1.对象数组
1.1定义对象数组
它是一个自定义对象类型的数组,数组元素是自己定义对象类型的对象,就是数组元素是对象,数组类型是自定义对象的类型
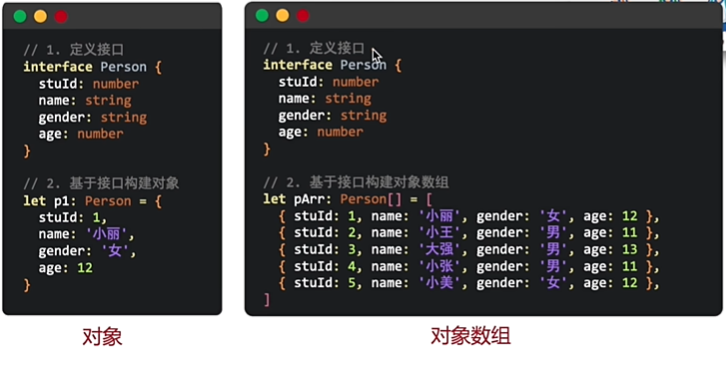
//第一步通过接口定义对象
interface student{stuID:number,name:string,gender:string,age:number
}//基于接口创建对象数组
let stuShuZu:student[]=[{stuID:1,name:'小明',gender:'高三',age:17},{stuID:1,name:'大明',gender:'高三',age:19},{stuID:1,name:'二明',gender:'高三',age:18},{stuID:1,name:'天明',gender:'高三',age:17}
]//这是一个对象数组类型
stuShuZu
//这是一个对象类型
stuShuZu[0]//需求:获取每一个学生的年龄,
//看到数组每一个XXX,就要想到遍历
for (let item of stuShuZu){console.log('学生的姓名是',item.name)
}@Entry
@Component
struct Index {//组件的状态变量@State count:number=1build() {Column(){}.width('100%').height('100%').backgroundColor('#eee').padding({top:15,right:15,left:15})}
}
1.2使用对象数组
- 访问某一个对象:
- **每一对象在数组中都是有对应的下标的, 可以通过 数组名[下标] 访问 **
- 访问某一对象的某一个属性
- 先找到要访问的对象, 在该对象的属性访问属性 数组名[下标].属性名 访问
- 依次访问每一个对象
- for ... of 进行访问即可
//第一步通过接口定义对象
interface student{stuID:number,name:string,gender:string,age:number
}//基于接口创建数组对象
let stuShuZu:student[]=[{stuID:1,name:'小明',gender:'高三',age:17},{stuID:1,name:'大明',gender:'高三',age:19},{stuID:1,name:'二明',gender:'高三',age:18},{stuID:1,name:'天明',gender:'高三',age:17}
]//使用数组, 因为数组对象不能直接在日志中显示, 想要在日志中显示需要调用方法转成字符串
console.log('打印数组对象',stuShuZu)//包含对象的复杂数据, 如果想在日志中打印, 需要需要调用一个方法, 转成字符串
//JSON.stringify(复杂类型)对象/数值
console.log('打印数组对象',JSON.stringify(stuShuZu))//具体使用(访问->数组下标)
console.log('数组中第二位是',stuShuZu[1].name)
console.log('数组中第二位的信息',stuShuZu[1])//没有调用方法, 打印出来是Object
console.log('数组中第二位的信息',JSON.stringify(stuShuZu[1]))//也支持遍历, for...of和普通for
