目录
〇、概念
一、string类的构造函数
二、赋值运算符重载
三、有关容量的操作
四、string对象的访问
五、遍历string对象的字符数组
六、string对象的修改
七、string对象的常用操作
八、字符串和数字间的转换
拓展】
练习】
源代码】
〇、概念
1. string类是什么?
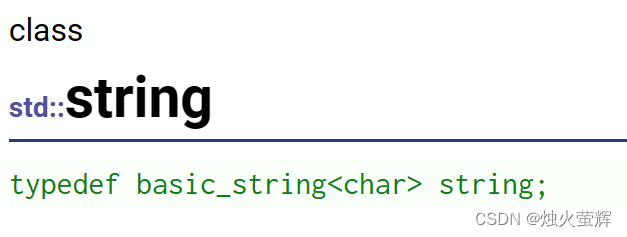
string类的底层是一个支持动态增长的char数组,它用new来动态分配内存,因此string也被称为变长字符串。
string的底层是一个叫 basic_string 的类模板,模板中存的是char。
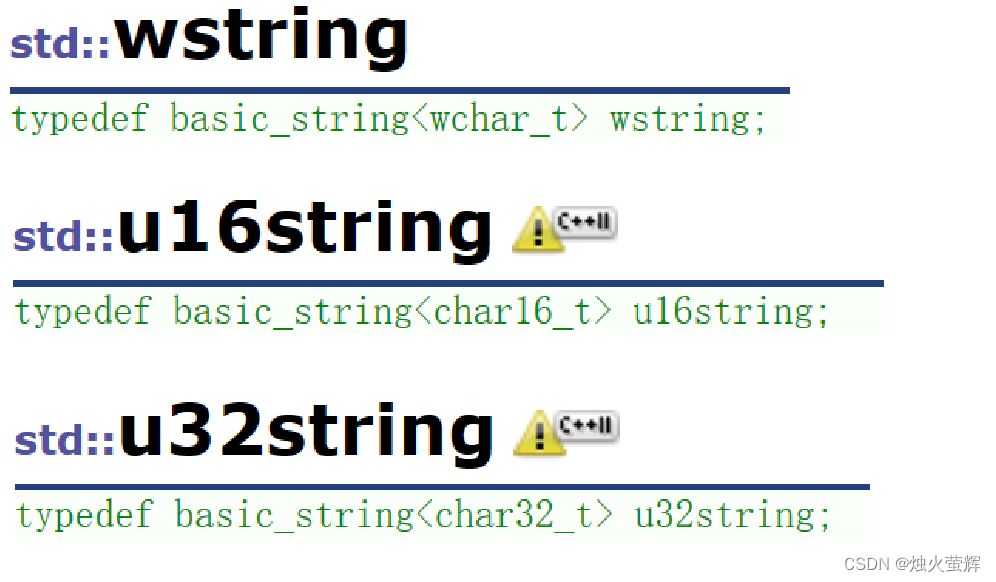
事实上string库中还用basic_string类模板实现了存储宽字符的wstring,存储16位字符的 u16string(C++11后支持),和存储32位字符的 u32string(C++11后支持):
2. string类的官方文档
博主在文章中只是讲述了有关string类的常用函数,对于一些不常用,可以查看官方文档: string类的官方文档
3. 导入string类
要使用官方的string类:
- 首先我们要引入头文件:#include<string>
- 其次展开命名空间std中的string类:using std::string;
严格来说string是属于C++ std标准库的,不在STL中,但是两者有许多相似之处,就放在一起总结了。
一、string类的构造函数
0. 全部构造函数
以下为C++98中string的所有构造函数
1. 常用的四个构造函数
string() (重点) 构造空的string类对象,即空字符 string(const char* s) (重点) 用字符数组来构造string对象 string(const string & s) (重点) 拷贝构造函数 string(size_t n, char c) 用n个c字符来构造string对象 string a; //注意空字符串的创建不是string a(); 这是在声明一个返回值为string 的无参函数。 string b("abc"); //使用字面字符串来构造对象 string c(b); //拷贝构造 string d(3, 'a');cout << a << endl; cout << b << endl; cout << c << endl; cout << d << endl;
唯一要注意的一点是创建空字符串不是string a(); 这是在声明一个返回值为string 的无参函数。是string a;
2. 可能用到的构造函数
string (const string& str, size_t pos, size_t len = npos); 从str的下标 pos 处开始复制 len 个字符,不设置len默认复制到结尾 string e("1abcdefg", 1); //abcdefg (从下标1开始复制) string f(e, 1); //bcdefg (从下标1开始复制) string g("1abcdefg", 1, 5); //abcde (从下标1开始复制5个字符) string h(e, 0, 3); //abc (从下标0开始复制3个字符)
唯一要注意的一点是:第二、三个参数的意义是,从下标pos处开始复制len个字符。不是复制它们之间的字符。不传第三个参数则默认复制到结尾。
拓1:string::npos
- npos是std命名空间中string类下的一个静态成员变量。(std::string::npos)
- npos用来表示一个非常非常大的数值(约为42亿9千万),因为size_t是无符号的整型,如果将-1的补码转化为无符号的整型将非常非常大,所以一般用string::npos来表示直到字符串的结尾。
二、赋值运算符重载
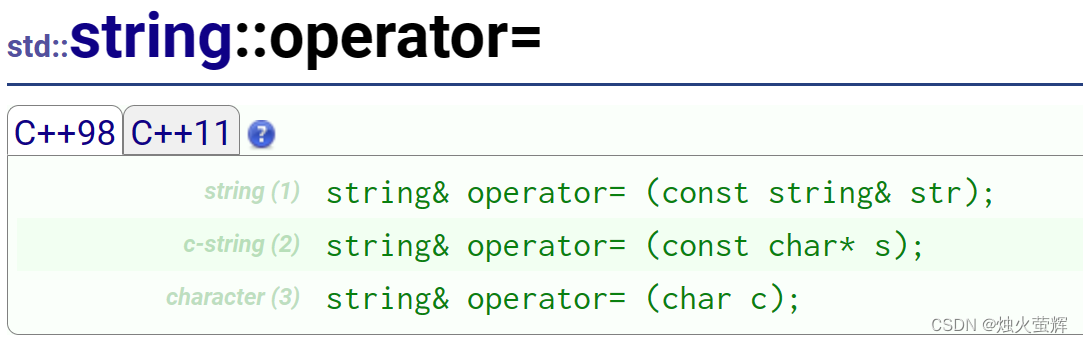
1. 三个赋值运算符重载函数
有三个重载,分别接受字符串,字符数组,字符作为参数。
以上三个运算符重载又互相构成函数重载。
2. 使用赋值运算符重载函数
string& operator= (const string & str); 使用string对象赋值 string& operator= (const char* s); 使用字面字符串/字符数组赋值 string& operator= (char c); 使用单个字符赋值 string a("abcd"); string b("bcde"); string c = b; // 注意这是在调用构造和拷贝构造函数 a = b; cout << a << endl; a = "fghi"; cout << a << endl; a = 'j'; cout << a << endl;
