文章目录
- 前言
- 项目下载
- 项目运行
- 自定义数据集训练
- 使用LabelImg
- 标注
- 制作数据集
- 划分训练文件
- 生成标签
- 聚合操作
- 辅助脚本
- 需要运行的脚本
- 开始训练
- 总结
前言
没啥意思,很简单,需要实现一个目标检测,但是,不能占用太多运算资源,同时需要保证一定的精度。并且要在移动端部署,要在一台ROS小车上面部署。那么此时常见的选择自然有yolov3-tiny等。但是考虑到onnx部署方案的成熟,目前的加持之下,python也有不错的效率,所以,这里就考虑使用到yolov5-lite版本。
可以看到官方的对比:
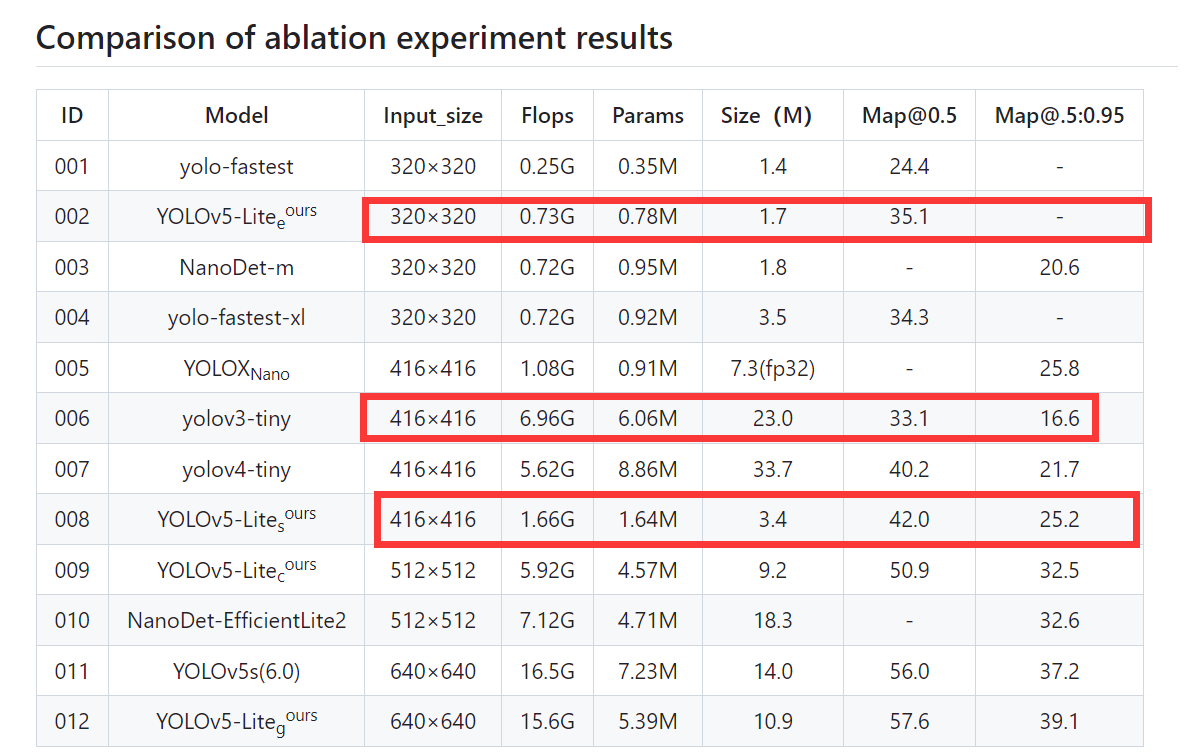
同时在我的本地机器上面也是做了对比。
在使用yolov3-tiny 使用opencv dnn部署的情况下,帧率只有30多,但是使用yolov5-Lite普遍100+。这就意味着,可以在边缘设备进行快部署。同时得益于onnx,俺们也可以很方便地进行部署。
此外的话,由于这玩意是基于yolov5做的,所以在训练的时候,和V5保持高度的一致,包括里面数据增强的方法等等,况且人家精度也比yolov3-tiny高。 在科大讯飞智能小车上实测,极限压缩一下分辨率可以达到80FPS左右,原始模型也可以达到30FPS。这里就很方便后期在整合其他的算法,例如+sort算法做一个目标跟踪。这个部分的话,我后续可能会做到。
项目下载
ok,那么首先第一步的话,还是说去下载项目即可,我们分为两个部分,一个是如何运行项目,一个是如何训练自己的数据集。这个是比较重要的,后面我们还需要定制化的需求。如何整合之类的是吧,那么这里的话不过多叙述。首先进入github下载,这个没啥好说的。
https://github.com/ppogg/YOLOv5-Lite
下载完成之后,你将见到这几个文件
这里的权重文件需要自己去下载~
选择你喜欢的版本即可。
项目运行
之后的话,我们可以运行我们的项目,首先这里也是分为几个部分第一个部分就是模型的转化。首先我们的目的还是为了部署我们的模型。所以的话,这里提供了三个版本:
当然是官方给到的
在这里的话,我主要演示Python的,因为我目前的主要认为就是基于Python的。
那么在这里我们的第一步是模型的转化,这里的话是转化到onnx模型,然后运行。
主要进入这里:
这里调整参数即可:
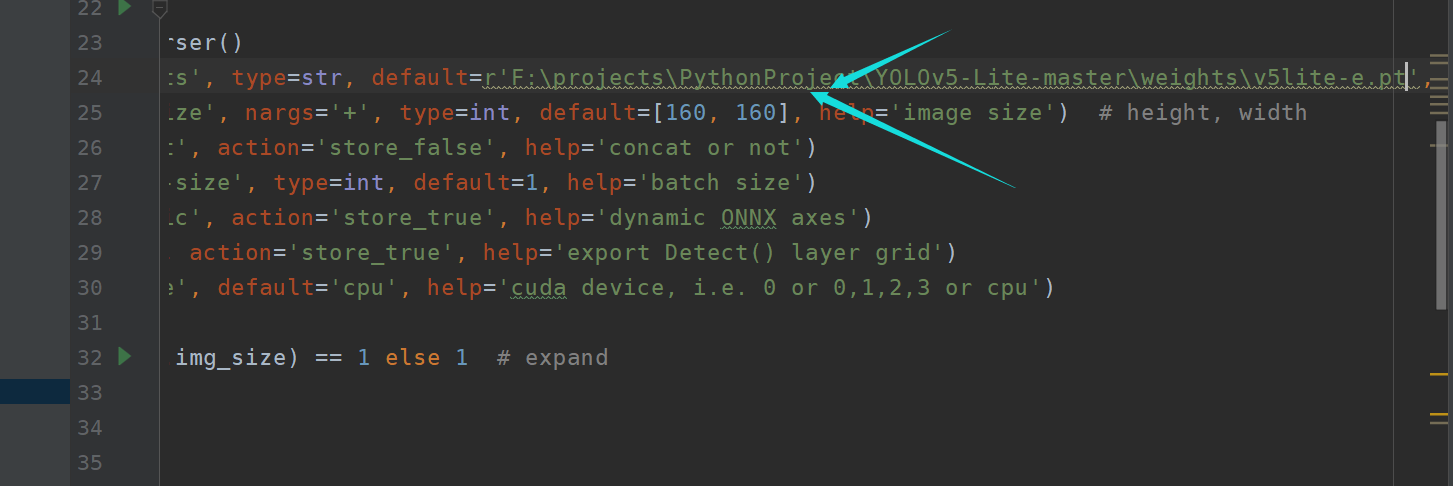
其中主要[160,160]是指输入的图片规格,默认是320 320
然后你将得到这个文件:
然后的话,我们在这里可以看到,部署文件:
这里我还进行了一点修改,源代码好像还有bug,我改了一下。
import cv2
import time
import numpy as np
import argparse
import onnxruntime as ortclass yolov5_lite():def __init__(self, model_pb_path, label_path, confThreshold=0.5, nmsThreshold=0.5, objThreshold=0.5):so = ort.SessionOptions()so.log_severity_level = 3self.net = ort.InferenceSession(model_pb_path, so)self.classes = list(map(lambda x: x.strip(), open(label_path, 'r').readlines()))self.num_classes = len(self.classes)anchors = [[10, 13, 16, 30, 33, 23],[30, 61, 62, 45, 59, 119],[116, 90, 156, 198, 373, 326]]self.nl = len(anchors)self.na = len(anchors[0]) // 2self.no = self.num_classes + 5self.grid = [np.zeros(1)] * self.nlself.stride = np.array([8., 16., 32.])self.anchor_grid = np.asarray(anchors, dtype=np.float32).reshape(self.nl, -1, 2)self.confThreshold = confThresholdself.nmsThreshold = nmsThresholdself.objThreshold = objThresholdself.input_shape = (self.net.get_inputs()[0].shape[2], self.net.get_inputs()[0].shape[3])def resize_image(self, srcimg, keep_ratio=True):top, left, newh, neww = 0, 0, self.input_shape[0], self.input_shape[1]if keep_ratio and srcimg.shape[0] != srcimg.shape[1]:hw_scale = srcimg.shape[0] / srcimg.shape[1]if hw_scale > 1:newh, neww = self.input_shape[0], int(self.input_shape[1] / hw_scale)img = cv2.resize(srcimg, (neww, newh), interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)left = int((self.input_shape[1] - neww) * 0.5)img = cv2.copyMakeBorder(img, 0, 0, left, self.input_shape[1] - neww - left, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT,value=0) # add borderelse:newh, neww = int(self.input_shape[0] * hw_scale), self.input_shape[1]img = cv2.resize(srcimg, (neww, newh), interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)top = int((self.input_shape[0] - newh) * 0.5)img = cv2.copyMakeBorder(img, top, self.input_shape[0] - newh - top, 0, 0, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=0)else:img = cv2.resize(srcimg, self.input_shape, interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)return img, newh, neww, top, leftdef _make_grid(self, nx=20, ny=20):xv, yv = np.meshgrid(np.arange(ny), np.arange(nx))return np.stack((xv, yv), 2).reshape((-1, 2)).astype(np.float32)def postprocess(self, frame, outs, pad_hw):newh, neww, padh, padw = pad_hwframeHeight = frame.shape[0]frameWidth = frame.shape[1]ratioh, ratiow = frameHeight / newh, frameWidth / neww# Scan through all the bounding boxes output from the network and keep only the# ones with high confidence scores. Assign the box's class label as the class with the highest score.classIds = []confidences = []box_index = []boxes = []outs = outs[outs[:, 4] > self.objThreshold]for detection in outs:scores = detection[5:]classId = np.argmax(scores)confidence = scores[classId]if confidence > self.confThreshold: # and detection[4] > self.objThreshold:center_x = int((detection[0] - padw) * ratiow)center_y = int((detection[1] - padh) * ratioh)width = int(detection[2] * ratiow)height = int(detection[3] * ratioh)left = int(center_x - width / 2)top = int(center_y - height / 2)classIds.append(classId)confidences.append(float(confidence))boxes.append([left, top, width, height])# Perform non maximum suppression to eliminate redundant overlapping boxes with# lower confidences.