Vue2
自定义创建项目
基于VueCli自定义创建项目架子
步骤:
-
安装VueCLI脚手架
npm i @vue/cli -g可以通过vue --version判断是否下载VueCLI -
在某个文件夹中创建vue项目
vue create 项目名称(项目名中不能包含大写字母) -
选择
Manually select features -
选择Babel(语法降级)、Router、CSS Pre-processors、Linter(ES规范) (空格可选中)
-
选中Vue2
-
选择CSS预处理器为less
-
选中Lint为
ESLint + Standard config无分号规范、Lint on save保存时校验 -
将所有文件放在单独的文件中进行管理
In dedicated config files
ESlint代码规范
代码规范:一套写代码的约定规则,如:赋值符号的左右是否需要空格,一句结束是否要加;
正规的团队需要统一的编码风格
JavaScript Standard Style规范说明:https://standardjs.com/rules-zhcn.html
如:
-
字符串使用单引号:'abc' (单引号的可阅读性高于双引号)
-
无分号:
const name='abc' -
关键字后加空格:
if (name='ls'){...} -
函数名后加空格:
function name (arg){...} -
坚持使用全等=== 而不是==
-
......
如果代码不符合standard规范,Eslint会报错,并准确告知具体的行数和字符数
-
可以根据错误提示来手动修正,参考文档规则参考 - ESLint - 插件化的 JavaScript 代码检查工具
-
自动修正:基于Vscode插件ESLint高亮错误,并配置实现自动修复错误
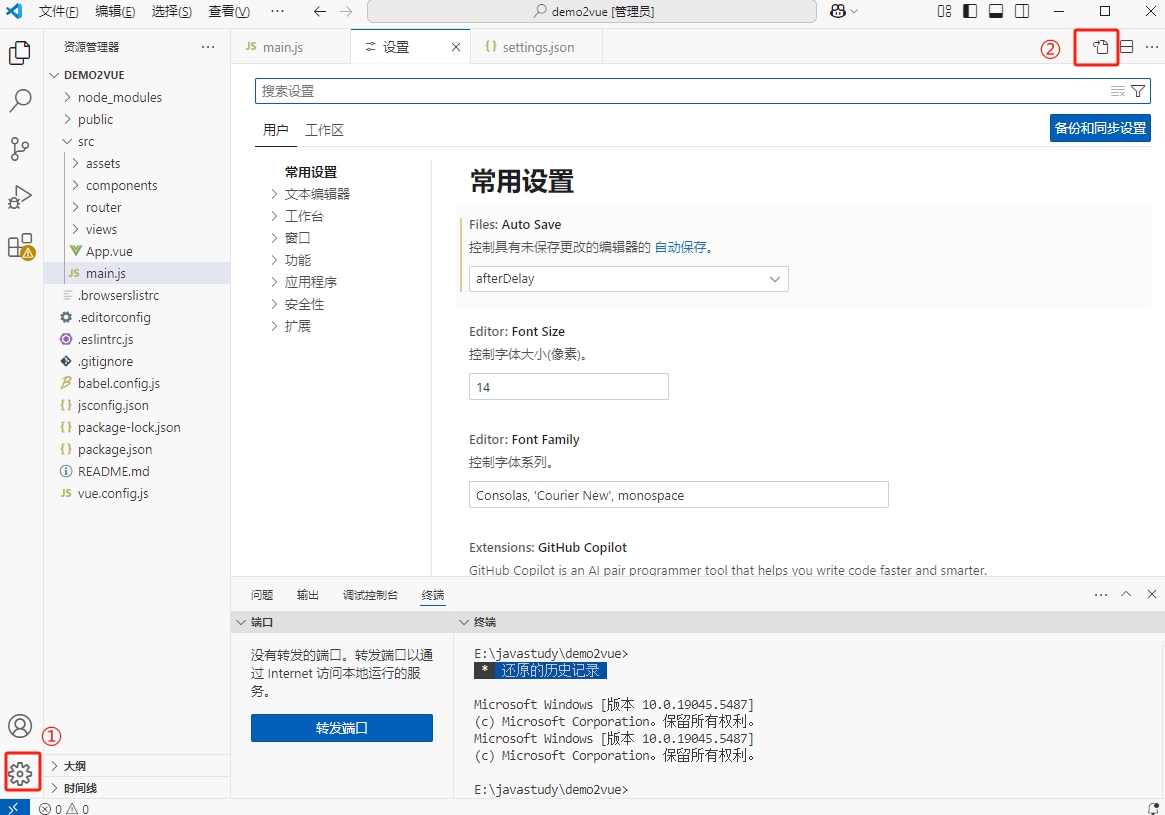
//当保存的时候eslint自动帮助修复错误"editor.codeActionsOnSave": {"source.fixAll":true},//保存代码 不自动格式化"editor.formatOnSave": false //如果是true会与修复错误冲突在vscode的设置>打开设置中进行上述配置(必须将vscode中的自动保存取消,手动保存才起作用)
Vuex
Vuex是Vue的一个状态管理工具,状态即数据(可以帮助我们管理Vue通用的数据(多组件共享的数据))
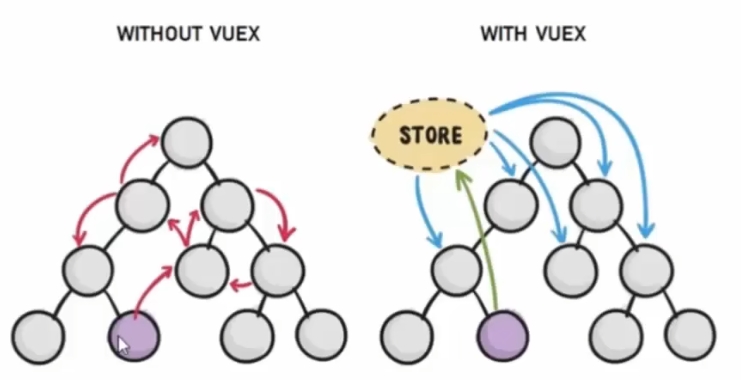
场景:
-
某个状态在很多个组件来使用(个人信息)
-
多个组件共同维护一份数据(购物车)
-
例:
-
三个组件共享一份数据
-
任意一个组件都可以修改数据
-
三个组件的数据是同步的
-
优势:
-
共同维护一份数据,数据集中化管理
-
响应式变化
-
操作简洁
Vuex的安装与使用
步骤:
-
安装Vuex:
npm i vuex@3或npm install -d vuex@3 -
新建Vuex模块文件:在src>store下新建
index.js专门存放Vuex -
创建仓库
// 存放vuex的核心代码import Vue from 'vue' import Vuex from 'vuex' // 插件安装 Vue.use(Vuex)// 创建仓库 const store = new Vuex.Store()// 导出 export default store -
main.js中导入挂载
import Vue from 'vue' import App from './App.vue' import store from '@/store/index'Vue.config.productionTip = falsenew Vue({render: h => h(App),store }).$mount('#app') -
在App.vue中打印store测试仓库是否成功创建
created () {console.log(this.$store)}
Vuex的state状态
提供数据
State提供唯一的公共数据源,所有的共享数据都要统一放到Store中的State中存储
