smallpt: Global Illumination in 99 lines of C++
首先在win平台需要添加函数erand48,修改为main函数,其中的samps是每个像素的采样率,越大越慢
修改后
#include <math.h> // smallpt, a Path Tracer by Kevin Beason, 2008
#include <stdlib.h> // Make : g++ -O3 -fopenmp smallpt4k.cpp -o smallpt4k
#include <stdio.h> // Remove "-fopenmp" for g++ version < 4.2
struct Vec { // Usage: time ./smallpt4k && xv image.ppmdouble x, y, z; // position, also color (r,g,b)Vec(double x_=0, double y_=0, double z_=0){ x=x_; y=y_; z=z_; }Vec operator+(const Vec &b) const { return Vec(x+b.x,y+b.y,z+b.z); }Vec operator-(const Vec &b) const { return Vec(x-b.x,y-b.y,z-b.z); }Vec operator*(double b) const { return Vec(x*b,y*b,z*b); }Vec mult(const Vec &b) const { return Vec(x*b.x,y*b.y,z*b.z); }Vec& norm(){ return *this = *this * (1/sqrt(x*x+y*y+z*z)); }double dot(const Vec &b) const { return x*b.x+y*b.y+z*b.z; } // cross:Vec operator%(Vec&b){return Vec(y*b.z-z*b.y,z*b.x-x*b.z,x*b.y-y*b.x);}
};
struct Ray { Vec o, d; Ray(Vec o_, Vec d_) : o(o_), d(d_) {} };
enum Refl_t { DIFF, SPEC, REFR }; // material types, used in radiance()
struct Sphere {double rad; // radiusVec p, e, c; // position, emission, colorRefl_t refl; // reflection type (DIFFuse, SPECular, REFRactive)Sphere(){}Sphere(double rad_, Vec p_, Vec e_, Vec c_, Refl_t refl_):rad(rad_), p(p_), e(e_), c(c_), refl(refl_) {}double intersect(const Ray &r) const { // returns distance, 0 if nohitVec op = p-r.o; // Solve t^2*d.d + 2*t*(o-p).d + (o-p).(o-p)-R^2 = 0double t, eps=1e-4, b=op.dot(r.d), det=b*b-op.dot(op)+rad*rad;if (det<0) return 0; else det=sqrt(det);return (t=b-det)>eps ? t : ((t=b+det)>eps ? t : 0);}
};
Sphere spheres[9]; //Scene: radius, position, emission, color, material
inline double clamp(double x){ return x<0 ? 0 : x>1 ? 1 : x; }
inline int toInt(double x){ return int(pow(clamp(x),1/2.2)*255+.5); }
inline bool intersect(const Ray &r, double &t, int &id){double n=sizeof(spheres)/sizeof(Sphere), d, inf=t=1e20;for(int i=int(n);i--;) if((d=spheres[i].intersect(r))&&d<t){t=d;id=i;}return t<inf;
