目录
- 1 AOP
- 1.1 AOP案例引入
- 1.1.1 数据库事务说明
- 1.2 Spring实现事务控制
- 1.2.1 代码结构如下
- 1.2.2 编辑User
- 1.2.3 编辑UserMapper/UserMapperImpl
- 1.2.4 编辑UserService/UserServiceImpl
- 1.2.5 编辑配置类
- 1.2.6 编辑测试类
- 1.3 代码问题分析
- 1.4 代理模式
- 1.4.1 生活中代理案例
- 1.4.2 代理模式
- 1.5 静态代理
- 1.5.1 通过代理模式实现事务控制
- 1.5.2 修改目标对象名称
- 1.5.3 编辑代理类
- 1.5.4 编辑测试类
- 1.5 静态代理弊端
- 1.6 动态代理机制
- 1.6.1 动态代理分类
- 1.6.2 编辑JDK动态代理
- 1.6.3 JDK动态代理执行过程
- 1.7 动态代理优势
- 1.7.1 编辑DeptService/DeptServiceImpl
- 1.7.2 编辑测试类
- 1.8 动态代理实现Demo2
- 1.8.1 业务需求
- 1.8.2 编辑UserService/UserServiceImpl
- 1.8.3 编辑代理工厂
- 1.8.4 编辑测试案例
1 AOP
1.1 AOP案例引入
1.1.1 数据库事务说明
- 案例分析:
- userMapper.insert(User对象)
- deptMapper.insert(dept对象)
- 由于业务需求 要求方法要么同时入库,要么同时回滚.所以必须通过事务进行控制.
1.2 Spring实现事务控制
1.2.1 代码结构如下
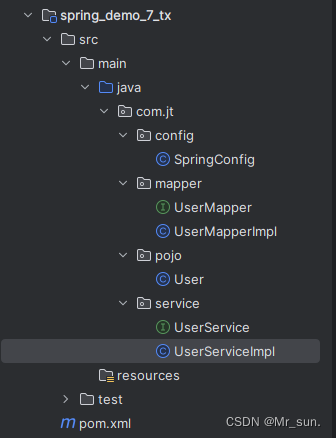
1.2.2 编辑User
public class User {private Integer id;private String name;public Integer getId() {return id;}public void setId(Integer id) {this.id = id;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "User{" +"id=" + id +", name='" + name + '\'' +'}';}
}
1.2.3 编辑UserMapper/UserMapperImpl
- 编辑UserMapper
import com.jt.pojo.User;public interface UserMapper {void addUser(User user);
}
- 编辑UserMapperImpl
import com.jt.pojo.User;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;@Repository
public class UserMapperImpl implements UserMapper {//??事务控制应该在哪一层完成!!dao/mapper service@Overridepublic void addUser(User user) {System.out.println("用户入库"+user);}
}
1.2.4 编辑UserService/UserServiceImpl
- 编辑UserService
import com.jt.pojo.User;public interface UserService {void addUser(User user);
}
- 编辑UserServiceImpl
import com.jt.mapper.UserMapper;
import com.jt.pojo.User;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{@Autowiredprivate UserMapper userMapper;//事务控制应该放在Service层中控制@Overridepublic void addUser(User user) {try {System.out.println("事务开始");userMapper.addUser(user);System.out.println("事务结束");} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();System.out.println("事务回滚");}}
}
1.2.5 编辑配置类
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;@Configuration//标识我是一个配置类
@ComponentScan("com.jt")
public class SpringConfig {
}
1.2.6 编辑测试类
import com.jt.config.SpringConfig;
import com.jt.pojo.User;
import com.jt.service.UserService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;public class TestUser {//Controller-Service-Mapper(Dao)//Spring中规定:// 如果传入的是接口的类型 则自动查找/注入 该接口的实现类// 该接口只有一个实现类@Testpublic void testTx(){ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);//写接口的类型/实现类的类型?UserService userService = context.getBean(UserService.class);
// UserService userService = (UserService) context.getBean("userServiceImpl");User user = new User();user.setId(101);user.setName("SpringAop测试入门案例");userService.addUser(user);}
}
1.3 代码问题分析
- Service层应该写代码业务,但是现在与事务控制紧紧的耦合在一起
- 代码冗余不便于大批量开发

- 解决方案:
- 采用代理模式进行编辑.