// 创建仓库
const store = new Vuex.Store({state: {title: '嘀嘀嘀',count: 100}
})
state状态即数据,类似于Vue组件中的data,但存在区别:
-
data是组件自己的数据
-
state是所有组件共享的数据
使用数据
-
通过store直接访问
-
模板中:
{{$store.state.xxx}} -
组件逻辑中:
this.$store.state.xxx -
JS模块中:
store.state.xxx
-
-
通过辅助函数:可以把state中的数据定义在计算属性 中,如
{{count}}computed(){count(){return this.$store.state.count} }mapState可以帮助把store中的数据自动映射到组件的计算属性中
-
导入mapState:
import {mapState} from 'vuex' -
数组方式引入state:
mapState(['count']) -
展开运算符映射:
computed:{ ...mapState(['count'])}
例:
<template><div class="App"><h1>根组件-{{ title }}-{{ count }}</h1><BaseA></BaseA><BaseB></BaseB></div> </template><script> import BaseA from './components/BaseA.vue' import BaseB from './components/BaseB.vue' import { mapState } from 'vuex'export default {components: {BaseA,BaseB},created () {console.log(this.$store)},computed: {...mapState(['count', 'title'])} } </script><style scoped>.App{border: 1px solid gainsboro;width: 550px;height: 800px;margin: auto;text-align: center;} </style>
-
修改数据-mutations
Vuex同样遵循单向数据流,组件中不能直接修改仓库的数据
可以通过在创建仓库时配置strict:true开启严格模式 如果组件直接修改仓库中的数据会报错
适合初学者,上线时需要关闭 会消耗运行性能
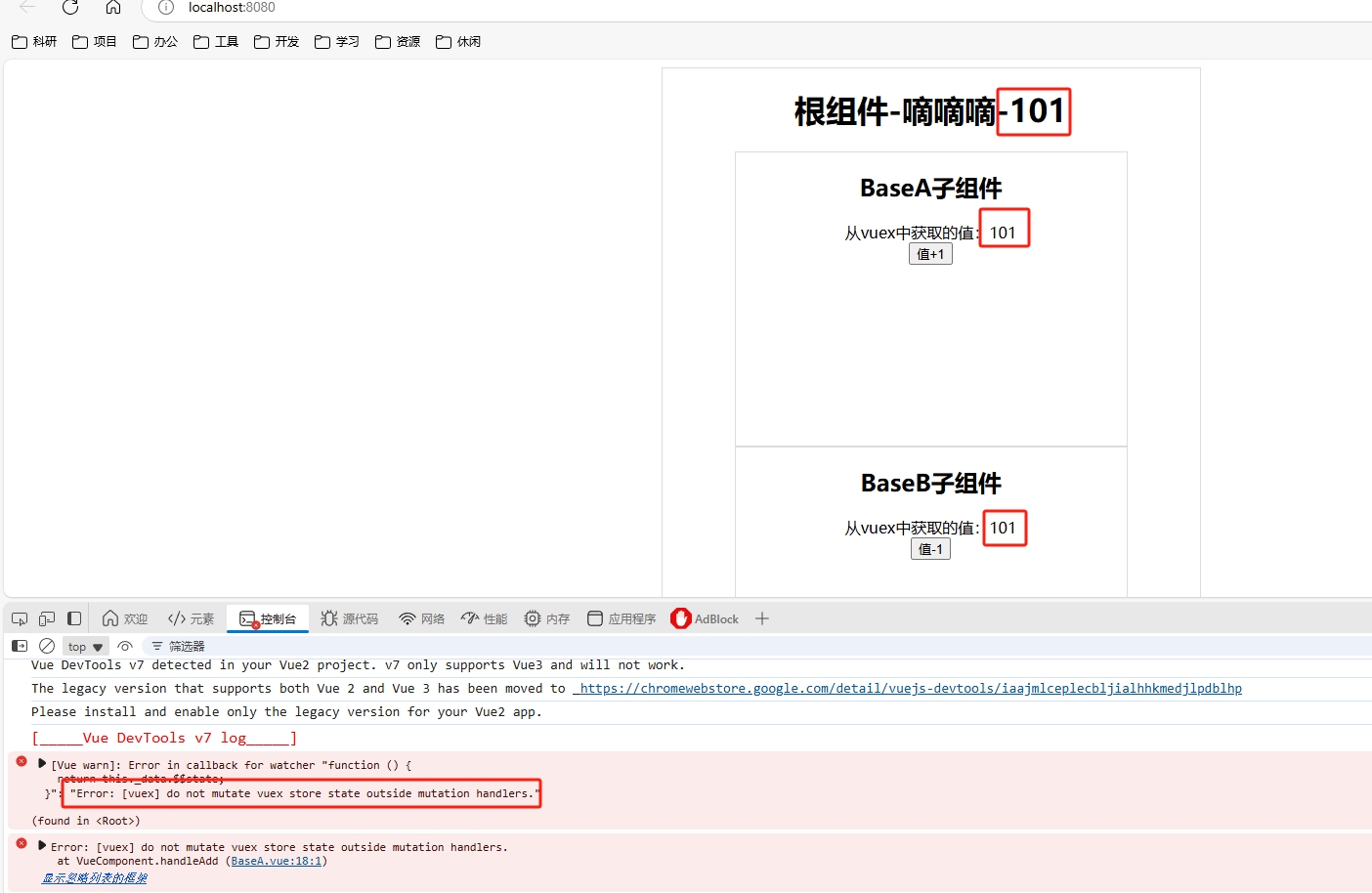
state数据的修改只能通过mutations 在实例化store对象的时候定义mutations对象,并在对象中存放修改state的方法
例:
const store = new Vuex.store({state:{count:0},mutations:{addCount(state){state.count+=1}}
})
组件中提交调用mutations
this.$store.commit('addCount')
提交的mutations是可以传递参数的this.$store.commit('xxx',参数)
需要注意的是:传递的参数只能有一个,如果实在要传递多个参数可写成对象的形式
例 :
const store = new Vuex.store({state:{count:0},mutations:{addCount(state,n){ //n被称为提交载荷state.count+=n}}
})
页面中的调用:
this.$store.commit('addCount',10)
如果想实现input组件与state数据的双向绑定:
-
输入框内容渲染:
:value="{{count}}" -
监听输入获取内容:
@input -
封装mutations处理函数:mutations传参
-
调用传参:commit调用
例:
store>index.js
// 存放vuex的核心代码import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