# print(boxes)indices = cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, self.confThreshold, self.nmsThreshold)for ix in indices:box_index.append(ix)for i in box_index:box = boxes[i]left = box[0]top = box[1]width = box[2]height = box[3]frame = self.drawPred(frame, classIds[i], confidences[i], left, top, left + width, top + height)return framedef drawPred(self, frame, classId, conf, left, top, right, bottom):# Draw a bounding box.cv2.rectangle(frame, (left, top), (right, bottom), (0, 0, 255), thickness=2)label = '%.2f' % conflabel = '%s:%s' % (self.classes[classId], label)# Display the label at the top of the bounding boxlabelSize, baseLine = cv2.getTextSize(label, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1)top = max(top, labelSize[1])# cv.rectangle(frame, (left, top - round(1.5 * labelSize[1])), (left + round(1.5 * labelSize[0]), top + baseLine), (255,255,255), cv.FILLED)cv2.putText(frame, label, (left, top - 10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_TRIPLEX, 0.5, (0, 255, 0), thickness=1)return framedef showFps(self,frame,fps):cv2.putText(frame, 'FPS:{}'.format(int(fps)),(50, 50),cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,0.6, (255, 0, 255), 2)return framedef detect(self, srcimg):img, newh, neww, top, left = self.resize_image(srcimg)img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)img = img.astype(np.float32) / 255.0blob = np.expand_dims(np.transpose(img, (2, 0, 1)), axis=0)t1 = time.time()outs = self.net.run(None, {self.net.get_inputs()[0].name: blob})[0].squeeze(axis=0)cost_time = time.time() - t1# print(outs.shape)row_ind = 0for i in range(self.nl):h, w = int(self.input_shape[0] / self.stride[i]), int(self.input_shape[1] / self.stride[i])length = int(self.na * h * w)if self.grid[i].shape[2:4] != (h, w):self.grid[i] = self._make_grid(w, h)outs[row_ind:row_ind + length, 0:2] = (outs[row_ind:row_ind + length, 0:2] * 2. - 0.5 + np.tile(self.grid[i], (self.na, 1))) * int(self.stride[i])outs[row_ind:row_ind + length, 2:4] = (outs[row_ind:row_ind + length, 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * np.repeat(self.anchor_grid[i], h * w, axis=0)row_ind += lengthsrcimg = self.postprocess(srcimg, outs, (newh, neww, top, left))infer_time = 'Inference Time: ' + str(int(cost_time * 1000)) + 'ms'cv2.putText(srcimg, infer_time, (5, 20), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_TRIPLEX, 0.5, (0, 0, 0), thickness=1)return srcimgclass RunTime:def __init__(self):self.net = yolov5_lite(args.modelpath, args.classfile, confThreshold=args.confThreshold,nmsThreshold=args.nmsThreshold)def run(self):"""打开摄像头:return:"""cam = cv2.VideoCapture(0)if not cam.isOpened():raise RuntimeError("无法打开摄像头")# 循环读取和处理每一帧图像while True:ret, frame = cam.read()if not ret:break# 进行目标检测start = time.time()#进行推理检测,返回的是绘制好的图片frame = self.net.detect(frame)end = time.time()fps = 1 / (end - start)# 绘制边界框,也是返回绘制好的图篇,把这个图片进行发布即可frame = self.net.showFps(frame,fps)# 显示图像cv2.imshow("Frame", frame)# 检测按键来退出循环if cv2.waitKey(1) == ord('q'):break# 释放摄像头资源cam.release()# 关闭所有窗口cv2.destroyAllWindows()if __name__ == '__main__':parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()parser.add_argument('--imgpath', type=str, default=r'F:\projects\PythonProject\YOLOv5-Lite-master\sample\bike.jpg', help="image path")#模型地址parser.add_argument('--modelpath', type=str, default=r'F:\projects\PythonProject\YOLOv5-Lite-master\weights\v5lite-e.onnx', help="onnx filepath")parser.add_argument('--classfile', type=str, default='coco.names', help="classname filepath")parser.add_argument('--confThreshold', default=0.5, type=float, help='class confidence')parser.add_argument('--nmsThreshold', default=0.6, type=float, help='nms iou thresh')args = parser.parse_args()runner = RunTime()runner.run()# srcimg = cv2.imread(args.imgpath)# net = yolov5_lite(args.modelpath, args.classfile, confThreshold=args.confThreshold, nmsThreshold=args.nmsThreshold)# srcimg = net.detect(srcimg.copy())## winName = 'Deep learning object detection in onnxruntime'# cv2.namedWindow(winName, cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)# cv2.imshow(winName, srcimg)# cv2.waitKey(0)# # cv2.imwrite('save.jpg', srcimg )# cv2.destroyAllWindows()自定义数据集训练
之后的话,就是自定义数据集训练了,这个的话和yolov5完全一致。比如自适应anchor,图片增强呀,都有。
不过在此之前,你需要去下载一个打标签的软件。当然你也可以使用在线的,不过需要科学上网,所以我这里就没必要介绍了。
所以咱们这里使用的是LabelImg。
使用LabelImg
关于这个软件呢,使用非常简单,主要是安装使用比较麻烦。
先下载源码。这个我稍后会给出百度云盘链接。
由于我是coda环境,所以我只需要先下载源码,解压
然后进入这个文件夹
安装 pyqt
conda install pyqt=5
pyrcc5 -o resources.py resources.qrc
此时还不够,大概率会出问题。所以你需要把
这个生成的文件,移动到libs里面
最后是运行
一切正常,接下来是获取这个软件
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/14y-0vqU7u9JkDBaAw7Odxg
提取码:6666
标注
这里的话,我就随便搞几张图片玩玩了。
制作数据集
前面我们其实还只是完成了准备工作,接下来才是比较复杂的点,那就是制作数据集,这个LabelImg打包好之后的数据集的格式其实是VOC格式的,当然那里也可以切换为yolo的格式,不过后面都还是要再转换的。