1.4 代理模式
1.4.1 生活中代理案例
- 房屋中介代理模式:
- 房东: 自己手里有房子 需要出租换钱
- 中介机构 1.本职工作 带客户看房/出租房屋 2.收取中介费(服务费)
- 租客: 满足自身需求 租房子
- 代码思维建模:
- 暴露一个公共的接口(租房子)
- 客户与中介机构进行沟通,中介看起来和房东功能一致.(代理看起来就是真实的对象)
- 完成用户额外的操作(收取中介费)
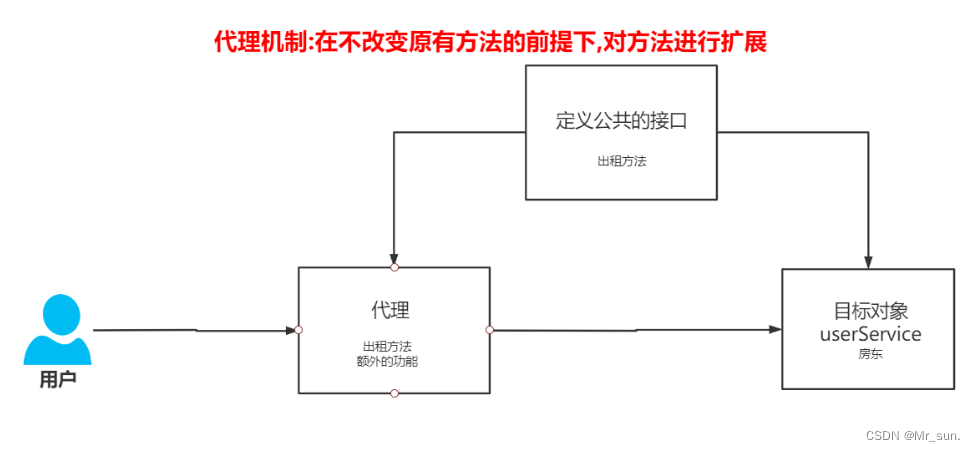
1.4.2 代理模式
- 组成部分
- 要求代理者实现与被代理者相同的接口
- 在代理方法中实现功能的扩展
- 用户调用代理对象完成功能(用户认为代理就是目标对象)
- 调用流程
1.5 静态代理
1.5.1 通过代理模式实现事务控制
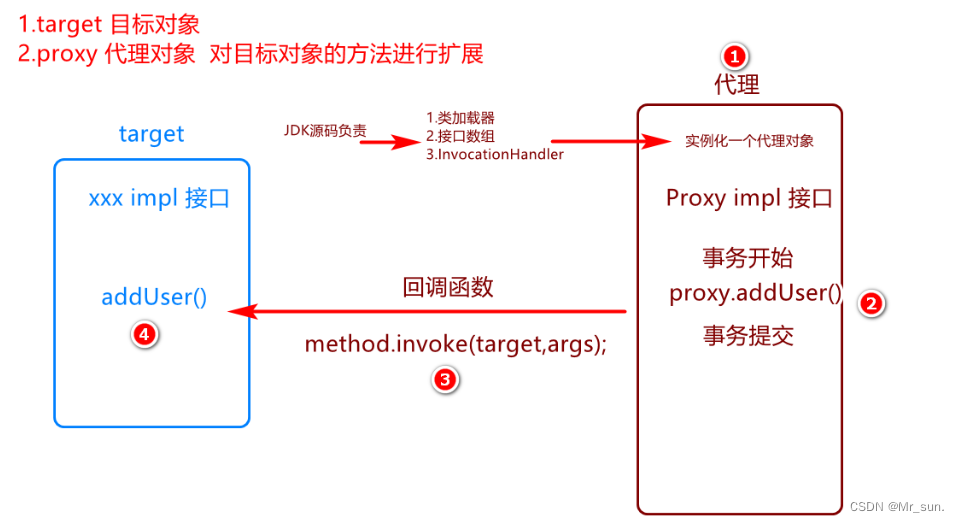
- 角色划分:
- 目标对象target UserServiceImpl类
- 目标方法 method addUser()方法
- 代理: 实现事务控制.
- 代理对象与目标对象实现相同的接口.