唯一一点要注意的就是要区分是在调用构造函数还是在赋值,上面代码中的第三行就是在调用构造函数。
拓2:构造还是赋值?
string a = b; // 注意这是在调用构造而不是赋值 string b("bcde"); a = b; // 这里才是赋值要注意第一行代码可不是在赋值,而是在通过隐式类型转换调用构造函数(先构造,再拷贝,编译器可能优化为直接构造)
如何区分是构造还是赋值?就看对象有没有创建出来,如上面第一行代码中的对象a正在创建,所以这是在调用构造函数;而第三行中使用的是已经创建好的a对象,所以是在赋值,调用了赋值运算符重载函数。
三、有关容量的操作
1. 有关容量的操作函数

2. 常用的容量操作函数
| size_t size() const noexcept; | 返回字符串有效字符长度 |
| size_t length() const noexcept; | 返回字符串有效字符长度 |
| size_t capacity() const noexcept; | 返回字符串占用空间总大小(字节) |
| bool empty() const noexcept; | 检测字符串是否为空串,是返回true,否则返回false |
| void clear() noexcept; | 清空字符串 |
| void reserve (size_t n = 0); | 为字符串预留空间 |
| void resize (size_t n); | 设置有效字符长度,用'\0'填充多出来的位置 |
| void resize (size_t n, char c); | 设置有效字符长度,用指定字符填充多出来的位置 |
a. 获取字符串有效字符长度
推荐使用size(),少用length()。虽然设计方面两个函数是一样的,但为了在学习后面的容器时不产生混乱(其它容器中都有size()来计算元素个数,但不一定有length()),使用推荐使用size()。
b. 获取字符串占用空间总大小
stirng对象中的字符数组的空间大小不一定等于有效字符长度size,因为扩容是有消耗的,所以一般扩容不是一个一个一个扩,而是以1.5或2倍大小来扩容,我们可以通过capacity()来获取stirng对象中的字符数组的空间大小。
c. 判空和清空字符串
- empty()通过检查有效字符长度来判断string对象是否为空,为空返回true。
- clear()通过将有效字符长度置为0来清空字符串。
d. 为字符串预留空间
当string对象的有效字符长度size等于容量capacity时会触发扩容,扩容是有消耗的,如果我们提前知道有效字符长度size,就可以通过reserve()来提前开好一片空间,就不需要频繁的扩容了。
当所给值小于容器当前的 capacity时,什么也不做(不会缩小容量)。
e. 设置有效字符长度
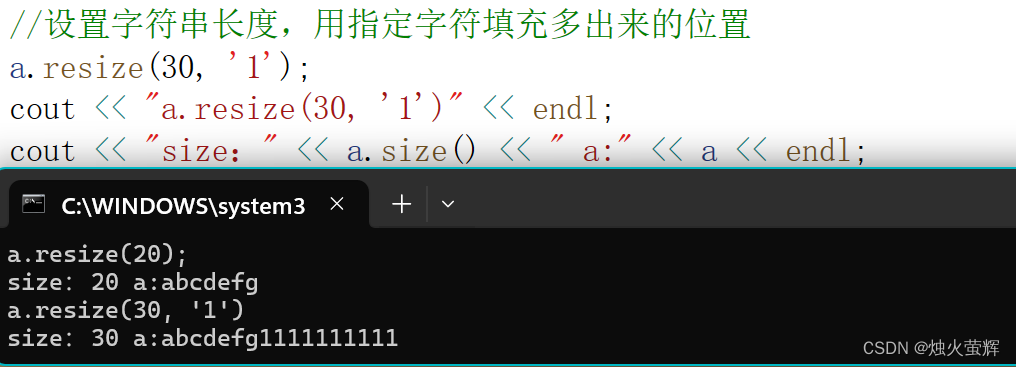
resize()通过设置有效字符长度size,来更新字符串的长度,如果新长度比当前字符串有效长度长,默认用'\0'填充。(string对象的打印不是遇到'\0'终止,但'\0'不会被显示)
我们也可以通过resize()的第二个参数来指定,当新长度比当前字符串有效长度长时的填充字符。
四、string对象的访问
1. string对象的三种访问方法
string对象主要三种访问方法:[ ]、at()、string::iterator
- [ ]没什么好说的,重载[ ]让string类能像数组一样使用。
- 成员函数at()用来返回指定下标处的字符,类似于Java中的charAt(),让string类符合封装的思想,但几乎不怎么用。
- string::iterator就是迭代器,string类的迭代器可以当作指针来用,begin(),end()返回的就是数组下标0和下标size处的迭代器。
2. operator [ ] 和 at()
operator [ ] 和 at() 返回的都是string对象的字符数组的i下标处的引用,所以可以用来修改string对象的字符数组。
- 重载[ ]让string类能像数组一样使用
- 成员函数at()用来返回指定下标处的字符
string a("abcdefghijklmn");cout << "使用[]遍历string对象的字符串" << endl; for (int i = 0; i < a.size(); i++) {//operator [ ]是string对象的字符数组的i下标处的引用。a[i]++;cout << a[i]; } putchar(10);cout << "使用at()遍历string对象的字符串" << endl; for (int i = 0; i < a.size(); i++) {// at() 返回的也是string对象的字符数组的i下标处的引用a.at(i)++;cout << a.at(i); } putchar(10);
