星际联邦 80pts
前连20条,后连20条80pts。。。
考虑正解,发现向前连最大,向后连最小会出现重边,所以避免出现这种情况,我们只需要在做完向前连最大以后,在向后连最小的时候连不是同一个连通块的即可;
时间复杂度:$ \Theta(n \log n) $ ,瓶颈在排序;
其实这个思想就是最小生成树的那个BUA算法(全名忘了);
点击查看代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
long long n;
long long a[500005];
int po[500005];
struct sss{int f, t, w;
}e[1000005];
bool cmpw(sss x, sss y) {return x.w < y.w;
}
int cnt;
int fa[500005];
int find(int x) {if (x != fa[x]) fa[x] = find(fa[x]);return fa[x];
}
long long Kru() {sort(e + 1, e + 1 + cnt, cmpw);for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) fa[i] = i;int sum = 0;long long ans = 0;for (int i = 1; i <= cnt; i++) {if (sum == n - 1) break;int x = find(e[i].f);int y = find(e[i].t);if (x != y) {fa[x] = y;ans += 1ll * e[i].w;sum++;}}return ans;
}
int main() {freopen("star.in", "r", stdin);freopen("star.out", "w", stdout);ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);cin >> n;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {cin >> a[i];}long long mi = a[n];int pos = n;for (int i = n - 1; i >= 1; i--) {e[++cnt] = {i, pos, (int)(mi - a[i])};if (mi > a[i]) {po[i] = pos;mi = a[i];pos = i;}}long long ma = a[1];pos = 1;for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {e[++cnt] = {i, pos, (int)(a[i] - ma)};if (ma < a[i]) {ma = a[i];pos = i;}if (po[i]) {e[++cnt] = {po[i], pos, (int)(a[po[i]] - ma)};}}cout << Kru();return 0;
}
和平精英 0pts
赛时的错解0pts;
考虑正解,发现如果我们枚举答案 $ x $,那么所有 $ \leq x $ 的都应该放到 $ or $ 集合里,所有 $ > x $ 的都应该放到 $ and $ 集合里,证明就考虑 $ x \And y \leq x, x | y > x $,这样就得到了一个 $ \Theta(qVn) $ 的复杂度;
考虑人类智慧优化,发现这玩意和 $ popcount $ 很像,于是考虑枚举答案的 $ popcount = x $,那么所有 $ popcount(a_i) < x $ 的都应该放到 $ or $ 集合里,所有 $ popcount(a_i) > x $ 的都应该放到 $ and $ 集合里,对于 $ popcount(a_i) = x $ 的数,这些数都应该相等(或者没有),且应该两个集合都要放,如果只有一个数的话就尝试分别放到两个集合中,最后判断一下两个集合的答案是否相等即可;
注意特判的情况,然后直接上线段树即可,时间复杂度:$ \Theta(n (\log n + \log V)) $;
点击查看代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <set>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int n, q;
int a[100005];
int sum[100005][35];
set<int> se;
vector<int> v;
namespace SEG{inline int ls(int x) {return x << 1;}inline int rs(int x) {return x << 1 | 1;}struct sss{int l, r, val[32], yu[32], huo[32];}tr[500005];inline void push_up(int s, int id) {if (tr[ls(id)].val[s] == -1e9) {tr[id].val[s] = tr[rs(id)].val[s];tr[id].yu[s] = tr[rs(id)].yu[s];tr[id].huo[s] = tr[rs(id)].huo[s];} else if (tr[rs(id)].val[s] == -1e9) {tr[id].val[s] = tr[ls(id)].val[s];tr[id].yu[s] = tr[ls(id)].yu[s];tr[id].huo[s] = tr[ls(id)].huo[s];} else {tr[id].val[s] = ((tr[ls(id)].val[s] == tr[rs(id)].val[s]) ? tr[ls(id)].val[s] : -2e9);tr[id].yu[s] = (tr[ls(id)].yu[s] & tr[rs(id)].yu[s]);tr[id].huo[s] = (tr[ls(id)].huo[s] | tr[rs(id)].huo[s]);}}void bt(int id, int l, int r) {tr[id].l = l;tr[id].r = r;for (int j = 0; j <= 30; j++) tr[id].val[j] = tr[id].yu[j] = tr[id].huo[j] = -1e9;if (l == r) return;int mid = (l + r) >> 1;bt(ls(id), l, mid);bt(rs(id), mid + 1, r);}void add(int