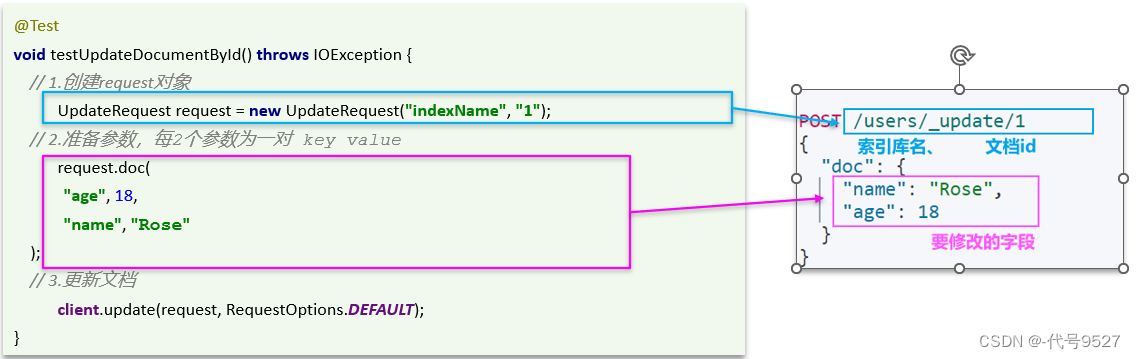
@Test
void testUpdateDocumentById() throws IOException {UpdateRequest request = new UpdateRequest("hotel","60359");request.doc("price","0.01","startName","四星级");client.update(request,RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}
4、删除文档
根据id删除文档数据:
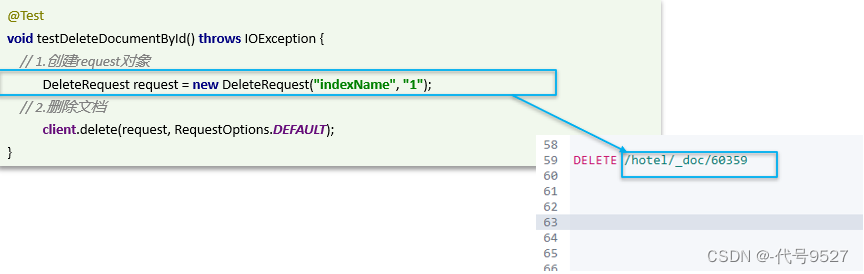
@Test
void testDeleteDocumentById() throws IOException {DeleteRequest request = new DeleteRequest("hotel","60359");client.delete(request,RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}
再get已经无数据:

小结:

5、批量导入文档
接下来批量查询酒店数据,然后批量导入索引库中,实现思路:
- 利用mybatis-plus查询酒店数据
- 将查询到的酒店数据(Hotel)转换为文档类型数据(HotelDoc)
- 利用JavaRestClient中的Bulk批处理,实现批量新增文档
代码逻辑:

@Test
void testBulk() throws IOException {//从MySQL查到所有数据List<Hotel> hotels = iHotelService.list();BulkRequest request = new BulkRequest();//遍历Hotel的对象集合for(Hotel hotel : hotels){//Hotel转HotelDocHotelDoc hotelDoc = new HotelDoc(hotel);//创建新增文档的Request对象request.add(new IndexRequest("hotel").id(hotelDoc.getId().toString()).source(JSON.toJSONString(hotelDoc),XContentType.JSON));}//发送请求client.bulk(request,RequestOptions.DEFAULT);}
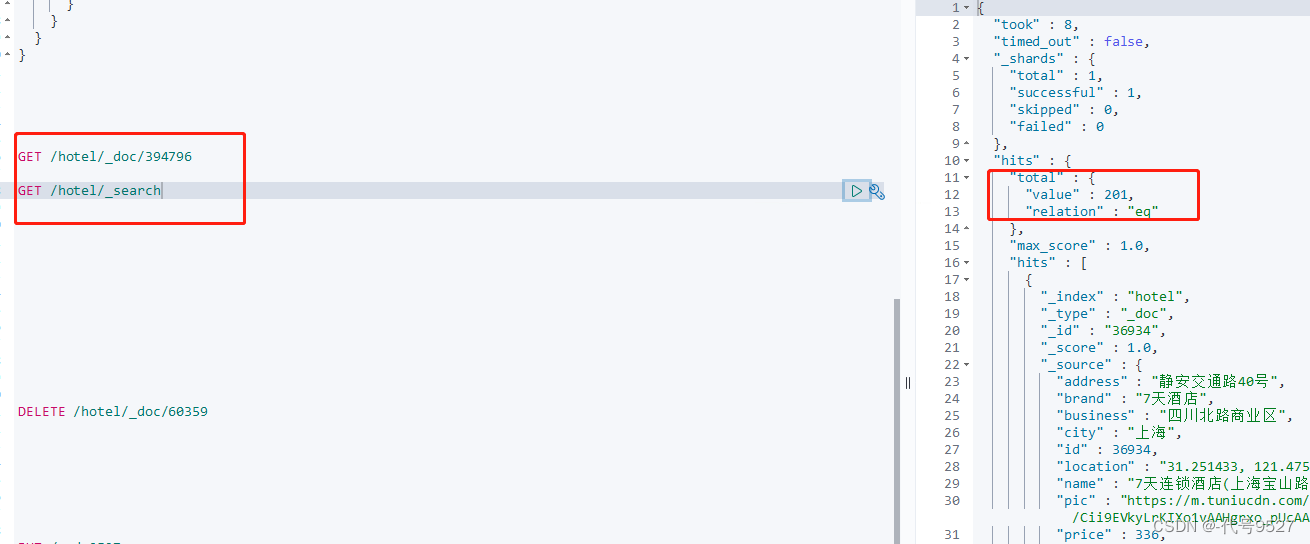
最后查询单个文档或者查所有:
//查所有
GET /hotel/_search
![[SWPUCTF 2022 新生赛]js_sign](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/eb35acb9c90c0307706621af5bb310fa.png)