我是南城余!阿里云开发者平台专家博士证书获得者!
欢迎关注我的博客!一同成长!
一名从事运维开发的worker,记录分享学习。
专注于AI,运维开发,windows Linux 系统领域的分享!
本章节对应知识库
https://www.yuque.com/nanchengcyu/java
本内容来自尚硅谷课程,此处在知识库做了个人理解
————————————————
5.4、基于注解的AOP
5.4.1、技术说明
- 动态代理分为JDK动态代理和cglib动态代理
- 当目标类有接口的情况使用JDK动态代理和cglib动态代理,没有接口时只能使用cglib动态代理
- JDK动态代理动态生成的代理类会在com.sun.proxy包下,类名为$proxy1,和目标类实现相同的接口
- cglib动态代理动态生成的代理类会和目标在在相同的包下,会继承目标类
- 动态代理(InvocationHandler):JDK原生的实现方式,需要被代理的目标类必须实现接口。因为这个技术要求代理对象和目标对象实现同样的接口(兄弟两个拜把子模式)。
- cglib:通过继承被代理的目标类(认干爹模式)实现代理,所以不需要目标类实现接口。
- AspectJ:是AOP思想的一种实现。本质上是静态代理,将代理逻辑“织入”被代理的目标类编译得到的字节码文件,所以最终效果是动态的。weaver就是织入器。Spring只是借用了AspectJ中的注解。
5.4.2、准备工作
①添加依赖
在IOC所需依赖基础上再加入下面依赖即可:
<dependencies><!--spring context依赖--><!--当你引入Spring Context依赖之后,表示将Spring的基础依赖引入了--><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-context</artifactId><version>6.0.2</version></dependency><!--spring aop依赖--><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId><version>6.0.2</version></dependency><!--spring aspects依赖--><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId><version>6.0.2</version></dependency><!--junit5测试--><dependency><groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId><artifactId>junit-jupiter-api</artifactId><version>5.3.1</version></dependency><!--log4j2的依赖--><dependency><groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId><artifactId>log4j-core</artifactId><version>2.19.0</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId><artifactId>log4j-slf4j2-impl</artifactId><version>2.19.0</version></dependency>
</dependencies>
②准备被代理的目标资源
接口:
public interface Calculator {int add(int i, int j);int sub(int i, int j);int mul(int i, int j);int div(int i, int j);}
实现类:
@Component
public class CalculatorImpl implements Calculator {@Overridepublic int add(int i, int j) {int result = i + j;System.out.println("方法内部 result = " + result);return result;}@Overridepublic int sub(int i, int j) {int result = i - j;System.out.println("方法内部 result = " + result);return result;}@Overridepublic int mul(int i, int j) {int result = i * j;System.out.println("方法内部 result = " + result);return result;}@Overridepublic int div(int i, int j) {int result = i / j;System.out.println("方法内部 result = " + result);return result;}
}
5.4.3、创建切面类并配置
// @Aspect表示这个类是一个切面类
@Aspect
// @Component注解保证这个切面类能够放入IOC容器
@Component
public class LogAspect {@Before("execution(public int com.atguigu.aop.annotation.CalculatorImpl.*(..))")public void beforeMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint){String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();String args = Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs());System.out.println("Logger-->前置通知,方法名:"+methodName+",参数:"+args);}@After("execution(* com.atguigu.aop.annotation.CalculatorImpl.*(..))")public void afterMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint){String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();System.out.println("Logger-->后置通知,方法名:"+methodName);}@AfterReturning(value = "execution(* com.atguigu.aop.annotation.CalculatorImpl.*(..))", returning = "result")public void afterReturningMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result){String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();System.out.println("Logger-->返回通知,方法名:"+methodName+",结果:"+result);}@AfterThrowing(value = "execution(* com.atguigu.aop.annotation.CalculatorImpl.*(..))", throwing = "ex")public void afterThrowingMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint, Throwable ex){String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();System.out.println("Logger-->异常通知,方法名:"+methodName+",异常:"+ex);}@Around("execution(* com.atguigu.aop.annotation.CalculatorImpl.