在进行 React 开发的时候,还有一个非常重要的功能模块,那就是 Hook,自定义 Hook 作为一块公共逻辑的抽离,也会像组件一样被用到多个地方,因此对 Hook 的测试也是非常有必要的。
Hook 没有办法像普通函数一样直接进行测试,因为在 React 中规中,Hook 必须要在组件里面使用,否则会报错。
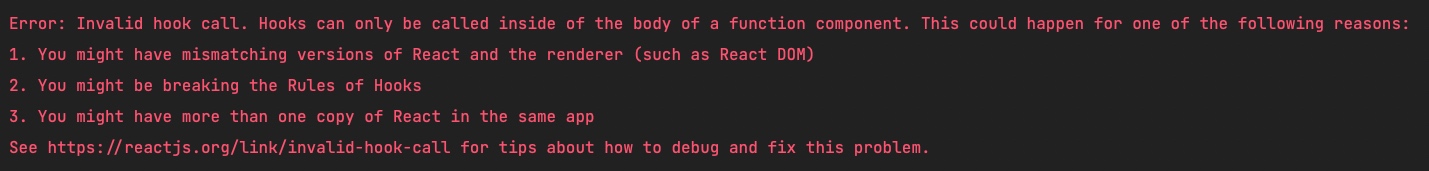
有一种方案,就是为了测试自定义 Hook,专门写一个组件,然后通过上一小节我们所讲的测试组件的方式来测试这些 Hook,这种方案是可以的,但是比较麻烦。
在 Testing library 里面就提供了一个 @testing-library/react-hooks 的扩展库,专门用于测试 react hooks。
该扩展库对应的官网地址:https://react-hooks-testing-library.com/
快速上手示例
首先我们有如下的自定义 Hook:
// 自定义 hook
// 这是一个计数器的自定义 hook
// 内部维护了一个计数的值,以及修改这个值的一些方法import { useState } from "react";interface Options {min?: number;max?: number;
}type ValueParam = number | ((c: number) => number);// 该方法主要是做一个边界的判断,如果超过了边界,那么就取边界值
function getTargetValue(val: number, options: Options = {}) {const { min, max } = options;let target = val;// 判断有没有超过最大值,如果超过了,那么我们就取最大值if (typeof max === "number") {target = Math.min(max, target);}// 判断有没有超过最小值,如果超过了,那么我们就取最小值if (typeof min === "number") {target = Math.max(min, target);}return target;
}// useCounter(100, {min : 1, max : 1000})
function useCounter(initialValue = 0, options: Options = {}) {const { min, max } = options;// 设置初始值,初始值就为 initialVaule// 初始值是该自定义 hook 内部维护的状态,用来表示计数器的数值const [current, setCurrent] = useState(() => {return getTargetValue(initialValue, {min,max,});});// 设置新的值// 在设置新的值的时候,调用了 getTargetValue 来判断新值是否越界const setValue = (value: ValueParam) => {setCurrent((c) => {const target = typeof value === "number" ? value : value(c);return getTargetValue(target, {max,min,});});};// 下面就是自定义 hook 提供的 4 个方法// 用于修改计数器的数值// 增加const inc = (delta = 1) => {setValue((c) => c + delta);};// 减少const dec = (delta = 1) => {setValue((c) => c - delta);};// 设置const set = (value: ValueParam) => {setValue(value);};// 重置const reset = () => {setValue(initialValue);};// 像外部暴露return [current,{inc,dec,set,reset,},] as const;
}export default useCounter;接下来我们要对这个自定义 Hook 进行一个测试,对应的测试代码如下:
import useCounter from "../hooks/useCounter";
import { renderHook, act } from "@testing-library/react";test("可以做加法", () => {// Arrange(准备)// result ---> {current : [0, {inc, dec, set, reset}]}const { result } = renderHook(() => useCounter(0));// Act(行为)act(() => result.current[1].inc(2));// Assert(断言)expect(result.current[0]).toEqual(2);
});test("可以做减法", () => {// Arrange(准备)// result ---> {current : [0, {inc, dec, set, reset}]}const { result } = renderHook(() => useCounter(0));// Act(行为)act(() => result.current[1].dec(2));// Assert(断言)expect(result.current[0]).toEqual(-2);
});test("可以设置值", () => {// Arrange(准备)// result ---> {current : [0, {inc, dec, set, reset}]}const { result } = renderHook(() => useCounter(0));// Act(行为)act(() => result.current[1].set(100));// Assert(断言)expect(result.current[0]).toEqual(100);
});test("可以重置值", () => {// Arrange(准备)// result ---> {current : [0, {inc, dec, set, reset}]}const { result } = renderHook(() => useCounter(0));// Act(行为)act(() => result.current[1].set(100));act(() => result.current[1].reset());// Assert(断言)expect(result.current[0]).toEqual(0);
});test("可以设置最大值", () => {// Arrange(准备)// result ---> {current : [0, {inc, dec, set, reset}]}const { result } = renderHook(() => useCounter(0, { max: 100 }));// Act(行为)act(() => result.current[1].set(1000));// Assert(断言)expect(result.current[0]).toEqual(100);
});test("可以设置最小值", () => {// Arrange(准备)// result ---> {current : [0, {inc, dec, set, reset}]}const { result } = renderHook(() => useCounter(0, { min: -100 }));// Act(行为)act(() => result.current[1].set(-1000));// Assert(断言)expect(result.current[0]).toEqual(-100);
});首先我们使用到了 renderHook,这个方法的背后,会去渲染一个测试组件,在组件中可以使用自定义 hook,从 renderHook 的返回值中可以解构出自定义 Hook 中返回的状态值以及修改状态值的方法。
接下来使用 act 方法,该方法主要是用来模拟 react 组件的交互行为,并且触发更新。
最后进行 expect 断言。
注意,上面的 renderHook 以及 act 方法是从 @testing-library/react 解构出来的,但是以前在旧版本中是需要安装 @testing-library/react-hooks 扩展库,然后从这个扩展库中解构 renderHook 和 act 方法,目前新版本已经将这两个方法整合到 @testing-library/react 这个扩展库里面了。
经过测试之后,就可以证明我们这个自定义 Hook 是没有问题,自然在组件中进行使用的时候也不会有任何问题:
import './App.css';
import useCounter from "./hooks/useCounter";
function App() {const [current, {inc, dec, set, reset}] = useCounter(5, {min : 0,max : 10});return (<div className="App"><div>{current}</div><button onClick={()=>dec(1)}>-</button><button onClick={()=>inc(1)}>+</button><button onClick={()=>set(100)}>set</button><button onClick={()=>reset()}>reset</button></div>);
}export default App;
测试异步的 Hook
有些时候我们的 Hook 会包含一些异步的代码,例如我们对上面的计数器进行一个修改,增加异步的方法,如下:
const asyncInc = (delta = 1) => {setTimeout(()=>{setValue((c) => c + delta);}, 2000);};
之后在进行测试的时候,就可以使用前面我们所学过的 fakeTime 来模拟时间流逝,代码如下:
test("测试异步的增加",async ()=>{jest.useFakeTimers();const {result} = renderHook(()=>useCounter(0));act(() => result.current[1].asyncInc(2));expect(result.current[0]).toEqual(0);await act(()=>jest.advanceTimersByTime(2000));expect(result.current[0]).toEqual(2);jest.useRealTimers();
});