for(let item of stuShuZu){console.log('数组对象中的每一项',JSON.stringify(item))
}@Entry
@Component
struct Index {//组件的状态变量@State count:number=1build() {Column(){}.width('100%').height('100%').backgroundColor('#eee').padding({top:15,right:15,left:15})}
}
2.ForEach - 渲染控制
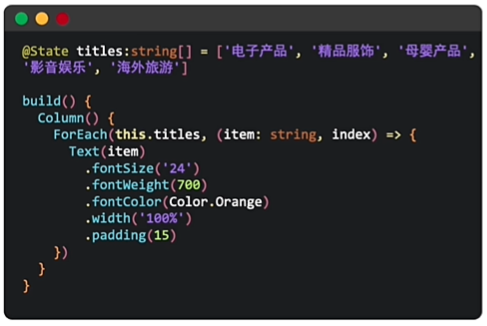
当我们页面中的区域中有多个样式相同的小区域,只有内容数据不一样的时候, 为了提升代码的复用率,不需要一个一个的编写UI组件,我们可以将所有的数据整合成一个数组, 并采取ForEach进行循环渲染.如下图区域,如果我们分别实现每个栏目,代码太过于冗余,这时就可以使用ForEach进行渲染了
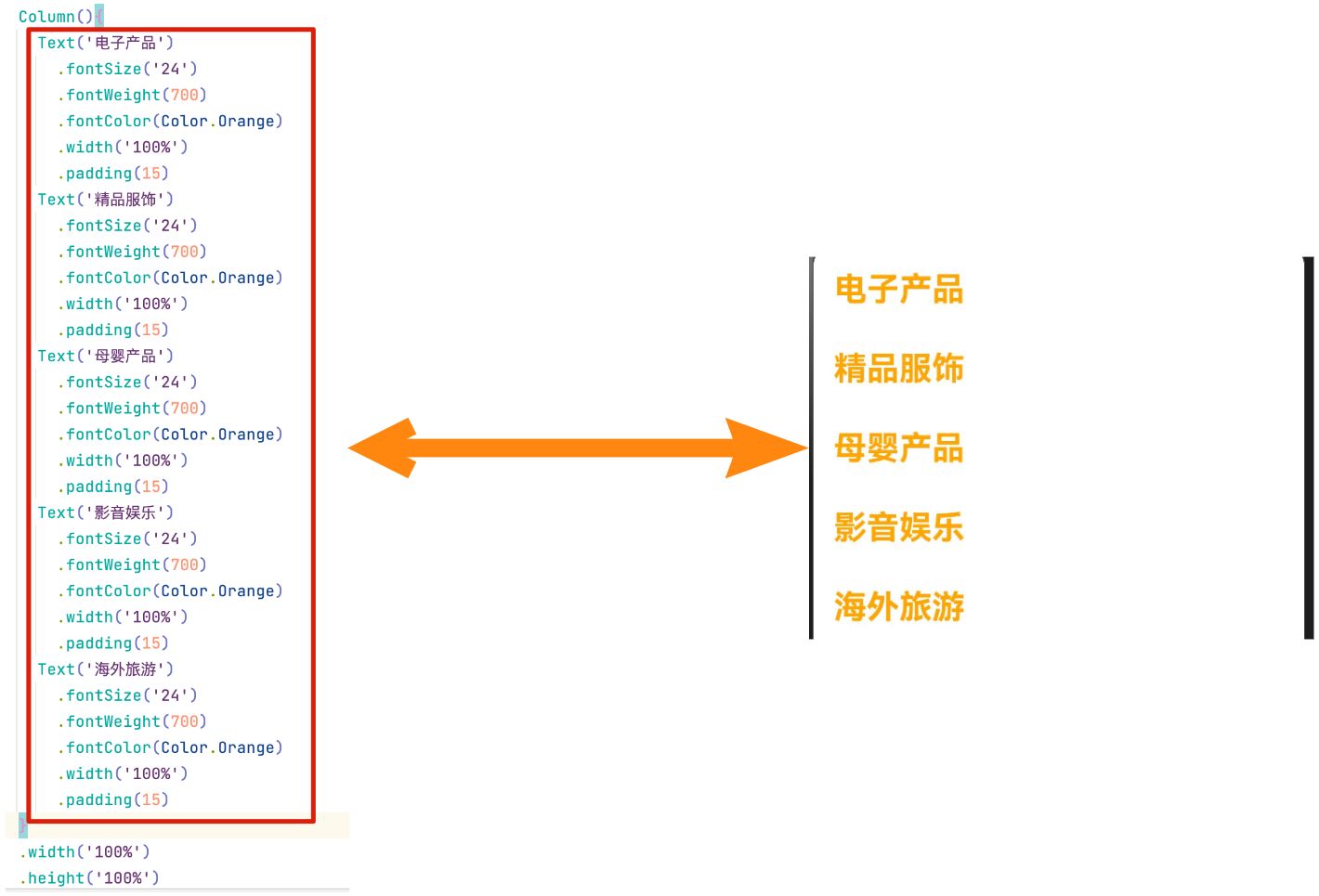
2.1ForEach语法
可以基于数组元素的个数, 来渲染组件的个数(简化代码),根据数组长度循环渲染组件个数
语法:** ForEach(arr, (item, index)=>{这里写循环渲染的内容})**
arr: 要渲染的数组,
(item, index): (item: 是每一项+类型, index: 是下标) -> 是形参
| 参数 | 参数类型 | 参数说明 |
|---|---|---|
| arr | Array | 数据源, 根据该数组生成对应的UI组件渲染到页面中: + 可以为空数组 |
| UI组件生成函数 | (item: any, index?: number) => void | UI组件生成函数 + 为数组中的每个元素创建对应的组件 + item: 代表每一个数组元素, 类型与数组元素保持一致,不可以省略 + index: 代表每一个数组元素的下标,可以省略 |
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {//用装饰器定义了一个数组@State stu:string[]=['大明','二明','小明','天命','耳顺','随心所欲']build() {Column(){//ForEach渲染控制, //item是形参,可以自己定义写法// ()=>{} 第一个 参数1 - 永远都是表示数组每一项 // 第二个 参数2 - 永远都是数组下标 - 不取决于命名,只取决于位置ForEach(this.stu,(item:string,index)=>{Text(`${item},${index+1}`).fontColor(Color.Green).fontSize(20).fontWeight(500).padding(10)}) }.width('100%').height('100%').backgroundColor('#eee').padding({top:15,right:15,left:15})}
}
//接口要定义到程序入口@Entry外
interface news{title:string,createTime:string,
}
