目录
介绍
Future介绍
CompletableFuture介绍
CompletableFuture常用的API介绍
常用的静态方法源码解析
runAsync
源码
案例
结果
supplyAsync
源码
案例
结果
规律
CompletableFuture获取返回值方法介绍
返回值区别
代码演示
返回结果
CompletableFuture其他常用的API
thenApply
源码
案例
结果
thenCompose
源码
案例
结果
thenAccept和thenRun
源码
案例
结果
complete
源码
案例
结果
whenComplete
源码
案例
结果
exceptionally
源码
案例
结果
whenComplete+exceptionally案例
结果
handle
源码
案例
结果
allof
源码
案例
结果
anyOf
源码
案例
结果
提示
介绍
Future介绍
了解CompletableFuture可以先了解Future,可以查看下面这篇文章
Callable、Future和FutrueTask详解-CSDN博客
CompletableFuture介绍
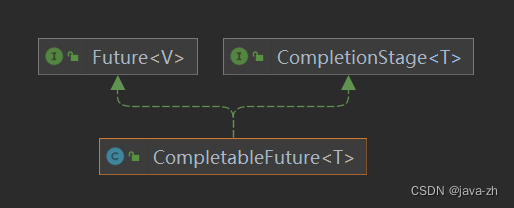
CompletableFuture是一个类,主要实现了Future和ComletionStage两个接口。因此,CompletableFuture包含了Futrure和CompletionStage的功能。
CompletableFuture常用的API介绍
官方推荐CompletableFutrue静态方法,所以我们先介绍它的静态方法
常用的静态方法源码解析
线程池工具类
线程池工具类_java线程池工具类-CSDN博客
runAsync
runAsync:无返回值,可以自定义线程池,如果没有自定义线程池,默认使用ForkJoinPool线程池
源码
// 默认线程池
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable) {return asyncRunStage(asyncPool, runnable);}
// 自定义线程池public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable,Executor executor) {return asyncRunStage(screenExecutor(executor), runnable);}案例
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " -------执行异步任务,无返回值结果---------");});CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " -----自定义线程执行异步任务,无返回结果------");}, ThreadPoolUtils.getThreadPool());}结果
ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-9 -------执行异步任务,无返回值结果---------
myPool-0 -----自定义线程执行异步任务,无返回结果------
supplyAsync
supplyAsync:有返回值,可以自定义线程池,如果没有自定义线程池,默认使用ForkJoinPool线程池
源码
//默认线程池public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier) {return asyncSupplyStage(asyncPool, supplier);}
// 自定义线程池
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier,Executor executor) {return asyncSupplyStage(screenExecutor(executor), supplier);}案例
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " ------执行异步任务,有返回值------");return "返回值1";});System.out.println(completableFuture1.get());CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " ------自定义线程池执行异步任务,有返回值------");return "返回值2";}, ThreadPoolUtils.getThreadPool());System.out.println(completableFuture2.get());}结果
ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-9 ------执行异步任务,有返回值------
返回值1
myPool-0 ------自定义线程池执行异步任务,有返回值------
返回值2
规律
- supply开头:可以返回异步执行的结果
- run开头:不会返回结果,只是执行线程任务
CompletableFuture获取返回值方法介绍
- join:返回结果或者抛出一个unchecked异常(CompletionException),不需要显式捕获异常
- get:此方法继承Future的get阻塞方法,返回结果或者一个具体的异常(ExecutionException,InterruptedException)
- getNow:如果当前任务执行完成,返回执行结果,否则返回默认值
返回值区别
- join与get区别在于join()返回计算的结果或者抛出一个异常,而get会返回一个具体的异常
- getNow与join和get的区别,getNow返回当前执行好的结果,如果当前未执行完,则返回设定好的默认值。
代码演示
public static void main(String[] args) {CompletableFuture completableFuture1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " ------执行异步任务,有返回值------");return "返回值1";});try {System.out.println("get():" + completableFuture1.get());} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (ExecutionException e) {e.printStackTrace();}CompletableFuture completableFuture2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " ------自定义线程池执行异步任务,有返回值------");return "返回值2";}, ThreadPoolUtils.getThreadPool());System.out.println("join():" + completableFuture2.join());CompletableFuture completableFuture3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " ------自定义线程池执行异步任务,有返回值------");try {Thread.sleep(5000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "返回值3";}, ThreadPoolUtils.getThreadPool());System.out.println("------这一步,直接返回默认值------");System.out.println("getNow():" + completableFuture3.getNow("默认值"));try {System.out.println("-----进行线程阻塞,等待completableFuture3内容执行完成-----");System.out.println("get():" + completableFuture3.get());} catch (ExecutionException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("-----当前异步任务已经执行完成,返回结果-----");System.out.println("getNow():" + completableFuture3.getNow("默认值"));}返回结果
ForkJoinPool.commonPool-worker-9 ------执行异步任务,有返回值------
get():返回值1
myPool-0 ------自定义线程池执行异步任务,有返回值------
join():返回值2
------这一步,直接返回默认值------
getNow():默认值
-----进行线程阻塞,等待completableFuture3内容执行完成-----
myPool-1 ------自定义线程池执行异步任务,有返回值------
get():返回值3
-----当前异步任务已经执行完成,返回结果-----
getNow():返回值3
CompletableFuture其他常用的API
thenApply
thenApply拿到上一步异步线程返回的结果进行后续处理。可以拿到上一次线程执行的返回结果,并且可以一直传递下去。
源码
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApply(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn) {return uniApplyStage(null, fn);}案例