3. string::iterator
string类的迭代器可以当作指针来用,begin(),end()相当于指向字符串开头和结尾('\0'处)的指针。通过+/- 能获取下一个或上一个地址。通过*(解引用)能取出地址中的内容。
五、遍历string对象的字符数组
上面的三种访问方式都可以用来遍历string对象。这里因为[]和at()区别不大,所以就演示使用[ ] 和 stirng::iterator 来遍历string对象。
1. 使用[ ]遍历string对象的字符数组
重载[ ]让string对象的访问和数组没有区别:
//operator [ ] 和 at() 返回的都是string对象的字符数组的i下标处的引用,所以可以用来修改string对象的字符数组。 a = "abcdefg"; for (int i = 0; i < a.size(); ++i) {a[i] += 1;cout << a[i]; }
2. 使用迭代器来遍历string对象的字符数组
string的迭代器可以当指针使用:
a = "abcdefg"; string::iterator it = a.begin(); while (it != a.end()) {cout << *it; //string的迭代器可以当指针使用。++it; }
使用迭代器来遍历string对象的最大优势在于:可以使用范围for。
上面代码中auto后面的e是临时变量,不会对原字符串造成改变
只有auto + &才能修改原字符串:
六、string对象的修改
0. string类中有关修改的函数

1. 追加
| 追加: | |
| operator +=() (常用) | 在字符串后追加字符串/string对象/字符。 |
| push_back() | 在字符串后尾插字符,只能尾插一个字符。 |
| append()(常用) | 在字符串后追加一个字符串 |
a. operator +=()
重载+=让我们可以在字符串后随意追加字符串/string对象/字符,一般情况下有operator +=即可。
string a("abcdefg"); a += "higk"; a += 'l'; string b("mn"); a += b; cout << a << endl;
b. append()
append()主要用于一些特殊情况:追加某个字符串的一部分、追加某个字符n次。
string a = "abcdefghijklmno"; a.append("lmn"); string c("opq"); a.append(c); cout << a << endl;a.append("rstuvw", 3); // 尾插一个字符串,取其前n个字符 cout << a << endl; a.append("rstuvwxyz123", 3, 8); // 尾插一个字符串,从下标n开始,取其前i个字符 cout << a << endl; a.append(3, ' '); //尾插n个相同的字符 cout << a << endl;
2. 插入
一般来说insert只用于要在字符串中间插入内容时。用的比较少。
插入: insert 在指定下标处插入一个字符串。 string a = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz "; a.insert(0, "123"); // 在n下标处插入一个字符串 cout << a << endl; a.insert(3, "456789", 3); // 在n下标处插入,一个字符串的前n个字符 cout << a << endl; a.insert(6, "7891011", 3, 5); //在n下标处插入,一个字符串从下标n开始的n个字符 cout << a << endl;
3. 删除
删除: erase 删除指定位置开始的n个字符。 a = "ab123456789cdefghigklmnopqrstuvwxyz111"; a.erase(2, 9); //删除从指定下标开始的n个字符。 cout << a << endl; a.erase(25); //删除从指定下标后的所有字符。 cout << a << endl; int n = 3; a.erase(a.begin() + n); //删除下标为n的字符 cout << a << endl;
七、string对象的常用操作
0. string对象的操作函数
其中copy()完全可以使用 operator =() 来替代,compare()也可以使用operator >()来替代。
常用的操作函数只有四个:
c_str() 返回C格式字符串(char* ) find() 从前往后查找子串,返回起始位置的下标 rfind() 从后往前查找子串,返回起始位置的下标 substr() 截取子串,并返回一个string对象