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {@State articles: news[]=[{title:'近200+自动驾驶数据集全面调研!一览如何数据闭环全流程', createTime:'2024-01-31 09-59:43'},{title:'近200+自动驾驶数据集全面调研!一览如何数据闭环全流程', createTime:'2024-01-31 09-59:43'},{title:'近200+自动驾驶数据集全面调研!一览如何数据闭环全流程', createTime:'2024-01-31 09-59:43'},{title:'近200+自动驾驶数据集全面调研!一览如何数据闭环全流程', createTime:'2024-01-31 09-59:43'},]build() {Column(){//ForEach渲染控制,ForEach(this.articles,(item:news,index)=>{Column(){Text(`${item.title}`).fontColor('#000').fontWeight(500).padding(10).width('100%')Text(`${item.createTime}`).fontColor('#999').fontSize(14).fontWeight(500).padding(10).width('100%')}}) }.width('100%').height('100%').backgroundColor('#eee').padding({top:15,right:15,left:15})}
}
2.2ForEach使用优化代码
原始代码
完整代码
3.Math对象
Math 是一个内置对象,它拥有一些数学常数属性和数学函数方法, Math 用于 Number 类型数据的处理.
| 对象方法 | 是否需要参数 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|---|
| Math.random() | 否 | + 随机数 + 取值范围 [0, 1)之间的随机小数,左闭右开, 可以取到0,但是取不到1 |
| Math.ceil() | 是 | + 需要一个数字形参数 + 总是向上取整 |
| Math.floor() | 是 | + 需要一个数字形参数 + 总是向下取整 |
- 代码测试
// 1. 随机数
console.log('Math对象', Math.random()) // 0-1 之间的随机小数// 2. 向上取整
console.log('Math对象', Math.ceil(1.1)) // 2
console.log('Math对象', Math.ceil(1.9)) // 2// 3. 向下取整
console.log('Math对象', Math.floor(1.1)) // 1
console.log('Math对象', Math.floor(1.9)) // 1
- 求0--10之间的随机整数
// 0-10 之间的随机数
console.log('Math对象', Math.random() * 11)// 0-10 之间的随机 整数
console.log('Math对象', Math.floor(Math.random() * 11))
- 求n--m之间的随机数
//计算n-m的随机数
let n:number=1
let m:number=10
console.log('n-m的随机数',Math.floor(Math.random()*(m-n+1))+1);//这种写法0是取不到的, 或者取到0的概率极小
console.log('随机数',Math.ceil(Math.random()*2));