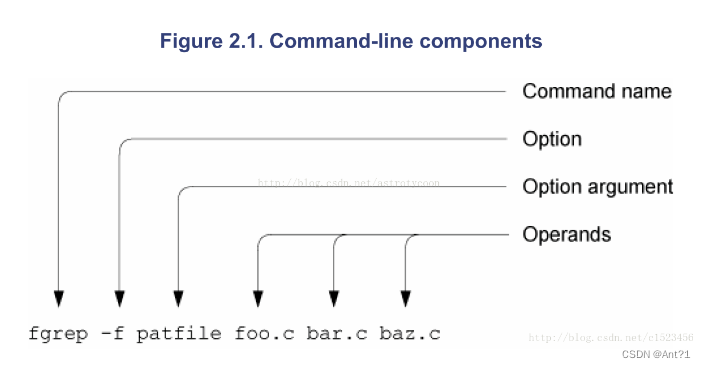
文章目录
- 一、Set的使用
- 1.Set的常用方法:
- 1.boolean add(E e)
- 2.void clear()
- 3.boolean contains(Object o)
- 4.boolean remove(Object o)
- 5.int size()
- 6.boolean isEmpty()
- 7.Object[] toArray()
- 8.boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c)
- 9.boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c)
- 10.Iterator<E> iterator()
- 2.Set的注意事项:
一、Set的使用
- 和Map不同的是,Set继承于Collection。Set中只存储了Key
1.Set的常用方法:
1.boolean add(E e)
- 添加元素,如果存在则无法添加。
Set<String>set = new TreeSet<>();set.add("Hello");set.add("World");boolean happy = set.add("Happy");boolean hello = set.add("Hello");System.out.println(set);//[Happy, Hello, World]System.out.println(happy);//trueSystem.out.println(hello);//false
2.void clear()
set.clear();
- 清空集合
3.boolean contains(Object o)
System.out.println(set.contains("Hello"));//trueSystem.out.println(set.contains("hello"));//false
- 判断元素在集合中是否存在
4.boolean remove(Object o)
System.out.println(set.remove("Hello"));//trueSystem.out.println(set.remove("hello"));//false
- 删除集合中的元素,返回值为布尔类型
5.int size()
System.out.println(set.size());//2
- 返回集合的大小
6.boolean isEmpty()
System.out.println(set.isEmpty());//false
- 判断集合是否为空
7.Object[] toArray()
System.out.println(set);//[Happy, World]System.out.println(set.toArray());//[Ljava.lang.Object;@4554617c
- 将Set中的元素转化为数组返回
8.boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c)
Deque<String> deque = new ArrayDeque<>();deque.add("Happy");deque.add("World");System.out.println(set.containsAll(deque));//true
-
判断集合c中的元素是否在set中全部存在,是返回true,否则返回 false
只要继承了Collection的类都可以比较
9.boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c)
Deque<String> deque = new ArrayDeque<>();deque.add("Happy");deque.add("World");deque.add("adddadd");System.out.println(set.containsAll(deque));//trueSystem.out.println(set.addAll(deque));//trueSystem.out.println(set);//[Happy, World, adddadd]
- 将集合c中的元素添加到set中,可以达到去重的效果
10.Iterator iterator()
- 返回迭代器
Iterator<String> iterator = set.iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()){System.out.println(iterator.next());}//Happy//World
如果有下一个,打印下一个
2.Set的注意事项:
1.Set是继承自Collection的一个借口类
2.Set中只存有Key,且Key唯一.Key不能修改,修改要先删除,再重新插入
3.TreeSet的底层是用Map实现的
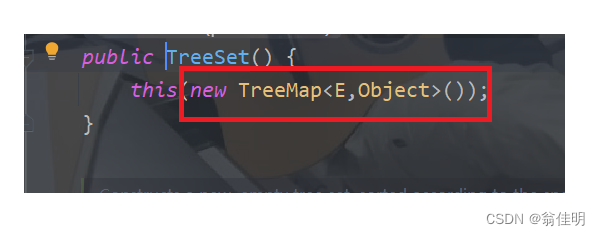
new 的TreeSet,实际上new的是一个TreeMap对象。这个TreeMap的Value都是一个Object对象
TreeSet不能插入为null的Key,HashSet可以,因为TreeSet是需要比较的
4.Set的最大功能是对集合进行去重。
Key不能重复且唯一
5.Set的常用接口的TreeSet和HashSet,
LinkedHashSet在HashSet的基础上,维护了双向链表,来记录元素的插入顺序
点击移步博客主页,欢迎光临~