1. c_str()
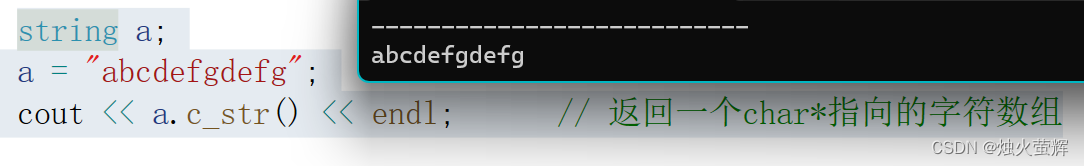
返回一个 const char* 指针,该指针指向一个和string对象有效内容相同的char数组,且是以'\0'结尾。该函数的作用是获取一个适用于C语言库函数的C风格字符串。
string a; a = "abcdefgdefg"; cout << a.c_str() << endl; // 返回一个char*指向的字符数组
2. find() 和 rfind()
都是用来查找子串的不过find()是从前往后找,rfind()是从后往前找。找到了就立即返回子串起始位置的下标,没找到就返回string::npos(约为42亿9千万)。
string a = "abcdefgdefg"; cout << a.find("defg") << endl; //查找子串,返回起始位置的下标 if(a.find("defgl") == string::npos) //找不到返回string::npos(约为42亿9千万);cout << "未找到该子串" << endl;cout << a.find("def", 3) << endl;//查找子串,从主串的第n个位置开始找。 cout << a.find("def", 4) << endl;//查找子串,从主串的第n个位置开始找。 cout << a.rfind("def", 4) << endl;//从主串的第n个位置开始从后往前查找子串。
3. substr()
从下标pos开始,截取len个字符,不传len就默认截取到结尾。然后返回一个string对象。
string a = "abcdefgdefg"; cout << a.substr(1) << endl; //从下标1的字开始截取到结尾 cout << a.substr(1).size() << endl; cout << a.substr(0, 3) << endl; //从下标0的字开始截取3个字符
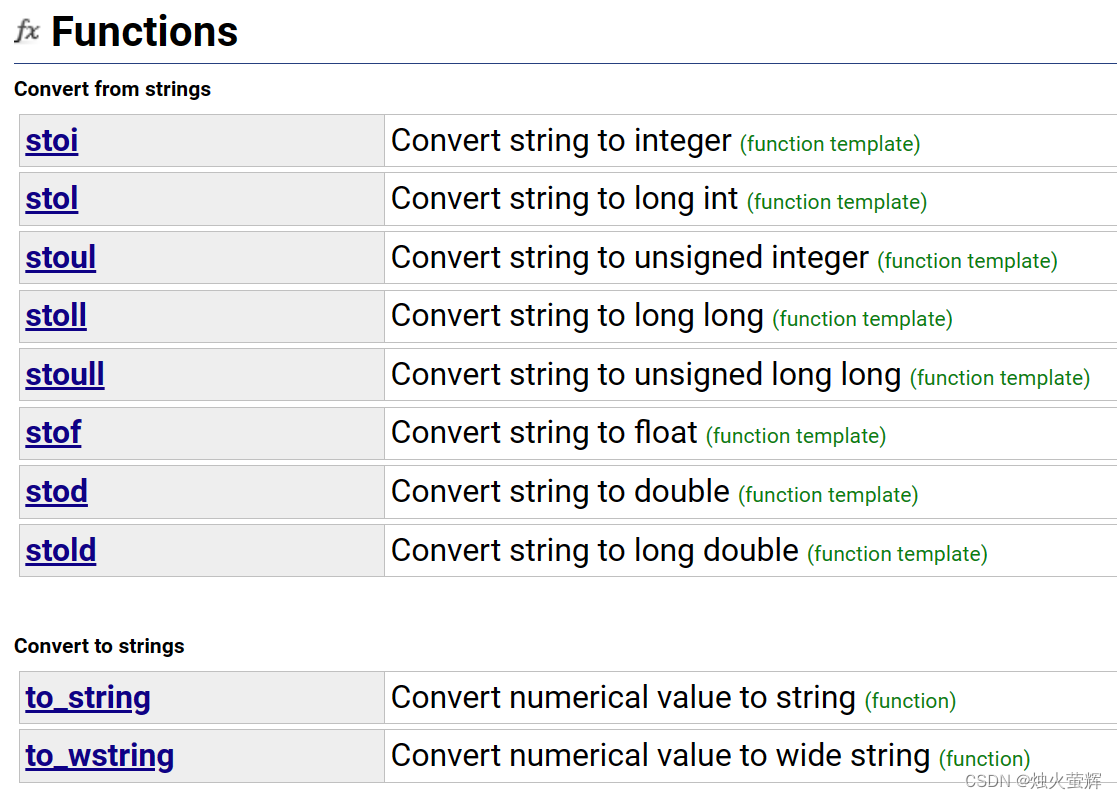
八、字符串和数字间的转换
以下函数都是string的非成员函数,不能通过对象来调用。
| to_string() | 将数字转为字符串 |
| stoi() | 将string对象转为整数 (只能接受string对象) |
| stod() | 将string对象转为浮点数 (只能接受string对象) |
| atoi() | 将字面字符串转为整数 (只能接受常量字符串) |
| atof() | 将字面字符串转为浮点数(只能接受常量字符串) |
//to_string()函数:将数字转为字符串cout << "---------------------------" << endl;double a = 1234.5678;string s = std::to_string(a);cout << s << endl;//stoi():将字符串转为整数int b = stoi(s);cout << b << endl;//stod():将字符串转为浮点数double c = std::stod(s);printf("%lf\n", c); //注意cout默认输出两位小数,所以在输出浮点数时最好使用printf()//atoi():将字面字符串转为整数const char* ss = "2345678";b = atoi(ss);cout << b << endl;//atof():将字面字符串转为浮点数c = atof("1234.5678");printf("%f\n", c);拓展】
1:operator +
重载+ 让string对象能自由的拼接字符/字符串/其他string对象:
string firstlevel("com"); string secondlevel("cplusplus"); string scheme("http://"); string hostname; string url;hostname = "www." + secondlevel + '.' + firstlevel; url = scheme + hostname;std::cout << "网址:" + url + '\n';
2:重载比较运算符
重载比较运算符 让string对象能和 字符串字符串/其他string对象 进行字典序比较(逐个按ASCII码比较):
string s1 = "abcd"; string s2 = "abcde"; cout << (s1 == "a") << endl;cout << (s1 > s2) << endl; cout << (s1 >= "abcd") << endl;cout << (s1 < s2) << endl; cout << (s1 <= s2) << endl;