1.5.2 修改目标对象名称

1.5.3 编辑代理类
import com.jt.pojo.User;
import com.jt.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;@Service("userService")
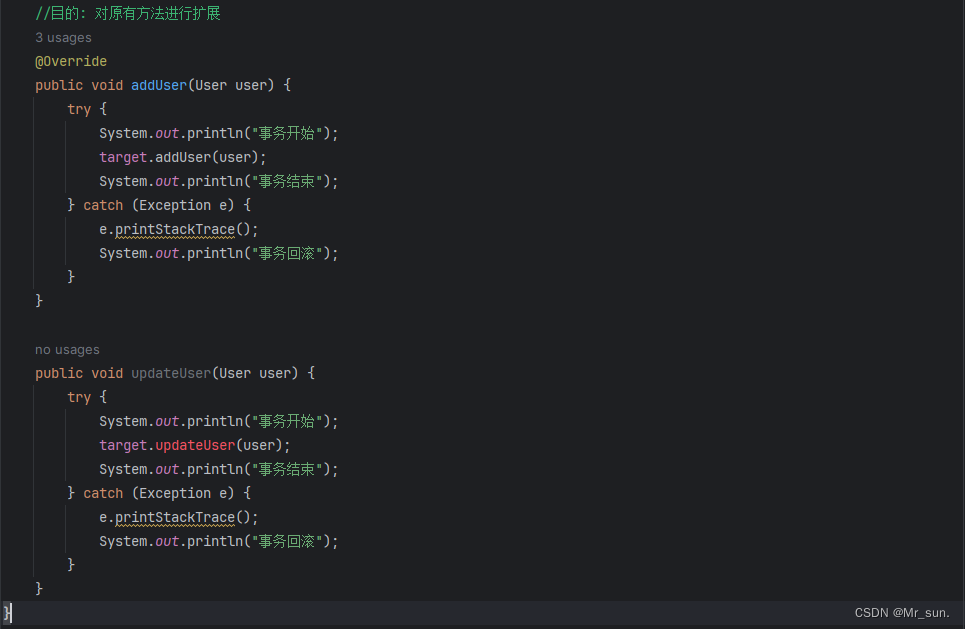
public class StaticProxy implements UserService {//要求引入目标对象@Autowired //ByType byName//@Qualifier("target")private UserService target;//目的: 对原有方法进行扩展@Overridepublic void addUser(User user) {try {System.out.println("事务开始");target.addUser(user);System.out.println("事务结束");} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();System.out.println("事务回滚");}}
}
1.5.4 编辑测试类
@Test
public void testStaticProxy(){ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);UserService userService = (UserService) context.getBean("userService");User user = new User();user.setId(10001);user.setName("测试代理机制");//执行用户调用userService.addUser(user);
}
1.5 静态代理弊端
- 静态代理只针对于某个接口 不能实现所有接口的代理 实用性较差

- 静态代理中所有的方法,都需要手动的添加事务开始/事务提交代码 代码冗余 不够简洁
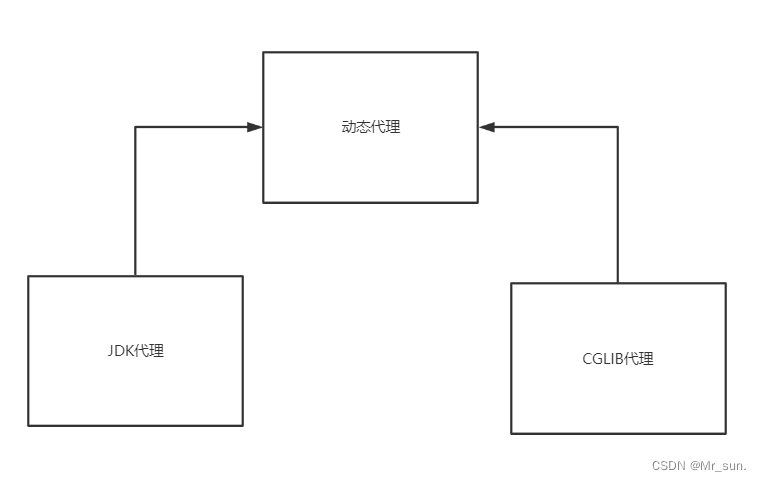
1.6 动态代理机制
1.6.1 动态代理分类
- JDK代理:
- 要求: 要求目标对象必须实现接口
- 代理要求: 代理对象也必须实现目标对象的接口
- 目标对象/代理关系: 目标对象与代理对象兄弟关系.
- CGlib代理
- 要求: 不管目标对象是否有接口,都可以为其创建代理对象
- 代理要求: 要求代理对象必须继承目标对象
- 目标对象/代理关系: 目标对象与代理对象是父子关系
1.6.2 编辑JDK动态代理
官网API:

- 知识点:
- 关于匿名内部类用法说明: 匿名内部类引用外部参数 要求参数必须final修饰
- 该方法标识 当代理对象执行时,"回调"该方法.