public static void main(String[] args) {String str = "上海";String str2 = "深圳";CompletableFuture<StringBuffer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {return new StringBuffer("北京");// a是上一步异步线程返回的结果}, ThreadPoolUtils.getThreadPool()).thenApply(a -> a.append(str)).thenApply(b -> b.append(str2));try {System.out.println(future.get());} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (ExecutionException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}结果
北京上海深圳
thenCompose
thenCompose方法功能跟thenApply相似,都是会在上一个任务执行完成以后,拿到上一步的执行结果,进行后续处理,不同的是,两个方法的参数不一致,并且,thenCompose在执行的时候,需要创建一个新的CompletableFuture。
源码
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenCompose(Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn) {return uniComposeStage(null, fn);}案例
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {/*** supply直接返回,会得到一个CompletableFuture<String>* 经过thenApply处理,CompletableFuture<String>会转成一个CompletableFuture<Integer>* 但CompletableFuture是同一个*/CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {// 返回一个字符串return "北京";// a是上一步异步线程返回的结果}, ThreadPoolUtils.getThreadPool()).thenApply(a -> {if ("北京".equals(a)) {return 1;} else {return 0;}});System.out.println(future.get());CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {// 返回一个字符串return "北京";// 重新再创建一个CompleteFuture}, ThreadPoolUtils.getThreadPool()).thenCompose(a -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {if ("北京".equals(a)) {return 1;} else {return 0;}}));System.out.println(completableFuture.get());}结果
1
1
1
1thenAccept和thenRun
thenAccept和thenRun:进行返回值回调。这样CompletableFuture就会没有返回值
源码
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAccept(Consumer<? super T> action) {return uniAcceptStage(null, action);}public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRun(Runnable action) {return uniRunStage(null, action);}
案例
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {//模拟计算 1+1+1CompletableFuture future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {return 1;}, ThreadPoolUtils.getThreadPool()).thenApply(a -> a + 1).thenAccept(b -> System.out.println(b + 1));System.out.println("thenAccept返回了什么?" + future.get());CompletableFuture future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {return 1;}, ThreadPoolUtils.getThreadPool()).thenApply(a -> a + 1).thenRun(()->{System.out.println("----------线程运行----------");});System.out.println("thenRun返回了什么?" + future2.get());}结果
3
thenAccept返回了什么?null
----------线程运行----------
thenRun返回了什么?null
两者区别:两者入参不同, thenRun参数是Runnable ,thenAccept参数是Consumer<? super T> action,thenAccept可以拿到上一步获取到的值。
complete
complete()方法用于手动完成一个异步任务,并设置其结果。一旦调用complete()方法,CompleteFuture对象的状态会立即变成已完成。如果多个线程尝试调用complete()方法,只有第一个成功的线程能够设置结果,其他线程调用将被忽略
源码
public boolean complete(T value) {boolean triggered = completeValue(value);postComplete();return triggered;
}案例
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {return "10";}, ThreadPoolUtils.getThreadPool());future.complete("1000");future.complete("10000");//输出1000System.out.println(future.get());}结果
调用complete以后:1000
whenComplete
whenComplete是一个回调方法,会将CompletableFuture执行的结果和异常传递给它,如果是正常执行,则异常为null,如果异常,则get()方法会抛出异常。
源码
public CompletableFuture<T> whenComplete(BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action) {return uniWhenCompleteStage(null, action);}案例
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {return "10";}, ThreadPoolUtils.getThreadPool()).whenComplete((v,e)->{System.out.println("获取到的异常:"+e);System.out.println("获取到的值:"+v);});// 这个地方会抛出异常System.out.println("whenComplete无异常回调以后以后:" + completableFuture.get());CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {int i = 1 / 0;return "10";}, ThreadPoolUtils.getThreadPool()).whenComplete((v,e)->{System.out.println("获取到的异常:"+e);System.out.println("获取到的值:"+v);});// 这个地方会抛出异常System.out.println("whenComplete有异常回调以后:" + future.get());}结果
获取到的异常:null 获取到的值:10 whenComplete无异常回调以后以后:10 获取到的异常:java.util.concurrent.CompletionException: java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero 获取到的值:null Exception in thread "main" java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException: java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zeroat java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture.reportGet(CompletableFuture.java:357)at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture.get(CompletableFuture.java:1895)at com.common.base.util.CompletableFutureTest2.main(CompletableFutureTest2.java:30) Caused by: java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zeroat com.common.base.util.CompletableFutureTest2.lambda$main$2(CompletableFutureTest2.java:23)at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture$AsyncSupply.run(CompletableFuture.java:1590)at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1149)at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:624)at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:748)