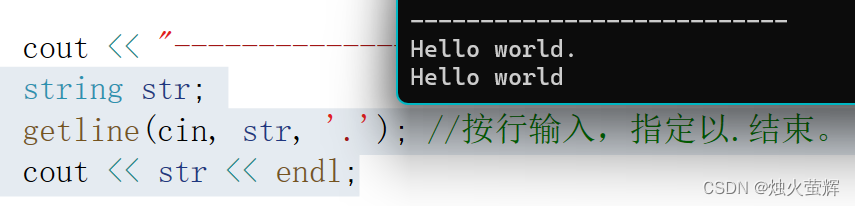
3:按行输入
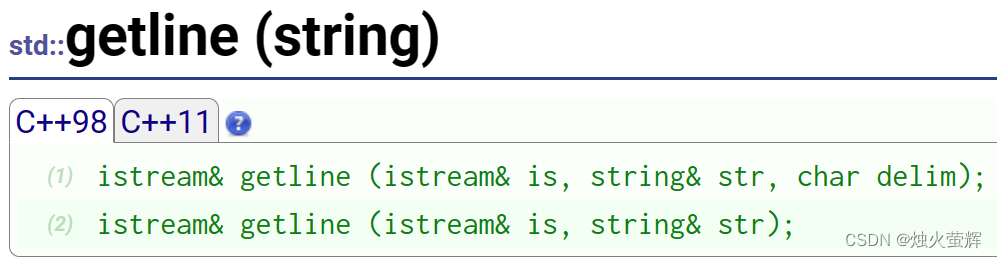
cin >> 是以空格进行分隔的,当我们希望输入一句英文时,使用cin >> 却只能接收到一个单词。所以这个时候我们就需要使用按行输入了:getline()
- 第一个参数是istream对象,传入std::cin即可。
- 第二个参数是用来接收的string对象。
- 第三个参数是控制输入结束的字符,不传该参数就默认以回车结束。
string str; getline(cin, str, '.'); //按行输入,指定以.结束。 cout << str << endl;
4:判断字符是字母还是数字
- isalpha() :用来判断一个字符是不是字母。
isdigit() :用来判断一个字符是不是数字。
如果记不住,自己写一个也很快,判断是否是字母就比较字符是否大于等于'a'/'A',小于等于'z'/'Z',判断是否是字母就比较字符是否大于等于'0',小于等于'9' 。或用它们的ASCII码:48 65 97 。
练习】
1:将字符串中的空格替换为%20
{// 法一:倒着找到后先删除后插入string s1("hello world lin");for (int i = s1.size(); i >= 0; i--){if (s1[i] == ' '){s1.erase(i, 1);s1.insert(i, "%20");}}// 法二:开一个新字符串string s2;for (int i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++){if (s1[i] == ' ')s2 += "20%";elses2 += s1[i];}cout << s1 << endl;cout << s2 << endl;}2:获取文件后缀
{// 用find找子串,用substr获取子串。string file_path = "test.cpp.zip.tar";size_t index = file_path.find(".");size_t index1 = file_path.rfind("."); // 从结尾开始找string suffix = file_path.substr(index);string suffix1 = file_path.substr(index1);cout << "使用find获取文件所有后缀:" << suffix << endl;cout << "使用rfind获取文件真后缀:" << suffix1 << endl;}源代码】
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::string;int main()
{std::ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);// string类的构造函数{//string() (重点) 构造空的string类对象,即空字符//string(const char* s) (重点) 用字符数组来构造string类对象//string(const string & s) (重点) 拷贝构造函数//string(size_t n, char c) 用n个c字符来构造string类对cout << "----------string类的构造函数---------" << endl;string a; //string a(); 不是在调用构造器创建一个空的string对象,而是在声明一个返回值为string的无参函数。string b("abcd"); //使用字符数组构造string c(b); //拷贝构造string d(3, 'a');const char* e = "abcdefg";string f(e);char g[] = { 'a', 'b' }; //char数组结尾一定要加一个'\0'string h(g);cout << a << endl;cout << b << endl;cout << c << endl;cout << d << endl;cout << e << endl;cout << f << endl;cout << g << endl;cout << h << endl;}// 赋值运算符重载{//string& operator= (const string & str);//string & operator= (const char* s);//string& operator= (char c);cout << "----------赋值运算符重载---------" << endl;string a("abcdefg");string b = a; //区分构造和赋值,这里b还没有创建所以调用的是构造函数b = a; //这里b已经创建,所以调用的是赋值运算符重载cout << b << endl;b = "abcd";cout << b << endl;b = 'a';cout << b << endl;}// 有关容量的操作{// size(重点) 返回字符串有效字符长度// length 返回字符串有效字符长度// capacity 返回空间总大小// empty(重点) 检测字符串是否为空串,是返回true,否则返回false// clear(重点) 清空有效字符// reserve(重点) 为字符串预留空间// resize(重点) 设置字符串长度,用指定字符填充多出来的位置cout << "-----------有关容量的操作---------" << endl;string a("abcdefg");cout << a.size() << endl;cout << a.length() << endl;cout << a.capacity() << endl;// 判空:根据size()判断cout << a.empty() << endl;// 不同于字符数组是以'\0'来判断结尾,stirng对象判断字符串的结尾是根据size属性。// 清空字符串:修改size()a.clear();cout << "a.clear();" << endl;cout << a.size() << endl;cout << a.empty() << endl;// 为stirng对象预留空间,修改capacity = n + 1;a.reserve(30);cout << "a.reserve(30);" << endl;cout << a.capacity() << endl;cout << a.size() << endl;// 设置string对象的有效长度,多出来的长度默认用'\0'填充cout << a << " 的长度: " << a.size() << endl;a.resize(10);cout << "a.resize(20);" << endl;cout << a << " 的长度: " << a.size() << endl;a.resize(20, '.');cout << "a.resize(20, '.');" << endl;cout << a << " 的长度: " << a.size() << endl;cout << "string对象是以size来判断结尾的,看不到的字符可能是'\0'";}//访问string对象的字符数组{cout << "---------访问string对象的字符数组--------" << endl;string a;a = "abcd";cout << a << endl; //重载<< 让我们能自己打印string对象的内容。cout << a[0] << endl;cout << a.at(1) << endl;cout << *a.begin() << endl;cout << *(a.begin() + 2) << endl;string::iterator it = a.end()-1;cout << *it << endl;}//遍历string对象的字符数组{cout << "---------遍历string对象的字符数组--------" << endl;string a("abcdefghijklmn");cout << "operator [ ]和at() 返回的是string对象的字符数组的i下标处的引用。" << endl;cout << "使用[]遍历string对象的字符串" << endl;for (int i = 0; i < a.size(); i++){//operator [ ]返回的是string对象的字符数组的i下标处的引用。a[i]++;cout << a[i];} putchar(10);cout << "使用at()遍历string对象的字符串" << endl;for (int i = 0; i < a.size(); i++){// at() 返回的也是string对象的字符数组的i下标处的引用a.at(i)++;cout << a.at(i);}putchar(10);cout << "使用迭代器遍历string对象的字符串" << endl;for (string::iterator i = a.begin(); i != a.end(); i++){(*i)++; //++的优先级大于*,所以要使用()cout << *i;}putchar(10);string::iterator it = a.begin();while (it != a.end()){(*it)++;cout << *it;it++; //如果会忘记写it++,建议使用for循环}putchar(10);cout << "使用范围for+迭代器遍历string对象的字符串" << endl;//不使用&的范围for是无法修改原数组的cout << "a. 