【LetMeFly】987.二叉树的垂序遍历:遍历时存节点信息,遍历完自定义排序
力扣题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/vertical-order-traversal-of-a-binary-tree/
给你二叉树的根结点 root ,请你设计算法计算二叉树的 垂序遍历 序列。
对位于 (row, col) 的每个结点而言,其左右子结点分别位于 (row + 1, col - 1) 和 (row + 1, col + 1) 。树的根结点位于 (0, 0) 。
二叉树的 垂序遍历 从最左边的列开始直到最右边的列结束,按列索引每一列上的所有结点,形成一个按出现位置从上到下排序的有序列表。如果同行同列上有多个结点,则按结点的值从小到大进行排序。
返回二叉树的 垂序遍历 序列。
示例 1:
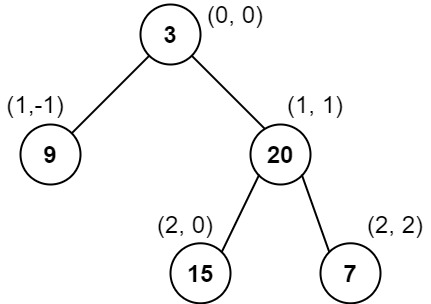
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] 输出:[[9],[3,15],[20],[7]] 解释: 列 -1 :只有结点 9 在此列中。 列 0 :只有结点 3 和 15 在此列中,按从上到下顺序。 列 1 :只有结点 20 在此列中。 列 2 :只有结点 7 在此列中。
示例 2:

输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7] 输出:[[4],[2],[1,5,6],[3],[7]] 解释: 列 -2 :只有结点 4 在此列中。 列 -1 :只有结点 2 在此列中。 列 0 :结点 1 、5 和 6 都在此列中。1 在上面,所以它出现在前面。5 和 6 位置都是 (2, 0) ,所以按值从小到大排序,5 在 6 的前面。 列 1 :只有结点 3 在此列中。 列 2 :只有结点 7 在此列中。
示例 3:
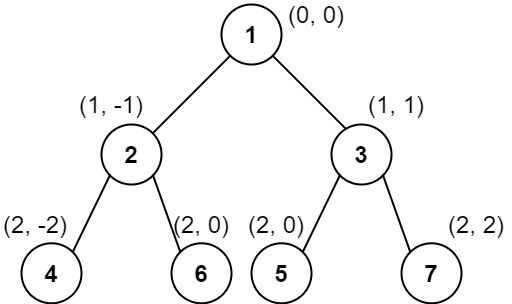
输入:root = [1,2,3,4,6,5,7] 输出:[[4],[2],[1,5,6],[3],[7]] 解释: 这个示例实际上与示例 2 完全相同,只是结点 5 和 6 在树中的位置发生了交换。 因为 5 和 6 的位置仍然相同,所以答案保持不变,仍然按值从小到大排序。
提示:
- 树中结点数目总数在范围
[1, 1000]内 0 <= Node.val <= 1000
方法一:遍历时存节点信息,遍历完自定义排序(以广度优先搜索为例)
广度优先搜索(BFS)相信大家都不陌生,因此我们可以二话不说将二叉树广搜一遍,在搜索过程中将所需要的信息计算并存下来,剩下的就是按照题目规则自定义排序了。
都需要哪些信息呢?需要“节点在哪一列”、“节点深度”、“节点值”。
遍历过程中将上述三元组存下来,遍历完成后依据这三个信息排序,作为答案并返回即可。
- 时间复杂度 O ( N log N ) O(N\log N) O(NlogN),其中 N N N是二叉树中节点的个数
- 空间复杂度 O ( N ) O(N) O(N)
AC代码
C++
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> verticalTraversal(TreeNode* root) {queue<NodeInfo> q; // [<node, <col, height>>, ...q.push({root, {0, 1}});vector<NodeInfo> v;while (q.size()) {NodeInfo thisNode = q.front();q.pop();v.push_back(thisNode);if (thisNode.first->left) {q.push({thisNode.first->left, {thisNode.second.first - 1, thisNode.second.second + 1}});}if (thisNode.first->right) {q.push({thisNode.first->right, {thisNode.second.first + 1, thisNode.second.second + 1}});}}sort(v.begin(), v.end(), [&](const NodeInfo& a, const NodeInfo& b) {return a.second == b.second ? a.first->val < b.first->val : a.second < b.second;});vector<vector<int>> ans;int lastCol = 1000000;for (NodeInfo& a : v) {if (a.second.first != lastCol) {lastCol = a.second.first;ans.push_back({});}ans.back().push_back(a.first->val);}return ans;}
};
Python
# from typing import List# # Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = rightclass Solution:def verticalTraversal(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[List[int]]:q = [(0, 0, root)] # [(col, depth, node), ...v = [] # [(col, depth, val), ...]while q:thisCol, thisDepth, thisNode = q.pop() # actually is't queue but a stackv.append((thisCol, thisDepth, thisNode.val))if thisNode.left:q.append((thisCol - 1, thisDepth + 1, thisNode.left))if thisNode.right:q.append((thisCol + 1, thisDepth + 1, thisNode.right))v.sort()ans = []lastCol = 100000for col, _, val in v:if col != lastCol:lastCol = colans.append([])ans[-1].append(val)return ans同步发文于CSDN,原创不易,转载经作者同意后请附上原文链接哦~
Tisfy:https://letmefly.blog.csdn.net/article/details/136106019


![洛谷: [CSP-J 2023] 小苹果](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/293f61c556fd41ae91db94fbe81a77a3.png)