*(..))")public Object aroundMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint){String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();String args = Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs());Object result = null;try {System.out.println("环绕通知-->目标对象方法执行之前");//目标对象(连接点)方法的执行result = joinPoint.proceed();System.out.println("环绕通知-->目标对象方法返回值之后");} catch (Throwable throwable) {throwable.printStackTrace();System.out.println("环绕通知-->目标对象方法出现异常时");} finally {System.out.println("环绕通知-->目标对象方法执行完毕");}return result;}}
在Spring的配置文件中配置:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttp://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsdhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/contexthttp://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsdhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/aophttp://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"><!--基于注解的AOP的实现:1、将目标对象和切面交给IOC容器管理(注解+扫描)2、开启AspectJ的自动代理,为目标对象自动生成代理3、将切面类通过注解@Aspect标识--><context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu.aop.annotation"></context:component-scan><aop:aspectj-autoproxy />
</beans>
执行测试:
public class CalculatorTest {private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CalculatorTest.class);@Testpublic void testAdd(){ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");Calculator calculator = ac.getBean( Calculator.class);int add = calculator.add(1, 1);logger.info("执行成功:"+add);}}
5.4.4、各种通知
- 前置通知:使用@Before注解标识,在被代理的目标方法前执行
- 返回通知:使用@AfterReturning注解标识,在被代理的目标方法成功结束后执行(寿终正寝)
- 异常通知:使用@AfterThrowing注解标识,在被代理的目标方法异常结束后执行(死于非命)
- 后置通知:使用@After注解标识,在被代理的目标方法最终结束后执行(盖棺定论)
- 环绕通知:使用@Around注解标识,使用try…catch…finally结构围绕整个被代理的目标方法,包括上面四种通知对应的所有位置
各种通知的执行顺序:
- Spring版本5.3.x以前:
- 前置通知
- 目标操作
- 后置通知
- 返回通知或异常通知
- Spring版本5.3.x以后:
- 前置通知
- 目标操作
- 返回通知或异常通知
- 后置通知
5.4.5、切入点表达式语法
①作用
②语法细节
-
用*号代替“权限修饰符”和“返回值”部分表示“权限修饰符”和“返回值”不限
-
在包名的部分,一个“*”号只能代表包的层次结构中的一层,表示这一层是任意的。
- 例如:*.Hello匹配com.Hello,不匹配com.atguigu.Hello
-
在包名的部分,使用“*…”表示包名任意、包的层次深度任意
-
在类名的部分,类名部分整体用*号代替,表示类名任意
-
在类名的部分,可以使用*号代替类名的一部分
- 例如:*Service匹配所有名称以Service结尾的类或接口
-
在方法名部分,可以使用*号表示方法名任意
-
在方法名部分,可以使用*号代替方法名的一部分
- 例如:*Operation匹配所有方法名以Operation结尾的方法
-
在方法参数列表部分,使用(…)表示参数列表任意
-
在方法参数列表部分,使用(int,…)表示参数列表以一个int类型的参数开头
-
在方法参数列表部分,基本数据类型和对应的包装类型是不一样的
- 切入点表达式中使用 int 和实际方法中 Integer 是不匹配的
-
在方法返回值部分,如果想要明确指定一个返回值类型,那么必须同时写明权限修饰符
- 例如:execution(public int …Service.(…, int)) 正确
例如:execution( int *…Service.(…, int)) 错误
- 例如:execution(public int …Service.(…, int)) 正确
5.4.6、重用切入点表达式
①声明
@Pointcut("execution(* com.atguigu.aop.annotation.*.*(..))")
public void pointCut(){}
②在同一个切面中使用
@Before("pointCut()")
public void beforeMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint){String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();String args = Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs());System.out.println("Logger-->前置通知,方法名:"+methodName+",参数:"+args);
}
③在不同切面中使用
@Before("com.atguigu.aop.CommonPointCut.pointCut()")
public void beforeMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint){String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();String args = Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs());System.out.println("Logger-->前置通知,方法名:"+methodName+",参数:"+args);
}
5.4.7、获取通知的相关信息
①获取连接点信息
获取连接点信息可以在通知方法的参数位置设置JoinPoint类型的形参
@Before("execution(public int com.atguigu.aop.annotation.CalculatorImpl.*(..))")