使用范围for访问,不用加&" << endl;for (auto e : a){e++; //这里的e不过是一个临时变量。cout << e;}putchar(10);cout << a << endl;//使用&的范围for才能修改原数组的cout << "b. 使用范围for修改,要加&" << endl;for (auto& e : a){e++;cout << e;}putchar(10);cout << a << endl;}//string对象的修改{cout << "-----------string对象的修改-----------" << endl;//追加//operator+=(重点) 在字符串后追加字符串/string对象/字符//push_back 在字符串后尾插字符//append(重点) 在字符串后追加一个字符串cout << "-----------追加-----------" << endl;string a("abc");a += 'd';a += "efg";string b("hij");a += b;cout << a << endl;a.push_back('k'); // 只能尾插一个字符。//a.push_back("lmn");a.append("lmn");string c("opq");a.append(c);cout << a << endl;a.append("rstuvw", 3); // 尾插一个字符串,取其前3个字符cout << a << endl;a.append("rstuvwxyz123", 3, 6); // 尾插一个字符串,从下标3开始,取其前6个字符cout << a << endl;a.append(3, ' '); //尾插3个' '字符cout << a << endl;//插入 insertcout << "-----------插入-----------" << endl;a = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz ";a.insert(0, "123"); // 在0下标处插入一个字符串cout << a << endl;a.insert(3, "456789", 3); // 在3下标处插入,一个字符串的前3个字符cout << a << endl;a.insert(6, "4567891011", 3, 5); //在6下标处插入,一个字符串从下标3开始的5个字符cout << a << endl;//删除 erasecout << "-----------删除-----------" << endl;a = "12345678910abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz .";a.erase(37, 3); //删除下标37开始的3个字符cout << a << endl;a.erase(10); //删除下标10后的所有字符cout << a << endl;a.erase(a.begin() + 9); //删除下标为9的字符cout << a << endl;}//string对象的常用操作{//c_str(重点) 返回C格式字符串//find(重点) 从前往后查找子串,返回起始位置的下标//rfind 从后往前查找子串,返回起始位置的下标//substr 截取子串,并返回一个string对象cout << "---------------------------" << endl;string a;a = "abcdefgdefg";cout << a.c_str() << endl;cout << a.find("defg") << endl; //找到就返回在主串中起始位置的下标if (a.find("defgh") == string::npos) //找不到返回string::npos(约为42亿9千万)cout << "未找到" << endl;cout << a.rfind("defg") << endl; //从后往前找。cout << a.rfind("defg", 3) << endl; //从第4个字符开始,从后往前找。cout << a.rfind("defg", 2) << endl; //从第3个字符开始,从后往前找。