// 插件安装
Vue.use(Vuex)// 创建仓库
const store = new Vuex.Store({strict: true, // 严格模式,任何直接修改仓库值的代码都会报错// 通过state提供数据state: {title: '嘀嘀嘀',count: 100},// 通过mutations提供修改state的方法mutations: {handleAdd (state, n) {state.count += n},changeCount (state, n) {state.count = n}}
})// 导出
export default storeApp.vue
<template><div class="App"><h1>根组件-{{ title }}-{{ count }}</h1><input type="text" :value="count" @input="handleInput"><BaseA></BaseA><BaseB></BaseB></div>
</template><script>
import BaseA from './components/BaseA.vue'
import BaseB from './components/BaseB.vue'
import { mapState } from 'vuex'export default {components: {BaseA,BaseB},created () {console.log(this.$store)},computed: {...mapState(['count', 'title'])},methods: {handleInput (e) {this.$store.commit('changeCount', +e.target.value)}}
}
</script><style scoped>.App{border: 1px solid gainsboro;width: 550px;height: 800px;margin: auto;text-align: center;}
</style>子组件BaseA.vue
<template><div class="box"><h2>BaseA子组件</h2>从vuex中获取的值:{{count }}<label for=""></label><br><button @click="handleAdd(1)">值+1</button><button @click="handleAdd(5)">值+5</button></div>
</template><script>
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {computed: {...mapState(['count', 'title'])},methods: {handleAdd (n) {this.$store.commit('handleAdd', n)}}
}
</script><style scoped>.box{border: 1px solid gainsboro;width: 400px;height: 300px;margin-bottom: 10px;margin: auto;}
</style>
可以通过mapMutations把位于mutations中的方法提取出来映射到组件methods中
例:
// 创建仓库
const store = new Vuex.Store({strict: true, // 严格模式,任何直接修改仓库值的代码都会报错// 通过state提供数据state: {title: '嘀嘀嘀',count: 100},// 通过mutations提供修改state的方法mutations: {handleAdd (state, n) {state.count += n},handleSub (state, n) {state.count -= n},changeCount (state, n) {state.count = n}}
})
