Collection集合的遍历方式主要有三种:
迭代器遍历
增强for遍历
Lambda表达式遍历
我们平时最常用到的 普通for遍历 怎么不见了呢?
这是因为普通for遍历只能用在 List 集合中,我们还需要考虑到 无索引 的 Set 结合
迭代器遍历
迭代器 有一个最大的特点 -- 不依赖索引 ,因此 Set 集合也可以使用
迭代器在Java中的类是 Iterator ,迭代器是集合专用的遍历方式
Collection中有一个方法 Iterator<E> iterator() -- 返回此集合中元素的迭代器
Iterator中的常用方法
- boolean hasNext() -- 判断当前位置是否有元素可以被取出
- E next(): -- 获取当前位置的元素,将迭代器对象移向下一个索引位置
加下来看案例
public class IteratorDemo1 {public static void main(String[] args) {//创建集合对象Collection<String> c = new ArrayList<>();//添加元素c.add("hello");c.add("world");c.add("java");c.add("javaee");//Iterator<E> iterator():返回此集合中元素的迭代器,通过集合的iterator()方法得到Iterator<String> it = c.iterator();//用while循环改进元素的判断和获取while (it.hasNext()) {String s = it.next();System.out.println(s);}}
}迭代器遍历完毕后,不会复位,如果要再次遍历,就再重新获取一个迭代器对象
我们知道,当用 普通for 对集合进行遍历删除时(如:删除集合中的所有 "A" 元素),容易出错
如果是迭代器,就不会出现该问题,如下
public class IteratorDemo2 {public static void main(String[] args) {ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add("a");list.add("b");list.add("b");list.add("c");list.add("d");Iterator<String> it = list.iterator();while(it.hasNext()){String s = it.next();if("b".equals(s)){//指向谁,那么此时就删除谁.it.remove();}}System.out.println(list);}
}增强for遍历(foreach)
增强for的底层就是迭代器,为了简化迭代器代码的书写
所有的单列结合 和 数组 才能用增强for遍历,双列集合不行
使用方法如下:
public class MyCollectonDemo1 {public static void main(String[] args) {ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add("a");list.add("b");list.add("c");list.add("d");list.add("e");list.add("f");//1,数据类型一定是集合或者数组中元素的类型//2,str仅仅是一个变量名而已,在循环的过程中,依次表示集合或者数组中的每一个元素//3,list就是要遍历的集合或者数组for(String str : list){System.out.println(str);}}
}注意:修改增强for中的变量,不会改变集合中原本的数据,如下代码
public class MyCollectonDemo1 {public static void main(String[] args) {ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add("a");list.add("b");list.add("c");for(String str : list){str="d";}}
}结束后,list中的值仍然为 "a","b","c" ,此处的str可以类比形参的概念
Lambda表达式遍历
利用forEach方法,再结合lambda表达式的方式进行遍历 (注意此处forEach方法与增强for遍历的foreach区分)
我们看下 ArrayList 的forEach方法源码
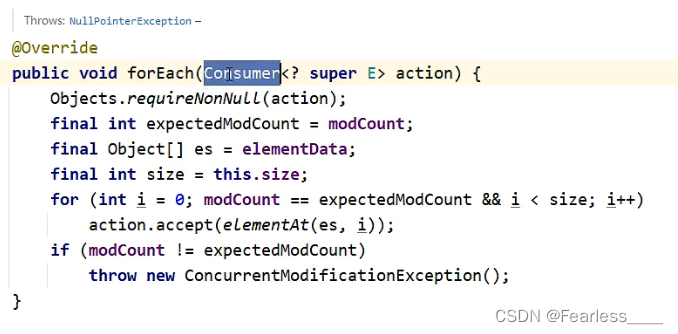
我们可以看到入参是Consumer,我们继续追踪
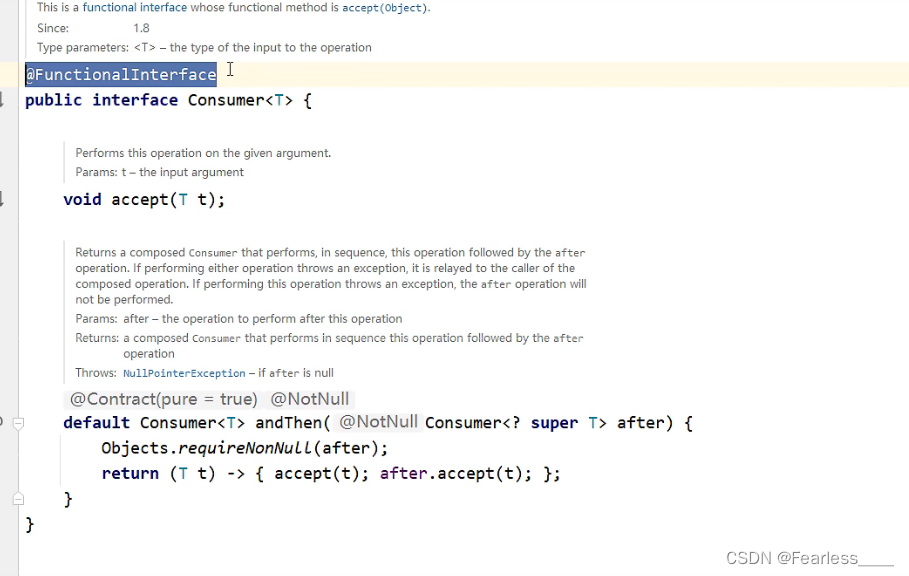 我们可以看到 Consumer 中有@FunctionInterface注解,表明是函数式接口,因此我们可以使用lambda表达式,并要实现 accept 方法
我们可以看到 Consumer 中有@FunctionInterface注解,表明是函数式接口,因此我们可以使用lambda表达式,并要实现 accept 方法
我们再看ArrayList的forEach方法源码,核心的代码就是一个 普通for(其他集合的实现方式不一定是),在 for 中逐个遍历出元素,然后传给 accept 方法,在accept中对元素逐个进行操作
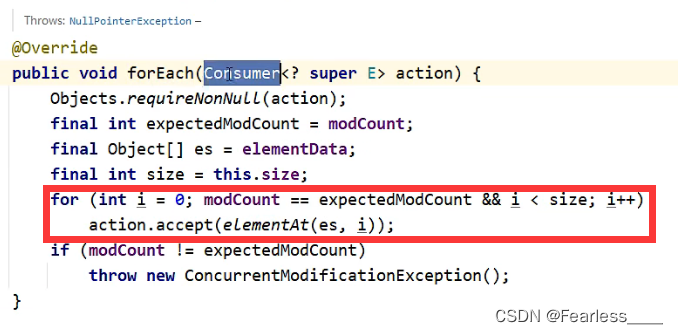
因此,使用方法如下
public class A07_CollectionDemo7 {public static void main(String[] args) {Collection<String> coll = new ArrayList<>();coll.add("zhangsan");coll.add("lisi");coll.add("wangwu");coll.forEach(s -> System.out.println(s));}
}





![[分布式] Ceph实战应用](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/7cadfc84100d415d8aec0faacdec083f.png)