a = "abcdefgdefg";cout << a.substr(1) << endl; //从下标1的字开始截取到结尾cout << a.substr(1).size() << endl; cout << a.substr(0, 3) << endl; //从下标0的字开始截取3个字符}//string对象和数字间的转换{//to_string()函数:将数字转为字符串cout << "---------------------------" << endl;double a = 1234.5678;string s = std::to_string(a);cout << s << endl;//stoi():将字符串转为整数int b = stoi(s);cout << b << endl;//stod():将字符串转为浮点数double c = std::stod(s);printf("%lf\n", c); //注意cout默认输出两位小数,所以在输出浮点数时最好使用printf()//atoi():将字面字符串转为整数const char* ss = "2345678";b = atoi(ss);cout << b << endl;//atof():将字面字符串转为浮点数c = atof("1234.5678");printf("%f\n", c);}// operator +{cout << "---------------------------" << endl;string firstlevel("com");string secondlevel("cplusplus");string scheme("http://");string hostname;string url;hostname = "www." + secondlevel + '.' + firstlevel;url = scheme + hostname;std::cout << "网址:" + url + '\n';}// 比较运算符:逐个按ASCII码比较{cout << "---------------------------" << endl;string s1 = "abcd";string s2 = "abcde";cout << (s1 == "a") << endl;cout << (s1 > s2) << endl;cout << (s1 >= "abcd") << endl;cout << (s1 < s2) << endl;cout << (s1 <= s2) << endl;}// 按行输入 : getline(cin, str){cout << "---------------------------" << endl;string str;getline(cin, str, '.'); //按行输入,指定以.结束。cout << str << endl;}// 练习1:实现字符串替换函数:{// 法一:倒着找到后先删除后插入string s1("hello world lin");for (int i = s1.size(); i >= 0; i--){if (s1[i] == ' '){s1.erase(i, 1);s1.insert(i, "%20");}}// 法二:开一个新字符串string s2;for (int i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++){if (s1[i] == ' ')s2 += "20%";elses2 += s1[i];}cout << s1 << endl;cout << s2 << endl;}// 练习2:获取文件后缀{// 用find找子串,用substr获取子串。string file_path = "test.cpp.zip.tar";size_t index = file_path.find(".");size_t index1 = file_path.rfind("."); // 从结尾开始找string suffix = file_path.substr(index);string suffix1 = file_path.substr(index1);cout << "使用find获取文件所有后缀:" << suffix << endl;cout << "使用rfind获取文件真后缀:" << suffix1 << endl;}// C++中涉及到char*的操作以'\0'为结尾,涉及string的操作以size的长度算结尾。{cout << "---------------------------" << endl;string s3 = "asdfg ";s3 += '\0';s3 += "hjkl";cout << s3 << endl;cout << s3.c_str() << endl;string s4 = s3;cout << s4 << endl;}return 0;
}------------------------END-------------------------
才疏学浅,谬误难免,欢迎各位批评指正。