exceptionally
exceptionally()对CompletableFuture异常进行捕获处理,并且设定一个返回值
源码
public CompletableFuture<T> exceptionally(Function<Throwable, ? extends T> fn) {return uniExceptionallyStage(fn);}案例
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {int i = 1 / 0;return "10";}, ThreadPoolUtils.getThreadPool()).exceptionally(e -> {//e.printStackTrace();System.out.println("执行的异常:" + e.getMessage());return "捕获异常以后自定义返回值";});System.out.println("捕获异常以后:" + future.get());}结果
执行的异常:java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
捕获异常以后:捕获异常以后自定义返回值注意:大多数的时候我们通常都会把whenComplete+exceptionally结合起来一起使用
whenComplete+exceptionally案例
Callable、Future和FutrueTask详解-CSDN博客
有这么一个问题,你的女朋友正在炒菜,发现厨房没盐了,需要你把新买的盐拿过来,如果使用FutureTask,那么会造成阻塞,现在使用CompletFuture来解决这个问题
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {System.out.println("------------女朋友开始炒菜----------------");try {CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {return "让男朋友去买盐";}, ThreadPoolUtils.getThreadPool()).whenComplete((v, e) -> {if (e == null) {System.out.println("获取到任务:" + v);}}).exceptionally(e -> {e.printStackTrace();System.out.println("执行异常:" + e.getCause());return null;});System.out.println("----------女朋友继续炒菜-----------------");Thread.sleep(2000);System.out.println("-----------------女朋友炒菜结束--------------");} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}结果
------------女朋友开始炒菜----------------
获取到任务:让男朋友去买盐
----------女朋友继续炒菜-----------------
-----------------女朋友炒菜结束--------------
通过上面代码我们可以知道,主线程女朋友炒菜可以一步都到底,不会出现线程阻塞的情况
handle
handle()方法是一个回调方法,跟whenComplete没有多大的区别,唯一的区别是handle有返回值
源码
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> handle(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn) {return uniHandleStage(null, fn);}案例
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {return "10";}, ThreadPoolUtils.getThreadPool()).handle((v, e) -> {System.out.println("不存在异常的值" + e);System.out.println("上一步返回值:" + v);return "100";});//这个地方会抛出异常System.out.println("无异常回调handle以后:" + future.get());CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {int i = 1 / 0;return "10";}, ThreadPoolUtils.getThreadPool()).handle((v, e) -> {System.out.println("不存在异常的值" + e);System.out.println("上一步返回值:" + v);return "返回异常" + e.getMessage();});//这个地方会抛出异常System.out.println("有异常回调handle以后:" + completableFuture.get());}结果
不存在异常的值:null
上一步返回值:10
无异常回调handle以后:100
不存在异常的值:java.util.concurrent.CompletionException: java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
上一步返回值:null
有异常回调handle以后:返回异常java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
allof
allof是将多个CompletableFuture合并在一起
源码
public static CompletableFuture<Void> allOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs) {return andTree(cfs, 0, cfs.length - 1);}案例
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {return "用户信息";}, ThreadPoolUtils.getThreadPool());//角色idCompletableFuture<String> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {Thread.sleep(5000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "角色信息";}, ThreadPoolUtils.getThreadPool());// 组合用户和角色idCompletableFuture future2 = CompletableFuture.allOf(future, future1);CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = future2.thenApply(a -> {return future.join()+" " + future1.join();});//通过回调函数,获取对应的结果集System.out.println("等待两个线程执行完毕,进行合并" + completableFuture.join());}结果
等待两个线程执行完毕,进行合并用户信息 角色信息
anyOf
多个任务中,那个任务先返回,就先返回哪个结果
源码
public static CompletableFuture<Object> anyOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs) {return orTree(cfs, 0, cfs.length - 1);}案例
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {return "用户信息";}, ThreadPoolUtils.getThreadPool());//角色idCompletableFuture<String> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {Thread.sleep(5000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "角色信息";}, ThreadPoolUtils.getThreadPool());// 组合用户和角色idCompletableFuture future2 = CompletableFuture.anyOf(future, future1);System.out.println("anyOf谁先执行完,谁就先返回:" + future2.join());}结果
anyOf谁先执行完,谁就先返回:用户信息
提示
CompletableFuture提供了很多方法,上面的方法都是CompletableFuture提供的同步方法,如果在上面的方法后缀加上Async,那么成了调用它的异步方法,比如thenApplyAsync()。
参考文章:CompletableFuture使用详解 - 简书