public void beforeMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint){//获取连接点的签名信息String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();//获取目标方法到的实参信息String args = Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs());System.out.println("Logger-->前置通知,方法名:"+methodName+",参数:"+args);
}
②获取目标方法的返回值
@AfterReturning中的属性returning,用来将通知方法的某个形参,接收目标方法的返回值
@AfterReturning(value = "execution(* com.atguigu.aop.annotation.CalculatorImpl.*(..))", returning = "result")
public void afterReturningMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result){String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();System.out.println("Logger-->返回通知,方法名:"+methodName+",结果:"+result);
}
③获取目标方法的异常
@AfterThrowing中的属性throwing,用来将通知方法的某个形参,接收目标方法的异常
@AfterThrowing(value = "execution(* com.atguigu.aop.annotation.CalculatorImpl.*(..))", throwing = "ex")
public void afterThrowingMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint, Throwable ex){String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();System.out.println("Logger-->异常通知,方法名:"+methodName+",异常:"+ex);
}
5.4.8、环绕通知
@Around("execution(* com.atguigu.aop.annotation.CalculatorImpl.*(..))")
public Object aroundMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint){String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();String args = Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs());Object result = null;try {System.out.println("环绕通知-->目标对象方法执行之前");//目标方法的执行,目标方法的返回值一定要返回给外界调用者result = joinPoint.proceed();System.out.println("环绕通知-->目标对象方法返回值之后");} catch (Throwable throwable) {throwable.printStackTrace();System.out.println("环绕通知-->目标对象方法出现异常时");} finally {System.out.println("环绕通知-->目标对象方法执行完毕");}return result;
}
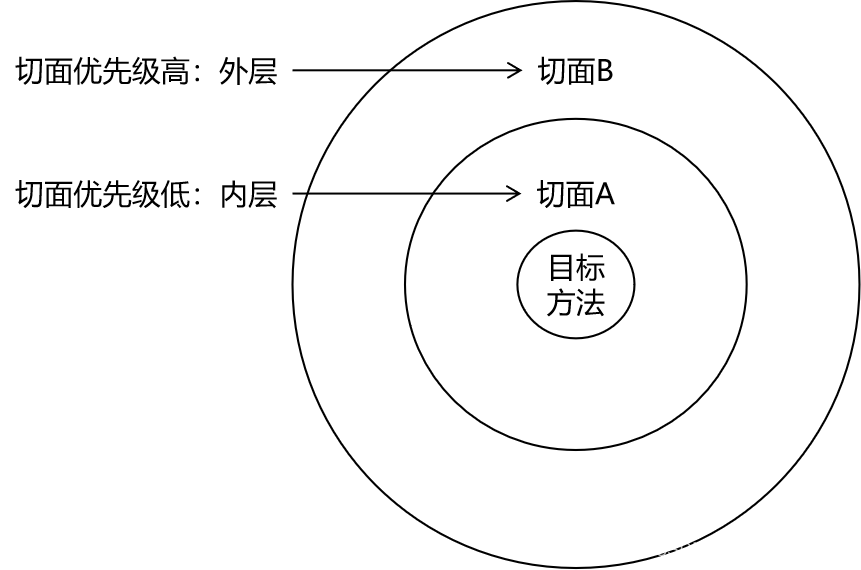
5.4.9、切面的优先级
相同目标方法上同时存在多个切面时,切面的优先级控制切面的内外嵌套顺序。
- 优先级高的切面:外面
- 优先级低的切面:里面
使用@Order注解可以控制切面的优先级:
- @Order(较小的数):优先级高
- @Order(较大的数):优先级低

5.5、基于XML的AOP
5.5.1、准备工作
参考基于注解的AOP环境
5.5.2、实现
<context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu.aop.xml"></context:component-scan><aop:config><!--配置切面类--><aop:aspect ref="loggerAspect"><aop:pointcut id="pointCut" expression="execution(* com.atguigu.aop.xml.CalculatorImpl.*(..))"/><aop:before method="beforeMethod" pointcut-ref="pointCut"></aop:before><aop:after method="afterMethod" pointcut-ref="pointCut"></aop:after><aop:after-returning method="afterReturningMethod" returning="result" pointcut-ref="pointCut"></aop:after-returning><aop:after-throwing method="afterThrowingMethod" throwing="ex" pointcut-ref="pointCut"></aop:after-throwing><aop:around method="aroundMethod" pointcut-ref="pointCut"></aop:around></aop:aspect>
</aop:config>