<template><div class="box"><h2>BaseB子组件</h2>从vuex中获取的值:{{ count }}<label for=""></label><br><button @click="handleSub(1)">值-1</button><button @click="handleSub(5)">值-5</button></div>
</template><script>
import { mapState, mapMutations } from 'vuex'
export default {computed: {...mapState(['count', 'title'])},methods: {...mapMutations(['handleSub'])}
}
</script>
调用:
this.subCount(10)
//或 @click="handleSub(10)
actions
actions用于专门处理异步操作 (mutations中的内容必须是同步的,便于监测数据变化,记录调试)
例:在1s之后将state中的count修改为111
// 创建仓库
const store = new Vuex.Store({strict: true, // 严格模式,任何直接修改仓库值的代码都会报错// 通过state提供数据state: {title: '嘀嘀嘀',count: 100},// 通过mutations提供修改state的方法mutations: {handleAdd (state, n) {state.count += n},handleSub (state, n) {state.count -= n},changeCount (state, n) {state.count = n}},// actions 处理异步,不能直接操作state,还是需要通过commit来操作actions: {// context 上下文 (由于此处未分模块,可以当成仓库store使用)// context.commit('mutations',参数)changeCountAction (context, num) {// 使用setTimeout模拟异步setTimeout(() => {context.commit('changeCount', num)}, 1000)}}
})
页面中调用:
<button @click="handleChange(111)">一秒后修改为111</button>methods: {handleAdd (n) {this.$store.commit('handleAdd', n)},handleChange (n) {this.$store.dispatch('changeCountAction', n)}}
可以通过辅助函数mapActions把位于actions中的方法提取出来映射到组件methods中
例:
action:{changeCountAction(context,num){setTimeout(()=>{context.commit('changeCount',num)},1000)}
}
import {mapActions} from 'vuex'methods:{...mapActions(['changeCountAction'])
}
调用:
this.changeCountAction(111)
getters
类似于计算属性,有时需要从state中派生出一些状态,这些状态是依赖state的,此时需要使用getters
例:
state中定义了list数组,范围是1-10,组件中需要显示出大于5的值
state:{list:[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]
}
定义getters:
getters:{filterList(state){return state.list.filter(item=>item>5)}
}
访问getters:必须有返回值
-
通过store访问getters:
{{$store.getters.filterList}} -
通过辅助函数mapGetters映射 由于映射的是属性,因此需要放在计算属性中调用
computed:{...mapGetters(['filterList']) }{{filterList}}