先来看看我们一开始的数据集的样子
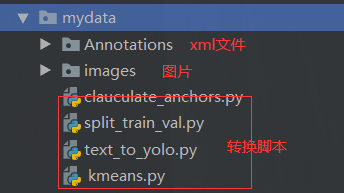
在让我们看看最后的文件长啥样
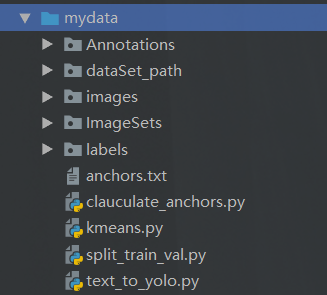
接下来我依次介绍这些脚本和处理操作。 这些代码都是copy的,目标只有一个制作一个标准的VOC数据集,然后给Yolo识别。
由于只是做演示,所以我的图片的数据集合不会太多。
关于图片的获取的话,可以自己写个爬虫是吧。这里一定要注意图片尺寸要一致(我后面翻车了)
划分训练文件
这里的话,我们主要运行这个脚本。
# coding:utf-8import os
import random
import argparseparser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
#xml文件的地址,根据自己的数据进行修改 xml一般存放在Annotations下
parser.add_argument('--xml_path', default='Annotations', type=str, help='input xml label path')
#数据集的划分,地址选择自己数据下的ImageSets/Main
parser.add_argument('--txt_path', default='ImageSets/Main', type=str, help='output txt label path')
opt = parser.parse_args()trainval_percent = 1.0 # 训练集和验证集所占比例。 这里没有划分测试集
train_percent = 0.9 # 训练集所占比例,可自己进行调整
xmlfilepath = opt.xml_path
txtsavepath = opt.txt_path
total_xml = os.listdir(xmlfilepath)
if not os.path.exists(txtsavepath):os.makedirs(txtsavepath)num = len(total_xml)
list_index = range(num)
tv = int(num * trainval_percent)
tr = int(tv * train_percent)
trainval = random.sample(list_index, tv)
train = random.sample(trainval, tr)file_trainval = open(txtsavepath + '/trainval.txt', 'w')
file_test = open(txtsavepath + '/test.txt', 'w')
file_train = open(txtsavepath + '/train.txt', 'w')
file_val = open(txtsavepath + '/val.txt', 'w')for i in list_index:name = total_xml[i][:-4] + '\n'if i in trainval:file_trainval.write(name)if i in train:file_train.write(name)else:file_val.write(name)else:file_test.write(name)file_trainval.close()
file_train.close()
file_val.close()
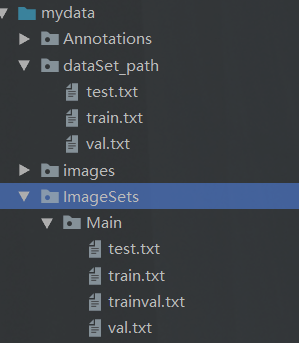
file_test.close()运行完之后,会出现这样的文件
生成标签
之后是生成我们的标签。
下面的路径自己看着改
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import os
from os import getcwdsets = ['train', 'val', 'test']
classes = ["猫羽雫", "喵喵~","女孩"] # 改成自己的类别
abs_path = os.getcwd()
print(abs_path)def convert(size, box):dw = 1. / (size[0])dh = 1. / (size[1])x = (box[0] + box[1]) / 2.0 - 1y = (box[2] + box[3]) / 2.0 - 1w = box[1] - box[0]h = box[3] - box[2]x = x * dww = w * dwy = y * dhh = h * dhreturn x, y, w, hdef convert_annotation(image_id):in_file = open('F:\projects\PythonProject\yolov5-5.0\mydata\Annotations\%s.xml' % (image_id), encoding='UTF-8')out_file = open('F:\projects\PythonProject\yolov5-5.0\mydata\labels\%s.txt' % (image_id), 'w')tree = ET.parse(in_file)root = tree.getroot()size = root.find('size')w = int(size.find('width').text)h = int(size.find('height').text)for obj in root.iter('object'):difficult = obj.find('difficult').text# difficult = obj.find('Difficult').textcls = obj.find('name').textif cls not in classes or int(difficult) == 1:continuecls_id = classes.index(cls)xmlbox = obj.find('bndbox')b = (float(xmlbox.find('xmin').text), float(xmlbox.find('xmax').text), float(xmlbox.find('ymin').text),float(xmlbox.find('ymax').text))b1, b2, b3, b4 = b# 标注越界修正if b2 > w:b2 = wif b4 > h:b4 = hb = (b1, b2, b3, b4)bb = convert((w, h), b)out_file.write(str(cls_id) + " " + " ".join([str(a) for a in bb]) + '\n')wd = getcwd()
for image_set in sets:if not os.path.exists('F:\projects\PythonProject\yolov5-5.0\mydata\labels'):os.makedirs('F:\projects\PythonProject\yolov5-5.0\mydata\labels')image_ids = open('F:\projects\PythonProject\yolov5-5.0\mydata\/ImageSets/Main/%s.txt' % (image_set)).read().strip().split()if not os.path.exists('F:\projects\PythonProject\yolov5-5.0\mydata\dataSet_path/'):os.makedirs('F:\projects\PythonProject\yolov5-5.0\mydata\dataSet_path/')list_file = open('dataSet_path/%s.txt' % (image_set), 'w')# 这行路径不需更改,这是相对路径for image_id in image_ids:list_file.write('F:\projects\PythonProject\yolov5-5.0\mydata/images/%s.jpg\n' % (image_id))convert_annotation(image_id)list_file.close()之后会出现两个文件夹
这里里面一个是我们图片的真实存放地址,还有一个是标签文本。
聚合操作
这个呢,主要是用来设置我们的目标框大小的,这里有两个脚本,这两个脚本的目的就是用来计算我们在数据集里面,手动框出来的框的平均大小,目的是为了,在我们得到的训练好后的模型,它给我们框出来的框的大小不会太奇怪,控制在一个合适的范围。
辅助脚本
import numpy as npdef iou(box, clusters):"""Calculates the Intersection over Union (IoU) between a box and k clusters.:param box: tuple or array, shifted to the origin (i. e. width and height):param clusters: numpy array of shape (k, 2) where k is the number of clusters:return: numpy array of shape (k, 0) where k is the number of clusters"""x = np.minimum(clusters[:, 0], box[0])y = np.minimum(clusters[:, 1], box[1])if np.count_nonzero(x == 0) > 0 or np.count_nonzero(y == 0) > 0:raise ValueError("Box has no area") # 如果报这个错,可以把这行改成pass即可intersection = x * ybox_area = box[0] * box[1]cluster_area = clusters[:, 0] * clusters[:, 1]iou_ = intersection / (box_area + cluster_area - intersection)return iou_def avg_iou(boxes, clusters):"""Calculates the average Intersection over Union (IoU) between a numpy array of boxes and k clusters.:param boxes: numpy array of shape (r, 2), where r is the number of rows:param clusters: numpy array of shape (k, 2) where k is the number of clusters:return: average IoU as a single float"""return np.mean([np.max(iou(boxes[i], clusters)) for i in range(boxes.shape[0])])def translate_boxes(boxes):"""Translates all the boxes to the origin.:param boxes: numpy array of shape (r, 4):return: numpy array of shape (r, 2)"""new_boxes = boxes.copy()for row in range(new_boxes.shape[0]):new_boxes[row][2] = np.abs(new_boxes[row][2] - new_boxes[row][0])new_boxes[row][3] = np.abs(new_boxes[row][3] - new_boxes[row][1])return np.delete(new_boxes, [0, 1], axis=1)def kmeans(boxes, k, dist=np.median):"""Calculates k-means clustering with the Intersection over Union (IoU) metric.:param boxes: numpy array of shape (r, 2), where r is the number of rows:param k: number of clusters:param dist: distance function:return: numpy array of shape (k, 2)"""rows = boxes.shape[0]distances = np.empty((rows, k))last_clusters = np.zeros((rows,))np.random.seed()# the Forgy method will fail if the whole array contains the same rowsclusters = boxes[np.random.choice(rows, k, replace=False)]while True:for row in range(rows):distances[row] = 1 - iou(boxes[row], clusters)nearest_clusters = np.argmin(distances, axis=1)if (last_clusters == nearest_clusters).all():breakfor cluster in range(k):clusters[cluster] = dist(boxes[nearest_clusters == cluster], axis=0)last_clusters = nearest_clustersreturn clustersif __name__ == '__main__':a = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 7, 6, 8]])print(translate_boxes(a))这个脚本不用运行,是一个工具类。
需要运行的脚本
这里也是注意路径修改
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# 根据标签文件求先验框import os
import numpy as np
import xml.etree.cElementTree as et
from kmeans import kmeans, avg_iouFILE_ROOT = "F:\projects\PythonProject\yolov5-5.0\mydata/" # 根路径
ANNOTATION_ROOT = "Annotations" # 数据集标签文件夹路径
ANNOTATION_PATH = FILE_ROOT + ANNOTATION_ROOTANCHORS_TXT_PATH = "F:\projects\PythonProject\yolov5-5.0\mydata/anchors.txt" #anchors文件保存位置CLUSTERS = 9