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {}- 目标方法执行
result = method.invoke(target,args);
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;//能否利用一个工厂动态为目标对象创建代理
public class JDKProxyFactory {//要求用户传递目标对象//关于匿名内部类用法说明: 匿名内部类引用外部参数 要求参数必须final修饰public static Object getProxy(final Object target) {//1.调用java API实现动态代理/*** 参数分析: 3个参数* 1.ClassLoader loader, 类加载器(获取目标对象的Class)* 2.类<?>[] interfaces, JDK代理要求 必须有接口* java中可以多实现* 3.InvocationHandler h 对目标方法进行扩展*///1.获取类加载器ClassLoader classLoader = target.getClass().getClassLoader();//2.获取接口数组Class[] interfaces = target.getClass().getInterfaces();//3.通过动态代理创建对象Object proxy = Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, interfaces, new InvocationHandler() {//invoke方法: 代理对象调用方法时invoke执行,扩展方法的编辑位置@Overridepublic Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {//proxy: 代理对象本身//method: 用户调用的方法对象//args: 用户调用方法的参数// result 标识目标方法执行的返回值Object result = null;try {//添加事务的控制System.out.println("事务开始");//执行目标方法// target真实的目标对象,method方法对象,args方法参数result = method.invoke(target, args);System.out.println("事务提交");} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();System.out.println("事务回滚");}return result;}});return proxy;}
}
- 测试代码
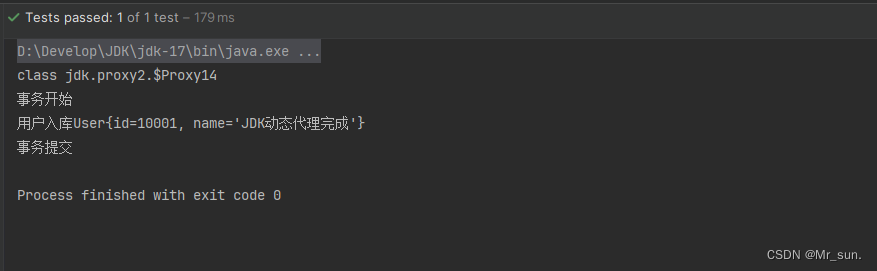
/*** 测试JDK动态代理*/@Testpublic void testJDKProxy(){ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);//1.获取用户目标对象UserService target = (UserService) context.getBean("target");//2.获取代理对象UserService userService = (UserService) JDKProxyFactory.getProxy(target);//3.打印代理对象的类型System.out.println(userService.getClass());//4.用户完成调用User user = new User();user.setId(10001);user.setName("JDK动态代理完成");//执行用户调用userService.addUser(user);}
1.6.3 JDK动态代理执行过程
1.7 动态代理优势
将公共的部分写到动态代理中,之后其他的业务类调用即可
1.7.1 编辑DeptService/DeptServiceImpl
- 编辑DeptService
public interface DeptService {void addDept();
}
- 编辑DeptServiceImpl
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;@Service("deptService")
public class DeptServiceImpl implements DeptService {@Overridepublic void addDept() {//添加事务System.out.println("调用DeptMapper实现入库操作");//提交事务}
}
1.7.2 编辑测试类
@Testpublic void testTx() {//1.获取目标对象ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);DeptService target = (DeptService) context.getBean("deptService");//2.获取代理对象DeptService deptService = (DeptService) JDKProxyFactory.getProxy(target);//通过代理对象 调用方法 扩展了方法!!!!!deptService.addDept(); //invoke}
1.8 动态代理实现Demo2
1.8.1 业务需求
- 要求:
- 对Service层的方法记录其执行的时间
- service中 有 addUser方法/deleteUser方法.
- 要求代码结构扩展性好,耦合性低.
1.8.2 编辑UserService/UserServiceImpl
- 编辑UserService
public interface UserService {void addUser();void deleteUser();
}
- 编辑UserServiceImpl
@Service("target")
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{@Overridepublic void addUser() {System.out.println("新增用户");}@Overridepublic void deleteUser() {System.out.println("删除用户");}
}
1.8.3 编辑代理工厂
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;public class JDKProxyFactory {//编辑静态方法获取代理对象public static Object getProxy(final Object target) {//3个参数 1.类加载器 2.对象的接口ClassLoader classLoader = target.getClass().getClassLoader();Class[] interfaces = target.getClass().getInterfaces();Object proxy = Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, interfaces, new InvocationHandler() {//代理对象执行目标方法时执行@Overridepublic Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {//让用户执行目标方法Long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); //开始时间//执行目标方法 获取返回值 可能为nullObject result = method.invoke(target);Long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); //结束时间System.out.println("程序执行:" + (endTime - startTime) + "毫秒");//将返回值传递给调用者return result;}});return proxy;}
}
1.8.4 编辑测试案例
@Testpublic void test01(){ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);//1.获取目标对象UserService target = (UserService) context.getBean("target");//2.获取代理对象UserService proxy = (UserService) JDKProxyFactory.getProxy(target);System.out.println(proxy.getClass());//3.调用业务方法proxy.addUser();proxy.deleteUser();}