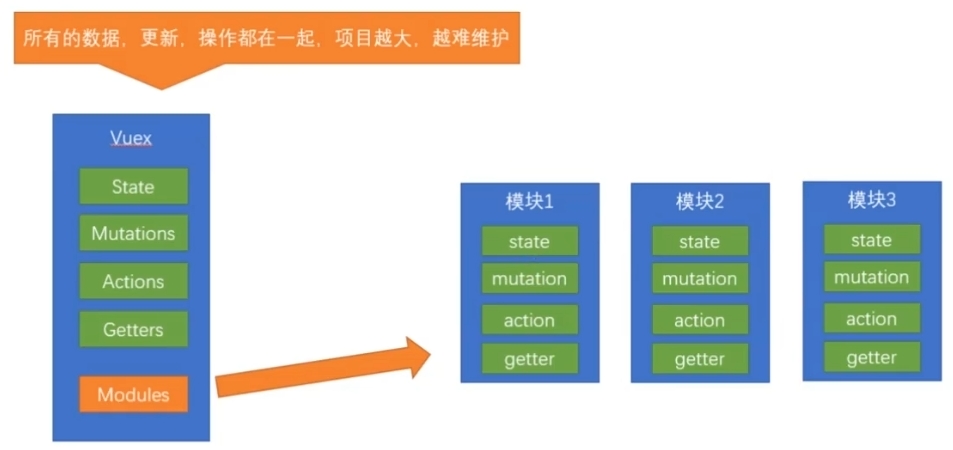
module模块
由于vuex使用单一状态树,应用的所有状态会集中到一个较大的对象
当应用变得非常复杂时,store对象就有可能变得相当臃肿
(当项目变得越来越大的时候,vuex会变得越来越难以维护)
//单一状态树
state:{userInfo:{name:'yuanyu'age:24},theme:'dark',desc:'嘀嘀嘀'
}
步骤:
-
在store文件夹下新建modules文件夹,在文件夹中新建各模块的JS文件,如user.js、setting.js
-
每个模块有自己对应的state、mutations、actions、getters
const state = {} const mutations = {} const actions = {} const getters = {} -
将这四个配置项导出
export default {state,mutations,actions,getters } -
将创建的模块文件导入store文件夹下的
index.js中import user from './modules/user'const store = new Vuex.Store({strict: true, // 严格模式,任何直接修改仓库值的代码都会报错// 通过state提供数据state: {title: '嘀嘀嘀',count: 100},// 通过mutations提供修改state的方法mutations: {handleAdd (state, n) {state.count += n},handleSub (state, n) {state.count -= n},changeCount (state, n) {state.count = n}},// actions 处理异步,不能直接操作state,还是需要通过commit来操作actions: {// context 上下文 (由于此处未分模块,可以当成仓库store使用)// context.commit('mutations',参数)changeCountAction (context, num) {// 使用setTimeout模拟异步setTimeout(() => {context.commit('changeCount', num)}, 1000)}},modules: {user} })
模块中的state
尽管已经分模块了,但是子模块的state还是会挂到根级别的state中,属性名就是模块名
-
直接通过模块名访问
$store.state.模块名.xxx如:
<div>{{ $store.state.user.userInfo.name }}</div> -
通过mapState映射
-
默认根级别的映射
mapState(['xxx']) -
子模块的映射
mapState('模块名',['xxx'])需要开启命名空间namespaced:trueexport default {namespaced: true,state,mutations,actions,getters }例:
import { mapState } from 'vuex' export default {computed: {...mapState(['count', 'title', 'user']),...mapState('user', ['userInfo']) //'模块名',['模块中的数据']}}<div>{{ user.userInfo.name }}</div> <div>{{ userInfo.name }}</div>
-
模块中的getters
-
直接通过模块名访问
$store.getters['模块名/xxx'] -
通过mapGetters映射
-
默认根级别映射
mapGetters(['xxx'])如:
<div>{{ $store.getters['user/UpperCaseName'] }}</div> -
子模块的映射