s, int id, int pos, int d) {if (tr[id].l == tr[id].r) {tr[id].val[s] = d;tr[id].yu[s] = d;tr[id].huo[s] = d;return;}int mid = (tr[id].l + tr[id].r) >> 1;if (pos <= mid) add(s, ls(id), pos, d);else add(s, rs(id), pos, d);push_up(s, id);}void dfs(int id) {for (int j = 1; j <= 30; j++) {if (tr[id].huo[j - 1] == -1e9) continue;if (tr[id].huo[j] == -1e9) {tr[id].huo[j] = tr[id].huo[j - 1];} else {tr[id].huo[j] |= tr[id].huo[j - 1];}}for (int j = 29; j >= 0; j--) {if (tr[id].yu[j + 1] == -1e9) continue;if (tr[id].yu[j] == -1e9) {tr[id].yu[j] = tr[id].yu[j + 1];} else {tr[id].yu[j] &= tr[id].yu[j + 1];}}if (tr[id].l == tr[id].r) return;dfs(ls(id));dfs(rs(id));}void ask(int s, int id, int l, int r) {if (tr[id].l >= l && tr[id].r <= r) {se.insert(tr[id].val[s]);return;}int mid = (tr[id].l + tr[id].r) >> 1;if (r <= mid) ask(s, ls(id), l, r);else if (l > mid) ask(s, rs(id), l, r);else {ask(s, ls(id), l, mid);ask(s, rs(id), mid + 1, r);}}void ask_yu(int s, int id, int l, int r) {if (tr[id].l >= l && tr[id].r <= r) {if (tr[id].yu[s] != -1e9) v.push_back(tr[id].yu[s]);return;}int mid = (tr[id].l + tr[id].r) >> 1;if (r <= mid) ask_yu(s, ls(id), l, r);else if (l > mid) ask_yu(s, rs(id), l, r);else {ask_yu(s, ls(id), l, mid);ask_yu(s, rs(id), mid + 1, r);}}void ask_huo(int s, int id, int l, int r) {if (tr[id].l >= l && tr[id].r <= r) {if (tr[id].huo[s] != -1e9) v.push_back(tr[id].huo[s]);return;}int mid = (tr[id].l + tr[id].r) >> 1;if (r <= mid) ask_huo(s, ls(id), l, r);else if (l > mid) ask_huo(s, rs(id), l, r);else {ask_huo(s, ls(id), l, mid);ask_huo(s, rs(id), mid + 1, r);}}
}
using namespace SEG;
int main() {freopen("peace.in", "r", stdin);freopen("peace.out", "w", stdout);ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);cin >> n >> q;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {cin >> a[i];}bt(1, 1, n);for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {int su = 0;for (int j = 0; j <= 30; j++) {sum[i][j] = sum[i - 1][j];if ((a[i] >> j) & 1) su++;}sum[i][su]++;add(su, 1, i, a[i]);}dfs(1);int l, r;for (int i = 1; i <= q; i++) {cin >> l >> r;if (l == r) {cout << "NO" << '\n';continue;}bool ans = false;for (int j = 0; j <= 30; j++) {if (sum[r][j] - sum[l - 1][j] == 0) {int yu = 0;v.clear();if (j != 30) ask_yu(j + 1, 1, l, r);for (int i = 1; i < v.size(); i++) {v[0] &= v[i];}if (v.empty()) continue;else yu = v[0];v.clear();int huo = 0;if (j != 0) ask_huo(j - 1, 1, l, r);for (int i = 1; i < v.size(); i++) {v[0] |= v[i];}if (v.empty()) continue;else huo = v[0];// cout << yu << ' ' << huo << endl;if (yu == huo) {ans = true;break;}continue;}int val = 0;se.clear();ask(j, 1, l, r);se.erase(-1e9);auto it = se.lower_bound(-2e9);if (it != se.end() && *it == -2e9) continue;if (se.size() != 1) continue;val = *se.begin();if (sum[r][j] - sum[l - 1][j] == 1) {int yu = 0;v.clear();if (j != 30) ask_yu(j + 1, 1, l, r);for (int i = 1; i < v.size(); i++) {v[0] &= v[i];}bool yy = false;if (!v.empty()) yu = v[0];else yy = true;v.clear();int huo = 0;if (j != 0) ask_huo(j - 1, 1, l, r);for (int i = 1; i < v.size(); i++) {v[0] |= v[i];}bool hh = false;if (!v.empty()) huo = v[0];else hh = true;int yyu = yu;if (!yu) yu = val;else yu &= val;if (!hh && yu == huo) {ans = true;break;}yu = yyu;huo |= val;if (!yy && yu == huo) {ans = true;break;}continue;}int yu = val;v.clear();if (j != 30) ask_yu(j + 1, 1, l, r);for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++) {yu &= v[i];}v.clear();int huo = val;if (j != 0) ask_huo(j - 1, 1, l, r);for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++) {huo |= v[i];}if (yu == huo) {ans = true;break;}}if (ans) cout << "YES" << '\n';else cout << "NO" << '\n';}return 0;
}
摆烂合唱 5pts
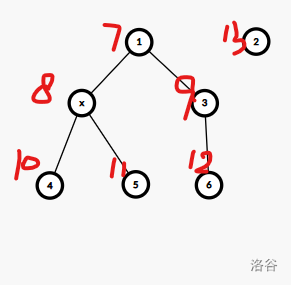
一个套路:表达式树;
考虑建出来这个树(叶子是值,上面的节点都是运算符号),然后在这上面DP;
设 $ f_{x, 0/1} $ 表示 $ x $ 的左或右儿子值不同时,最终到 $ x $ 这个表达式的值不同的概率,那对于单个点的答案就是它到根路径上的 $ f_{x, 0/1} $ 乘积(具体看是左儿子还是右儿子);
例如更新 $ f_{x, 0} $,我们发现它的值和两个东西有关:
-
这一位的运算符;
-
它的右儿子值为 $ 1 $ 的概率;
对于 $ 1 $ 是好知道的,对于 $ 2 $,我们设 $ g_x $ 表示 $ x $ 这个节点值为 $ 1 $ 的概率,转移是容易的;
所以我们直接 $ DFS $,回溯时同时转移 $ f, g $,对于 $ f $ 的转移,只需简单分情况即可;
时间复杂度:$ \Theta(n) $;
这个题主要在建树,可以参考一下代码(建树时记一个 $ fa $,完事回来的时候直接跳一步 $ fa $ 即可);
点击查看代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const long long mod = 998244353;
int n;
char s[2000005];
int len, tot, rt;
struct sss{int ls, rs, x, fa;
}tr[2000005];
long long f[2000005][2], g[2000005];
int val[2000005], cnt;
long long ksm(long long a, long long b) {long long ans = 1;while(b) {if (b & 1) ans = ans * a % mod;a = a * a % mod;b >>= 1;}return ans;
}
void dfs(int x) {if (tr[x].x == 0) {g[x] = ksm(2, mod - 2);return;}dfs(tr[x].ls);dfs(tr[x].rs);if (tr[x].x == 1) {f[x][0] = (1 - g[tr[x].rs] + mod) % mod;f[x][1] = (1 - g[tr[x].ls] + mod) % mod;g[x] = (g[tr[x].ls] + g[tr[x].rs] % mod - g[tr[x].ls] * g[tr[x].rs] % mod + mod) % mod;} else if (tr[x].x == 2) {f[x][0] = g[tr[x].rs];f[x][1] = g[tr[x].ls];g[x] = g[tr[x].ls] * g[tr[x].rs] % mod;} else if (tr[x].x == 3) {f[x][0] = 1;f[x][1] = 1;g[x] = ((g[tr[x].ls] * ((1 - g[tr[x].rs] + mod) % mod)) % mod + ((1 - g[tr[x].ls] + mod) % mod) * g[tr[x].rs] % mod) % mod;}
}
void afs(int x, long long ans) {if (tr[x].x == 0) {cout << ans << '\n';return;}afs(tr[x].ls, ans * f[x][0] % mod);afs(tr[x].rs, ans * f[x][1] % mod);
}
int main() {freopen("binary.in", "r", stdin);freopen("binary.out", "w", stdout);ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);cin >> n;if (n == 1) {cout << 1;return 0;}cin >> (s + 1);len = strlen(s + 1);int now = 0;for (int i = 1; i <= len; i++) {if (s[i] == '(') {tot++;if (!tr[now].ls) {tr[now].ls = tot;} else {tr[now].rs = tot;}tr[tot].fa = now;now = tot;}if (s[i] == ')') now = tr[now].fa;if (s[i] == 'x') {tot++;if (!tr[now].ls) {tr[now].ls = tot;} else {tr[now].rs = tot;}tr[tot].fa = now;}if (s[i] == '|') tr[now].x = 1;if (s[i] == '&') tr[now].x = 2;if (s[i] == '^') tr[now].x = 3;}dfs(1);afs(1, 1);return 0;
}