}
inline double erand48(unsigned short xsubi[3]) {return (double)rand() / (double)RAND_MAX;
}
Vec radiance(const Ray &r, int depth, unsigned short *Xi){double t; // distance to intersectionint id=0; // id of intersected objectif (!intersect(r, t, id)) return Vec(); // if miss, return blackconst Sphere &obj = spheres[id]; // the hit objectVec x=r.o+r.d*t, n=(x-obj.p).norm(), nl=n.dot(r.d)<0?n:n*-1, f=obj.c;double p = f.x>f.y && f.x>f.z ? f.x : f.y>f.z ? f.y : f.z; // max reflif (++depth>5) if (erand48(Xi)<p) f=f*(1/p); else return obj.e; //R.R.if (obj.refl == DIFF){ // Ideal DIFFUSE reflectiondouble r1=2*M_PI*erand48(Xi), r2=erand48(Xi), r2s=sqrt(r2);Vec w=nl, u=((fabs(w.x)>.1?Vec(0,1):Vec(1))%w).norm(), v=w%u;Vec d = (u*cos(r1)*r2s + v*sin(r1)*r2s + w*sqrt(1-r2)).norm();return obj.e + f.mult(radiance(Ray(x,d),depth,Xi));} else if (obj.refl == SPEC) // Ideal SPECULAR reflectionreturn obj.e + f.mult(radiance(Ray(x,r.d-n*2*n.dot(r.d)),depth,Xi));Ray reflRay(x, r.d-n*2*n.dot(r.d)); // Ideal dielectric REFRACTIONbool into = n.dot(nl)>0; // Ray from outside going in?double nc=1, nt=1.5, nnt=into?nc/nt:nt/nc, ddn=r.d.dot(nl), cos2t;if ((cos2t=1-nnt*nnt*(1-ddn*ddn))<0) // Total internal reflectionreturn obj.e + f.mult(radiance(reflRay,depth,Xi));Vec tdir = (r.d*nnt - n*((into?1:-1)*(ddn*nnt+sqrt(cos2t)))).norm();double a=nt-nc, b=nt+nc, R0=a*a/(b*b), c = 1-(into?-ddn:tdir.dot(n));double Re=R0+(1-R0)*c*c*c*c*c,Tr=1-Re,P=.25+.5*Re,RP=Re/P,TP=Tr/(1-P);return obj.e + f.mult(depth>2 ? (erand48(Xi)<P ? // Russian rouletteradiance(reflRay,depth,Xi)*RP:radiance(Ray(x,tdir),depth,Xi)*TP) :radiance(reflRay,depth,Xi)*Re+radiance(Ray(x,tdir),depth,Xi)*Tr);
}
int main() {
spheres[0]=Sphere(1e5, Vec( 1e5+1,40.8,81.6), Vec(),Vec(.75,.25,.25),DIFF);//Left
spheres[1]=Sphere(1e5, Vec(-1e5+99,40.8,81.6),Vec(),Vec(.25,.25,.75),DIFF);//Rght
spheres[2]=Sphere(1e5, Vec(50,40.8, 1e5), Vec(),Vec(.75,.75,.75),DIFF);//Back