mapGetters('模块名',['xxx'])需要开启命名空间<div>{{ UpperCaseName }}</div>import { mapState, mapGetters } from 'vuex' export default {computed: {...mapState(['count', 'title', 'user']),...mapState('user', ['userInfo']),...mapGetters('user', ['UpperCaseName'])}}
-
模块中的mutations
默认模块中的mutation和actions会被挂载到全局,需要开启命名空间才会被挂载到子模块
调用子模块中的mutations:
-
直接通过store调用:
$store.commit('模块名/xxx',额外参数)例:
<button @click="updateUser">更新个人信息</button>methods: {updateUser () {this.$store.commit('user/setUser', {name: '111',age: 22})}}const mutations = {setUser (state, newUserInfo) {state.userInfo = newUserInfo} }
-
通过mapMutations映射
-
默认根级别的映射
mapMutations(['xxx']) -
子模块的映射
mapMutations('模块名',['xxx'])需要开启命名空间<button @click="setUser({name:'2222',age:12})">更新个人信息</button>methods: {...mapMutations('user', ['setUser'])}
-
模块中的actions调用
-
直接通过store调用
$store.dispatch('模块名/xxx',额外参数) -
通过mapActions映射
-
默认根级别的映射
mapAction(['xxx'])例:
<button @click="update2">一秒后更新信息</button>update2 () {this.$store.dispatch('user/setUserSecond', {name: '111',age: 22})}const actions = {setUserSecond (context, newInfo) {setTimeout(() => {context.commit('setUser', newInfo)}, 1000)} }
-
子模块的映射
mapActions('模块名',['xxx'])需要开启命名空间<button @click="setUserSecond({name: '111',age: 22})">一秒后更新信息</button>methods:{...mapActions('user', ['setUserSecond']) }const actions = {setUserSecond (context, newInfo) {setTimeout(() => {context.commit('setUser', newInfo)}, 1000)} }
-
综合案例-购物车
功能模块分析:
-
请求动态渲染购物车,数据存vuex
-
数字框控件修改数据
-
动态计算总价和总数量
步骤:
-
使用VueCLI新建项目(勾选less、ESLint、Vuex、Babel)
-
创建子组件并在根组件中引入,搭建框架
-
构建购物车store模块
export default {namespaced: true,state () {return {// 购物车数据list: []}},mutations: {},getters: {},actions: {} }import Vue from 'vue' import Vuex from 'vuex' import cart from './modules/cart'Vue.use(Vuex)export default new Vuex.Store({modules: {cart} }) -
请求获取数据:
当后端接口还为准备就绪时,可利用
json-server快速生成增删改查的接口