CLASS_NAMES = ['猫羽雫', '喵喵~','女孩'] #类别名称def load_data(anno_dir, class_names):xml_names = os.listdir(anno_dir)boxes = []for xml_name in xml_names:xml_pth = os.path.join(anno_dir, xml_name)tree = et.parse(xml_pth)width = float(tree.findtext("./size/width"))height = float(tree.findtext("./size/height"))for obj in tree.findall("./object"):cls_name = obj.findtext("name")if cls_name in class_names:xmin = float(obj.findtext("bndbox/xmin")) / widthymin = float(obj.findtext("bndbox/ymin")) / heightxmax = float(obj.findtext("bndbox/xmax")) / widthymax = float(obj.findtext("bndbox/ymax")) / heightbox = [xmax - xmin, ymax - ymin]boxes.append(box)else:continuereturn np.array(boxes)if __name__ == '__main__':anchors_txt = open(ANCHORS_TXT_PATH, "w")train_boxes = load_data(ANNOTATION_PATH, CLASS_NAMES)count = 1best_accuracy = 0best_anchors = []best_ratios = []for i in range(10): ##### 可以修改,不要太大,否则时间很长anchors_tmp = []clusters = kmeans(train_boxes, k=CLUSTERS)idx = clusters[:, 0].argsort()clusters = clusters[idx]# print(clusters)for j in range(CLUSTERS):anchor = [round(clusters[j][0] * 640, 2), round(clusters[j][1] * 640, 2)]anchors_tmp.append(anchor)print(f"Anchors:{anchor}")temp_accuracy = avg_iou(train_boxes, clusters) * 100print("Train_Accuracy:{:.2f}%".format(temp_accuracy))ratios = np.around(clusters[:, 0] / clusters[:, 1], decimals=2).tolist()ratios.sort()print("Ratios:{}".format(ratios))print(20 * "*" + " {} ".format(count) + 20 * "*")count += 1if temp_accuracy > best_accuracy:best_accuracy = temp_accuracybest_anchors = anchors_tmpbest_ratios = ratiosanchors_txt.write("Best Accuracy = " + str(round(best_accuracy, 2)) + '%' + "\r\n")anchors_txt.write("Best Anchors = " + str(best_anchors) + "\r\n")anchors_txt.write("Best Ratios = " + str(best_ratios))anchors_txt.close()然后会生成这样的文件
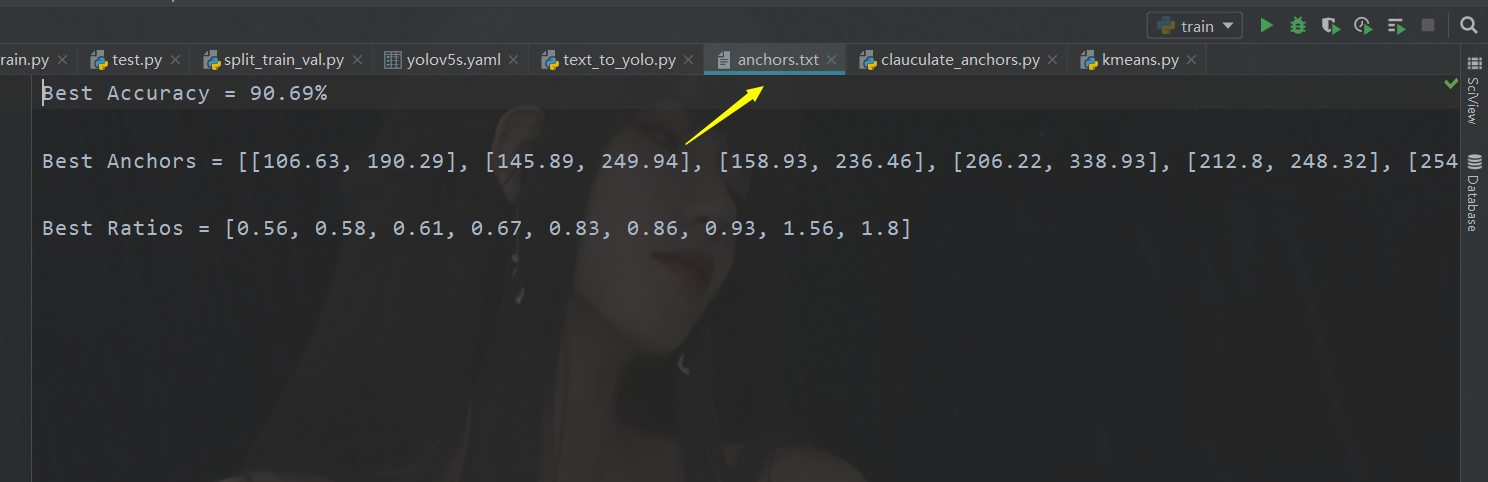
开始训练
首先打开咱们的这个文件夹
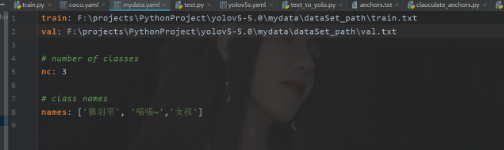
train: F:\projects\PythonProject\yolov5-5.0\mydata\dataSet_path\train.txt
val: F:\projects\PythonProject\yolov5-5.0\mydata\dataSet_path\val.txt# number of classes
nc: 3# class names
names: ['猫羽雫', '喵喵~','女孩']之后是修改我们的模型
我们使用的是 5s
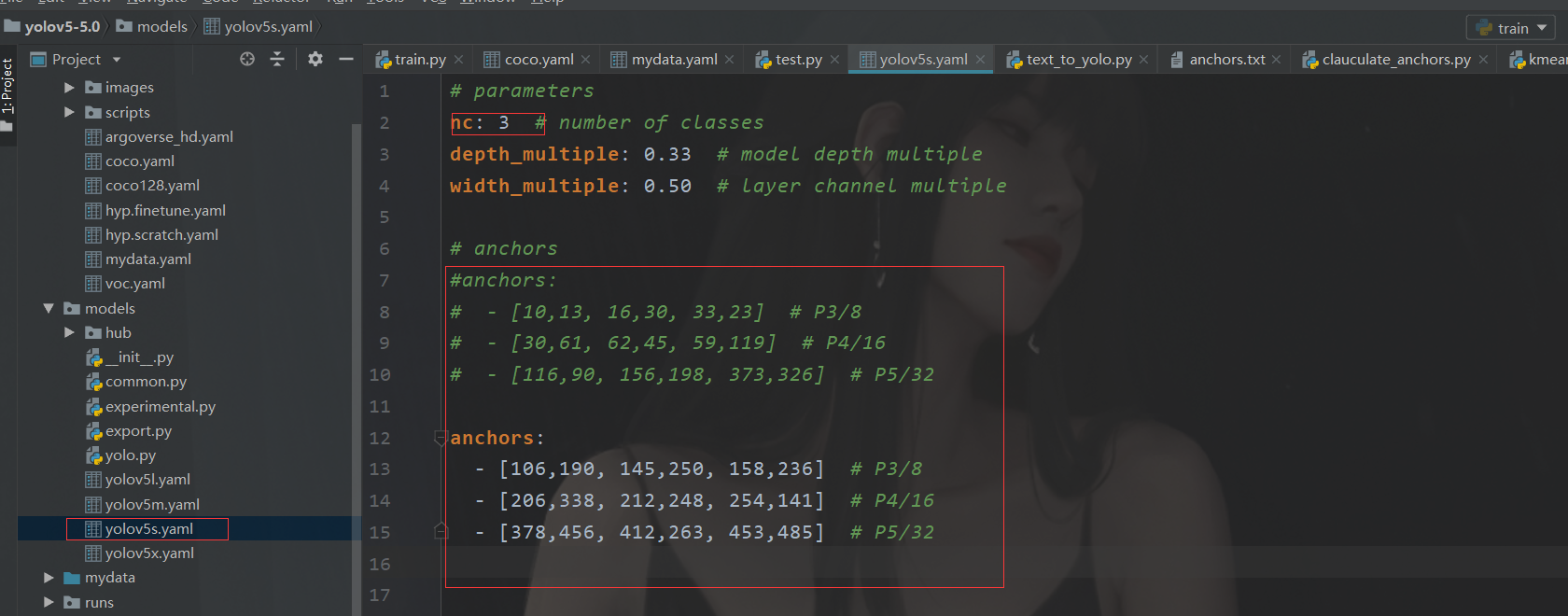
这里注意到那个anchors的参数修改
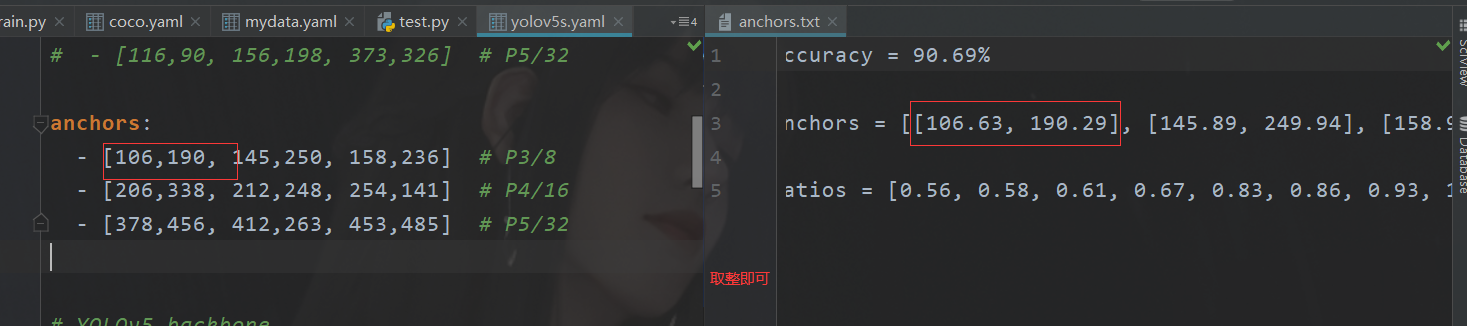
这个其实就是咱们原来聚类生成的玩意儿。
之后其老规矩运行train设置好参数即可。
总结
前人栽树,后人乘凉,只能这么说,后面,我在集成一下sort算法,这样一来就可以实现边缘设备的目标跟踪了,用在,区域内的物体计数里面。