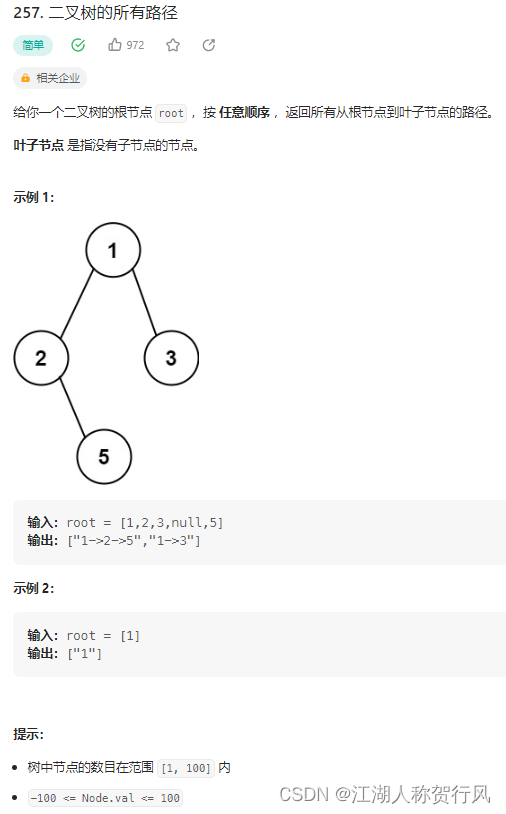
题目来源:https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-paths/description/
C++题解1:使用递归,声明了全局变量result,遇到叶子节点就将字符串添加到result中。
递归三步法:
1. 确认传入参数:当前节点+已有路径(字符串);
2. 确认终止条件:遇到叶子节点,即左右节点都为空时,将当前节点添加到路径中,再将此条路径添加到result中;
3. 确认单层递归逻辑:路径添加 “->”,分别获取左右子树的路径。
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* struct TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode *left;* TreeNode *right;* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:vector<string> result;void getlujing(TreeNode* node, string s) {if(node->left == nullptr && node->right == nullptr) {s = s + to_string(node->val);result.push_back(s);return ;}s = s + to_string(node->val) + "->";if(node->left) getlujing(node->left, s);if(node->right) getlujing(node->right, s);}vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) {getlujing(root, "");return result;}
};C++题解2(来自代码随想录):同样使用递归,明显看出回溯,对路径和result的调用均为引用。
class Solution {
private:void traversal(TreeNode* cur, vector<int>& path, vector<string>& result) {path.push_back(cur->val); // 中,中为什么写在这里,因为最后一个节点也要加入到path中 // 这才到了叶子节点if (cur->left == NULL && cur->right == NULL) {string sPath;for (int i = 0; i < path.size() - 1; i++) {sPath += to_string(path[i]);sPath += "->";}sPath += to_string(path[path.size() - 1]);result.push_back(sPath);return;}if (cur->left) { // 左 traversal(cur->left, path, result);path.pop_back(); // 回溯}if (cur->right) { // 右traversal(cur->right, path, result);path.pop_back(); // 回溯}}public:vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) {vector<string> result;vector<int> path;if (root == NULL) return result;traversal(root, path, result);return result;}
};C++题解3(来自代码随想录):迭代法,除了模拟递归需要一个栈,同时还需要一个栈来存放对应的遍历路径。
class Solution {
public:vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) {stack<TreeNode*> treeSt;// 保存树的遍历节点stack<string> pathSt; // 保存遍历路径的节点vector<string> result; // 保存最终路径集合if (root == NULL) return result;treeSt.push(root);pathSt.push(to_string(root->val));while (!treeSt.empty()) {TreeNode* node = treeSt.top(); treeSt.pop(); // 取出节点 中string path = pathSt.top();pathSt.pop(); // 取出该节点对应的路径if (node->left == NULL && node->right == NULL) { // 遇到叶子节点result.push_back(path);}if (node->right) { // 右treeSt.push(node->right);pathSt.push(path + "->" + to_string(node->right->val));}if (node->left) { // 左treeSt.push(node->left);pathSt.push(path + "->" + to_string(node->left->val));}}return result;}
};