从下面论文看到这个方法:
Wang, Xin, et al. "Deep learning using bulk RNA-seq data expands cell landscape identification in tumor microenvironment." Oncoimmunology 11.1 (2022): 2043662.
这篇论文基于 AI 方法对 bulk RNA-seq 数据识别肿瘤微环境中的细胞景观。
一、描述这个聚类方法的段落:
The R package of ConsensusCluster [REF], which provides a consensus clustering approach was used to classify pancancer patients into different cancer subtypes according the cell landscape identified by DCNet model. In brief, using a manhattan distance, the cluster method of partition around medoids (PAM) was resampled by 0.8% from all cell type features in 1000 iterations. The result is a co-classification matrix with the matrix element value equal to the frequency at which each pair of samples was found in the same cluster in the 1000 iterations. The consensus cluster result was obtained by a final k-mean clustering. In order to select the number of clusters K, the cophenetic correlation coefficient was calculated and the optimal number of consensus cluster was selected as K preceding the largest drop in the cophenetic correlation coefficient.
REF: Wilkerson MD, Hayes DN. ConsensusClusterPlus: a class discovery tool with confidence assessments and item tracking. Bioinformatics. 2010;26(12):1572–1573. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btq170.
二、方法详细描述
共识聚类是一种用于稳健地划分样本群集的方法。在这个情境下,研究人员想要将泛癌患者划分为不同的亚型。
Step1: DCNet模型用于识别细胞景观,可能通过基因表达或其他分子数据揭示不同的细胞类型或状态。
Step2: 基于曼哈顿距离,使用PAM (Partition Around Medoids)聚类:它通过选择中心点(medoids)来划分样本。这里,PAM通过0.8%的重采样在1000次迭代中应用于所有细胞类型特征。
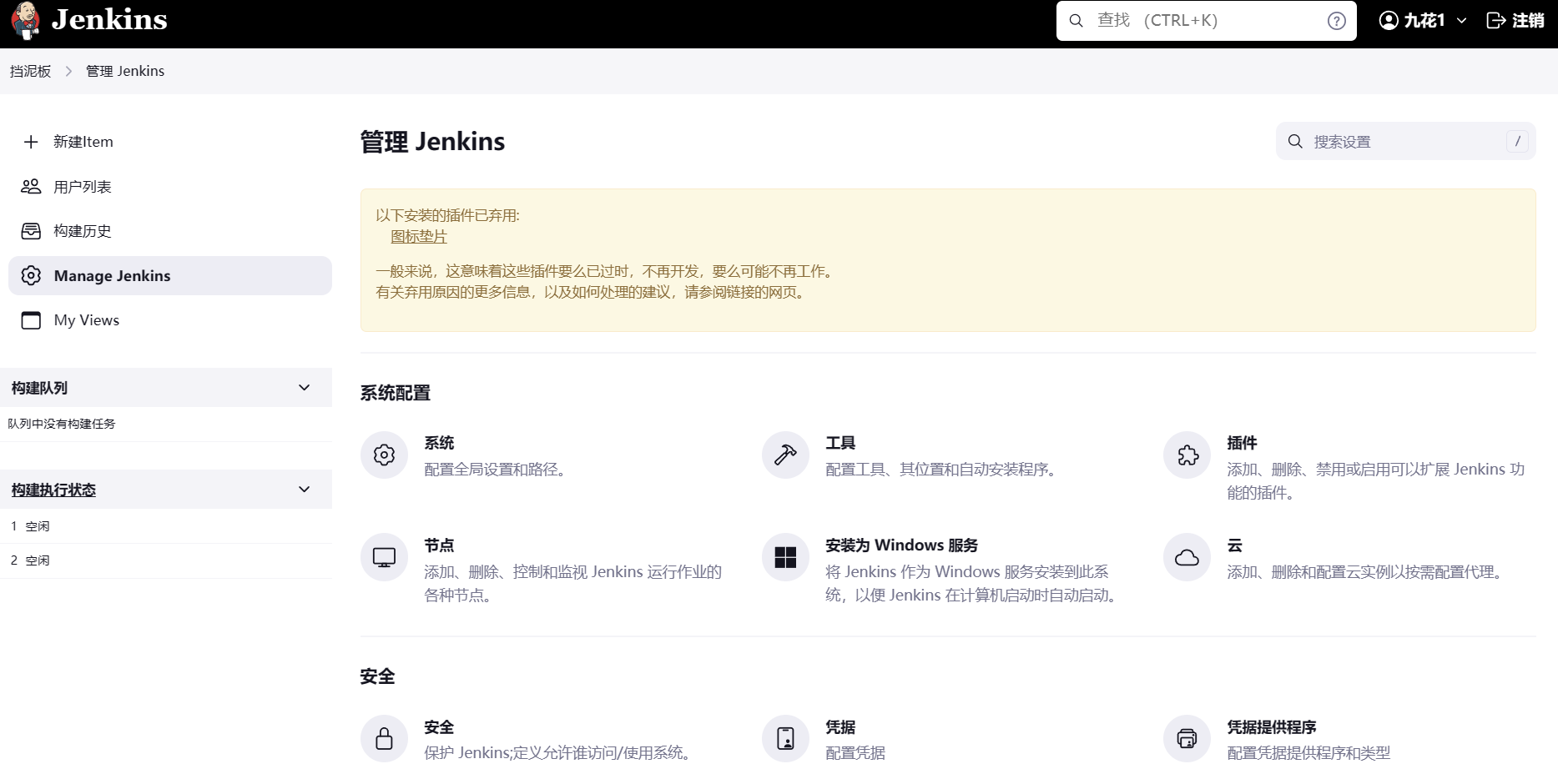
Step3: 结果是一个共同分类矩阵,其中每个元素表示每对样本在1000次迭代中位于相同聚类中的频率。
其中:
Step4: 最后,通过应用k均值聚类,得到了最终的共识聚类结果。
Step5: 为了选择聚类数K,计算了共形相关系数 cophenetic correlation coefficient。共形相关系数衡量了原始数据和聚类结果之间的拓扑相似性。选择具有共形相关系数下降最大的K,这可能是聚类结果的拐点。

其中“如何根据聚类结果,计算一个相似性矩阵”:
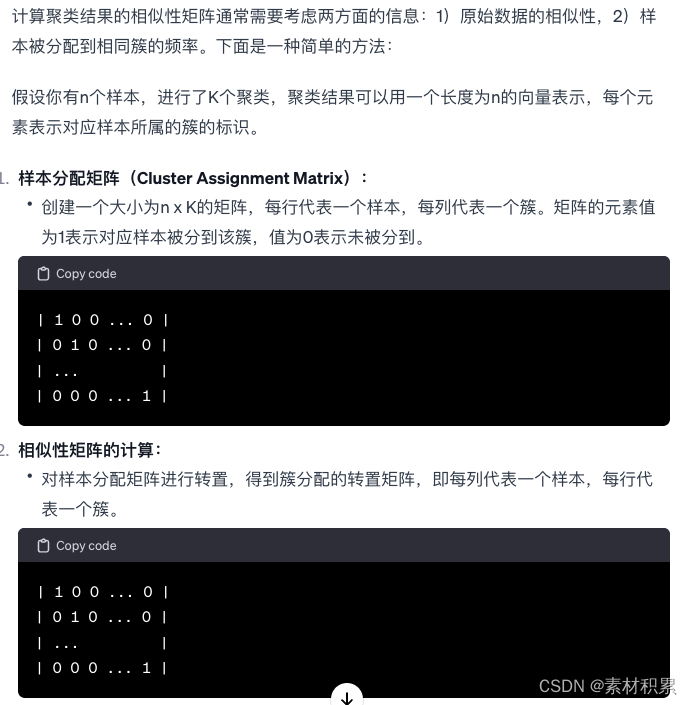

根据原始数据计算一个相似性矩阵 常用方法: