基本类型

深度学习中最常使用的便是秘密定点数sfix,有关定点数的高级运算协议请参阅Paper: Secure Computation With Fixed-Point Numbers.
容器类型
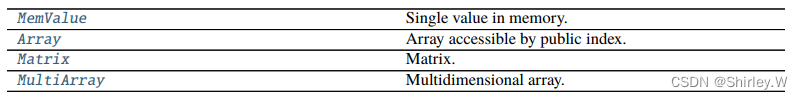
SPDZ的深度学习框架主要基于TensorFlow实现,其中使用的容器是张量Tensor,在库中的定义如下:
def Tensor(cls, shape):"""Type-dependent tensor of any dimension::a = sfix.Tensor([10, 10])"""if len(shape) == 1:return Array(shape[0], cls)else:return MultiArray(shape, cls)可以看出使用Tensor在大多数情况就是在使用MultiArray,类比Python基础类型的多维列表。
这里举一个例子:
a = sint.Tensor([3, 10, 10]) #创建张量,类型为sint,内容是3个10×10的矩阵
a[0].input_from(0) #第一个矩阵从第0方读取数据
a[1].input_from(1) #第二个矩阵从第1方读取数据
a[2][:] = a[0][:] * a[1][:] #第三个矩阵由前两个矩阵元素对应相乘实现;[:] 表示选择这个矩阵的所有元素。MultiArray的其它用法
assign(other, base=0)
Assign container to content. Not implemented for floating-point.
Parameters other – container of matching size and type
assign_all(value)
Assign the same value to all entries.
Parameters value – convertible to relevant basic type
assign_part_vector(vector, base=0)
Assign vector from range of the first dimension, including all entries in further dimensions.
Parameters
• vector – updated entries
• base – index in first dimension (regint/cint/int)
assign_vector(vector, base=0)
Assign vector to content. Not implemented for floating-point.
Parameters
• vector – vector of matching size convertible to relevant basic type
• base – compile-time (int)
direct_mul(other, reduce=True, indices=None, res_type=None)
Matrix multiplication in the virtual machine. Unlike dot(), this only works for sint and sfix, and it returns a vector instead of a data structure.
Parameters
• self – Matrix / 2-dimensional MultiArray
• other – Matrix / 2-dimensional MultiArray
• indices – 4-tuple of regint vectors for index selection (default is complete multiplication)
Returns Matrix as vector of relevant type (row-major)
PS: 不常用,因为泛用性很差,只能针对二维数组;也是库里自带函数的通病,以至于很多tf的很多高级函数在库中都是不存在的。
dot(other, res_params=None, n_threads=None)
Matrix-matrix and matrix-vector multiplication.
Parameters
• self – two-dimensional
• other – Matrix or Array of matching size and type
• n_threads – number of threads (default: all in same thread)
Return type Matrix or Array of appropriate size and type
input_from(player, budget=None, raw=False, **kwargs)
Fill with inputs from player if supported by type.
Parameters player – public (regint/cint/int)
randomize(*args, n_threads=None)
Randomize according to data type. If it is sfix, the following will sample an individual uniformly random entry of the multi-array M roughly in the range [𝑎, 𝑏]:
M.randomize(a, b)reveal()
Reveal to MultiArray of same shape.
reveal_list()
Reveal as list.
sort(key_indices=None, n_bits=None)
Sort sub-arrays (different first index) in place. This uses radix sort.
Parameters
• key_indices – indices to sorting keys, for example (1, 2) to sort three-dimensional array a by keys a[*][1][2]. Default is (0, ..., 0) of correct length.
• n_bits – number of bits in keys (default: global bit length)
…………
重要模块 - Compiler.library
Compiler.library.do_while(loop_fn, g=None)
Do-while loop. The loop is stopped if the return value is zero. It must be public. The following executes exactly once:
@do_while
def _():...return regint(0)Compiler.library.for_range(start, stop=None, step=None)
Decorator to execute loop bodies consecutively. Arguments work as in Python range(), but they can be any public integer. Information has to be passed out via container types such as Array or using update(). Note that changing Python data structures such as lists within the loop is not possible, but the compiler cannot warn about this.
Parameters start/stop/step – regint/cint/int
PS: 勘误-默认参数应为stop,同Python中的 for i in range(stop)。
例:The following should output 10:
n = 10
a = sint.Array(n)
x = sint(0)
@for_range(n)
def _(i):a[i] = ix.update(x + 1)
print_ln('%s', x.reveal())其它函数详情请参阅SPDZ手册。
…………
重要模块 - Compiler.mpc_math
这块其实没啥好说的,库中都已经给了各种数学运算,直接调用就好,原理可以参阅源代码或相关论文。
重要模块 - Compiler.ml
这块是使用SPDZ框架实现深度学习的关键,手册中直接举了几个机器学习的例子和现成的深度学习的例子,紧接着便是具体类的基和参数介绍。我们以一个深度学习的具体代码为例进行介绍。
# this trains a dense neural network on MNIST
# see https://github.com/csiro-mlai/mnist-mpc for data preparation
# 该代码在根目录的Programs/Source中program.options_from_args() #表示程序可以从外界(终端)获取输入#SPDZ在0.3.7版本后有了torch导入数据的功能
if 'torch' in program.args:import torchvisiondata = []for train in True, False:ds = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(root='/tmp', train=train, download=True)# normalize to [0,1] before inputsamples = sfix.input_tensor_via(0, ds.data / 255., binary=True)labels = sint.input_tensor_via(0, ds.targets, binary=True, one_hot=True)data += [(labels, samples)](training_labels, training_samples), (test_labels, test_samples) = data#这里是正常读取处理好的数据集的方法
else:training_samples = sfix.Tensor([60000, 28, 28]) #为样本与标签设置存储结构training_labels = sint.Tensor([60000, 10])test_samples = sfix.Tensor([10000, 28, 28])test_labels = sint.Tensor([10000, 10])training_labels.input_from(0) #读入数据,在根目录的Player-Data/Input-P0-0training_samples.input_from(0)test_labels.input_from(0)test_samples.input_from(0) #注意导入的顺序from Compiler import ml
tf = ml#构建网络层,这里的层都是库中写好的,用法同tf
layers = [tf.keras.layers.Flatten(),tf.keras.layers.Dense(128, activation='relu'),tf.keras.layers.Dense(128),tf.keras.layers.Activation('relu'),tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax')
]model = tf.keras.models.Sequential(layers) #构建模型optim = tf.keras.optimizers.SGD(momentum=0.9, learning_rate=0.01) #选择优化器,设置参数model.compile(optimizer=optim) #编译#Train model.
opt = model.fit(training_samples,training_labels,epochs=1,batch_size=128,validation_data=(test_samples, test_labels)
)#Use model for prediction
guesses = model.predict(test_samples)这是一段训练预测一体的代码,单独训练与预测也是可以的,只需要修改最后的代码。
目前使用这种模式的代码只可实现库中训练、库中保存秘密模型、使用库中训练好的模型预测,非常的不灵活;库中还提供了另一种模式的代码:
# this trains network D from SecureNN
# see https://github.com/csiro-mlai/mnist-mpc for data preparation
# 该代码在根目录的Programs/Source中import ml
import math
import re
import util #这里引用的应是Compiler中的包program.options_from_args()
sfix.set_precision_from_args(program, True)
MultiArray.disable_index_checks()#设置特征和标签数量
if 'profile' in program.args:print('Compiling for profiling')N = 1000n_test = 100
elif 'debug' in program.args:N = 100n_test = 100
elif 'debug1000' in program.args:N = 1000n_test = 1000
elif 'debug5000' in program.args:N = 5000n_test = 5000
else:N = 60000n_test = 10000#deep-mpc库中有预处理数据集的方法,默认就是N = 60000,n_test = 10000
n_examples = N
n_features = 28 ** 2try: #设置轮数n_epochs = int(program.args[1])
except:n_epochs = 100try: #设置batch大小batch_size = int(program.args[2])
except:batch_size = Nassert batch_size <= N
ml.Layer.back_batch_size = batch_sizetry: #设置线程数ml.set_n_threads(int(program.args[3]))
except:passif program.options.ring:assert sfix.f * 4 == int(program.options.ring)if 'stride1' in program.args: #设置步长stride = (1, 1)
else:stride = (2, 2)if 'valid' in program.args: #设置padding方式padding = 'VALID'inner_dim = (28 - 4) // stride[0]
else:padding = 'SAME'inner_dim = 28 // stride[0]layers = [ #层ml.FixConv2d([N, 28, 28, 1], (5, 5, 5, 1), (5,),[N, inner_dim, inner_dim, 5], stride, padding),ml.Relu([N, inner_dim, inner_dim, 5]),
]#填充层
if 'maxpool' in program.args:layers += [ml.MaxPool((N, inner_dim, inner_dim, 5))]inner_dim //= 2n_inner = inner_dim ** 2 * 5dropout = 'dropout' in program.argsif '1dense' in program.args:if dropout:layers += [ml.Dropout(N, n_inner)]layers += [ml.Dense(N, n_inner, 10),]
elif '2dense' in program.args:if dropout:layers += [ml.Dropout(N, n_inner)]layers += [ml.Dense(N, n_inner, 100),ml.Relu([N, 100]),ml.Dense(N, 100, 10),]if dropout or 'dropout1' in program.args:layers.insert(-1, ml.Dropout(N, 100))
else:raise Exception('need to specify number of dense layers')layers += [ml.MultiOutput(N, 10)]Y = sint.Matrix(n_test, 10) #存储测试集标签
X = sfix.Matrix(n_test, n_features) #存储测试集特征if not ('no_acc' in program.args and 'no_loss' in program.args):layers[-1].Y.input_from(0) #读取训练集标签layers[0].X.input_from(0) #读取训练集特征Y.input_from(0) #读取测试集标签X.input_from(0) #读取测试集特征optim = ml.Optimizer.from_args(program, layers) #外部读入优化器
optim.run_by_args(program, n_epochs, batch_size, X, Y) #训练FixConv2d参数:(input_shape, weight_shape, (out_channels,), output_shape, stride, padding)
#weight_shape:过滤器大小,就是滑动的那个框
Relu参数:([N, d, d_out])
MaxPool参数:(input_shape, pool_size, strides, padding))
Dense参数:(N, d_in, d_out)
Dropout参数:(N, d1, d2=1, alpha=0.5)
#d1: 总维度,这通常表示特定层输入或输出的特征数量或维度。
#d2: 另一个维度,默认值为1。在某些场景下,如当需要将数据处理为三维结构(例如,在处理时间序列数据或具有多个特征映射的卷积层输出时),这个参数变得有用。
#alpha: 概率(必须是2的幂),表示每个神经元被置零的概率。默认值是0.5,意味着在每次前向传播时,有50%的概率每个神经元的输出会被置为0。
MultiOutput参数:(N, d_out) #这一般就是最后一层了,d_out是最终分类数目
优化器
class Compiler.ml.Optimizer(layers=[], report_loss=None)
Bases: object
Base class for graphs of layers.
backward(**kwargs)
Compute backward propagation.
eval(**kwargs)
Compute evaluation after training.
Parameters
• data – sample data (Compiler.types.Matrix with one row per sample)
• top – return top prediction instead of probability distribution
Returns sfix/sint Array (depening on top)
class Compiler.ml.SGD(layers, n_epochs=1, debug=False, report_loss=None)
Bases: Compiler.ml.Optimizer
Stochastic gradient descent.
Parameters
• layers – layers of linear graph
• n_epochs – number of epochs for training
• report_loss – disclose and print loss
backward(**kwargs)
Compute backward propagation.
eval(**kwargs)
Compute evaluation after training.
Parameters
• data – sample data (Compiler.types.Matrix with one row per sample)
• top – return top prediction instead of probability distribution
Returns sfix/sint Array (depening on top)
run/run_in_batches/run_by_args 皆是进行训练,通过run_by_args的参数可知,顺便它也能进行预测。(源码太长不再放这里了,仅简单介绍一下整个函数:)
run_by_args(self, program, n_runs, batch_size, test_X, test_Y,acc_batch_size=None)主要逻辑和功能 - run_by_args
-
参数解析: 方法首先解析
program.args中的参数,如学习率(gamma), 折旧率(depreciation), 动量(momentum), 是否打印损失(print_losses)等。 -
动态配置: 根据提供的参数动态调整训练和评估配置,如是否使用动量(
nomom), 是否记录每层的时间(time_layers), 是否在训练之前首先进行模型评估(acc_first), 以及是否对卷积操作进行特定的处理(full_cisc). -
训练和评估: 根据
n_runs参数指定的次数,执行训练循环。在每次循环中,根据配置执行前向传播(forward), 反向传播(backward), 和参数更新(update). 如果设置了测试集(test_X和test_Y), 也会执行测试集上的评估,并计算准确率和损失。 -
特殊条件处理: 支持特殊的命令行参数来执行一些特定操作,如
one_iter用于执行一次完整的前向和反向传播并打印权重,bench1和bench10用于性能基准测试。 -
学习率调整: 如果检测到模型发散(
crash)或准确率低于阈值,学习率(gamma)会减半以尝试恢复训练。此外,如果设置了折旧率(depreciation), 学习率将按该比率递减。 -
输出权重: 如果指定了
model_output, 最后会输出模型的权重。
注意:这种模式的代码编译时要加额外的参数,具体的参数请参阅csiro-mlai/deep-mpc (github.com)中的common.sh第69行。这里给一个具体的例子:
#原运行命令
./run-local.sh emul D prob 2 2 64 #实际编译命令(实际上原命令包括编译与运行)
python3 ./compile.py -R 64 -K '' -CD mnist_full_D 2 128 2 trunc_pr f64 k127 2dense | grep -v WARNING (未完待续)