spheres[3]=Sphere(1e5, Vec(50,40.8,-1e5+170), Vec(),Vec(), DIFF);//Frnt
spheres[4]=Sphere(1e5, Vec(50, 1e5, 81.6), Vec(),Vec(.75,.75,.75),DIFF);//Botm
spheres[5]=Sphere(1e5, Vec(50,-1e5+81.6,81.6),Vec(),Vec(.75,.75,.75),DIFF);//Top
spheres[6]=Sphere(16.5,Vec(27,16.5,47), Vec(),Vec(1,1,1)*.999, SPEC);//Mirr
spheres[7]=Sphere(16.5,Vec(73,16.5,78), Vec(),Vec(1,1,1)*.999, REFR);//Glas
spheres[8]=Sphere(600, Vec(50,681.6-.27,81.6),Vec(12,12,12), Vec(), DIFF);//Liteint w=1024, h=768, samps = 5000/4; // # samplesRay cam(Vec(50,52,295.6), Vec(0,-0.042612,-1).norm()); // cam pos, dirVec cx=Vec(w*.5135/h), cy=(cx%cam.d).norm()*.5135, r,*c=(Vec*)malloc(sizeof(Vec)*w*h);
#pragma omp parallel for schedule(dynamic, 1) private(r) // OpenMPfor (int y=0; y<h; y++){ // Loop over image rowsfprintf(stderr,"\rRendering (%d spp) %5.2f%%",samps*4,100.*y/(h-1));for (unsigned short x=0, Xi[3]={0,0,y*y*y}; x<w; x++) // Loop colsfor (int sy=0, i=(h-y-1)*w+x; sy<2; sy++) // 2x2 subpixel rowsfor (int sx=0; sx<2; sx++, r=Vec()){ // 2x2 subpixel colsfor (int s=0; s<samps; s++){double r1=2*erand48(Xi), dx=r1<1 ? sqrt(r1)-1: 1-sqrt(2-r1);double r2=2*erand48(Xi), dy=r2<1 ? sqrt(r2)-1: 1-sqrt(2-r2);Vec d = cx*( ( (sx+.5 + dx)/2 + x)/w - .5) +cy*( ( (sy+.5 + dy)/2 + y)/h - .5) + cam.d;r = r + radiance(Ray(cam.o+d*140,d.norm()),0,Xi)*(1./samps);} // Camera rays are pushed ^^^^^ forward to start in interiorc[i] = c[i] + Vec(clamp(r.x),clamp(r.y),clamp(r.z))*.25;}}FILE *f = fopen("image.ppm", "w"); // Write image to PPM file.fprintf(f, "P3\n%d %d\n%d\n", w, h, 255);for (int i=0; i<w*h; i++)fprintf(f,"%d %d %d ", toInt(c[i].x), toInt(c[i].y), toInt(c[i].z));fclose(f);exit(0);
}然后需要安装MSYS2
安装完成后将
C:\msys64\mingw64\bin添加入环境变量
然后打开MSYS2 MINGW64,在里面创建文件,把代码复制进去
g++ -O3 -fopenmp smallpt.cpp -o smallpt 编译,
它的home目录一般在
C:\msys64\home运行编译后的结果
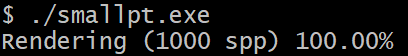
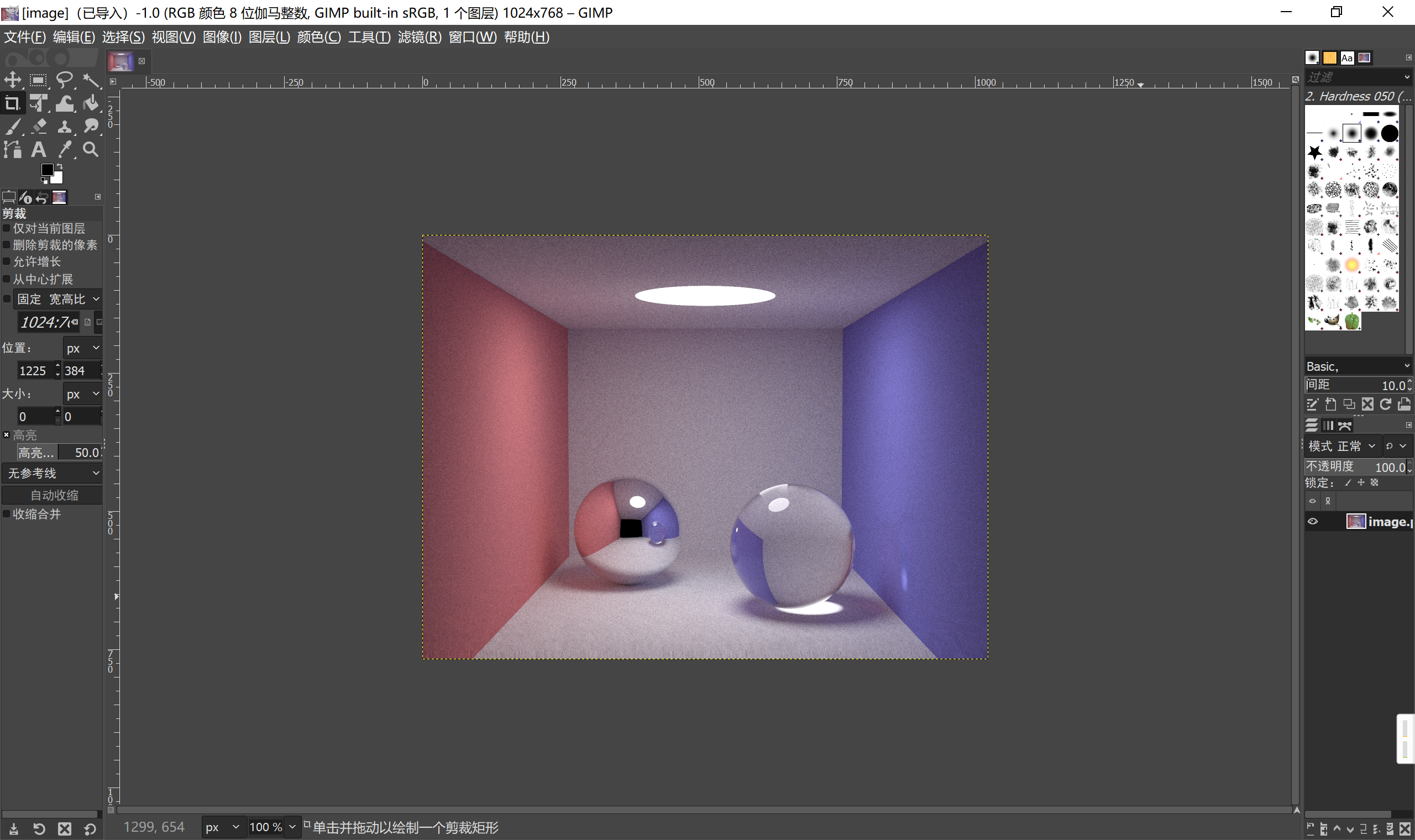
会生成ppm文件PPM Format Specification
可以用GIMP - Downloads打开