3D 凸包算法
- 一、概述
- 二、静态凸包构造
- 1. Traits 特征类
- 2. 极端点
- 3. 半空间相交
- 4. 凸性检验
- 三、动态凸包构造
- 四、性能
一、概述
一个点集 S∈R3 是凸的,如果对于任意两点 p 和 q 在集合中,具有端点的线段 p 和 q 包含在 S。集合的凸包 P 包含点集 S 的最小凸多边体。如果这个集合 S 的某些点是这个构成 P 凸多边体的顶点,则称其为(关于的)P的极值点。如果一个点集只包含极值点,就被称为强凸的。
本章描述了CGAL中用于生成三维凸包的函数,以及用于检查点集是否为强凸的函数。在CGAL中,可以通过两种方式计算三维空间中点集的凸包:使用静态算法或使用三角剖分来获得完全动态的计算。
二、静态凸包构造
函数convex_hull_3()提供了quickhull算法[1]的一个实现。这个函数有两个版本,一个在已知输出是多面体(即超过三个点且不共线)时可用,另一个处理所有退化情况并返回一个对象,可能是一个点、一个线段、一个三角形或一个多面体。这两个版本都接受一个输入迭代器范围,该迭代器定义要计算凸包的点集,以及一个traits类,定义用于计算凸包的几何类型和谓词。
1. Traits 特征类
函数 convex_hull_3() 由一个traits类参数化,它指定了计算中使用的类型和几何基元。由于该函数从三个输入点构建3D平面,我们不能简单地将具有不精确结构的内核作为traits类的可选参数传递。
如果使用了来自具有精确谓词和非精确构造的内核的输入点,并且期望得到经过验证的结果,则应该使用类Convex_hull_traits_3 (R是输入内核)。如果内核的结构是精确的,那么该内核可以直接用作traits类。
注意,默认的traits类会考虑到这一点,即上述考虑只对自定义traits类重要。
下面的程序从输入文件中读取点,并计算它们的凸包。我们假设这些点并不都相同,也不都共线,因此我们直接使用多面体作为输出。在这个例子中,你可以看到凸包函数可以写在任何MutableFaceGraph概念的模型中。
例子1.
#include <CGAL/Exact_predicates_inexact_constructions_kernel.h>
#include <CGAL/Polyhedron_3.h>
#include <CGAL/Surface_mesh.h>
#include <CGAL/convex_hull_3.h>
#include <vector>
#include <fstream>
typedef CGAL::Exact_predicates_inexact_constructions_kernel K;
typedef CGAL::Polyhedron_3<K> Polyhedron_3;
typedef K::Point_3 Point_3;
typedef CGAL::Surface_mesh<Point_3> Surface_mesh;
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{std::ifstream in( (argc>1)? argv[1] : CGAL::data_file_path("points_3/cube.xyz"));std::vector<Point_3> points;Point_3 p;while(in >> p){points.push_back(p);}// define polyhedron to hold convex hullPolyhedron_3 poly;// compute convex hull of non-collinear pointsCGAL::convex_hull_3(points.begin(), points.end(), poly);std::cout << "The convex hull contains " << poly.size_of_vertices() << " vertices" << std::endl;Surface_mesh sm;CGAL::convex_hull_3(points.begin(), points.end(), sm);std::cout << "The convex hull contains " << num_vertices(sm) << " vertices" << std::endl;return 0;
}
例子2 :低维结果示例
下面的程序从输入文件中读取点,并计算它们的凸包。根据结果的尺寸,我们将得到一个点、一个线段、一个三角形或一个多面体曲面。注意,后者也可以是带边框的平面多边形。
#include <CGAL/Exact_predicates_inexact_constructions_kernel.h>
#include <CGAL/Polyhedron_3.h>
#include <CGAL/convex_hull_3.h>
#include <vector>
#include <fstream>
typedef CGAL::Exact_predicates_inexact_constructions_kernel K;
typedef CGAL::Polyhedron_3<K> Polyhedron_3;
typedef K::Point_3 Point_3;
typedef K::Segment_3 Segment_3;
typedef K::Triangle_3 Triangle_3;
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{std::ifstream in( (argc>1)? argv[1] : CGAL::data_file_path("points_3/cube.xyz"));std::vector<Point_3> points;Point_3 p;while(in >> p){points.push_back(p);}CGAL::Object obj;// compute convex hull of non-collinear pointsCGAL::convex_hull_3(points.begin(), points.end(), obj);if(const Point_3* p = CGAL::object_cast<Point_3>(&obj)){std::cout << "Point " << *p << std::endl;}else if(const Segment_3* s = CGAL::object_cast<Segment_3>(&obj)){std::cout << "Segment " << *s << std::endl;}else if(const Triangle_3* t = CGAL::object_cast<Triangle_3>(&obj)){std::cout << "Triangle " << *t << std::endl;}else if(const Polyhedron_3* poly = CGAL::object_cast<Polyhedron_3>(&obj)){std::cout << "Polyhedron\n " << *poly << std::endl;std::cout << "The convex hull contains " << poly->size_of_vertices() << " vertices" << std::endl;}else {std::cout << "something else"<< std::endl;}return 0;
}
2. 极端点
除了 convex_hull_3() 函数外,还提供了函数 extreme_points_3(),用于只需要凸包上的点(不需要连通性信息)的情况。此外,还提供了traits类适配器CGAL::Extreme_points_traits_adapter_3,以获取索引或更一般地说,与凸包上的3D点相关联的任何给定实体。
下面的程序从一个OFF文件中读取一组点,并输出这些点在凸包上的索引。
#include <CGAL/Exact_predicates_inexact_constructions_kernel.h>
#include <CGAL/convex_hull_3.h>
#include <CGAL/Extreme_points_traits_adapter_3.h>
#include <CGAL/IO/read_points.h>
#include <boost/iterator/counting_iterator.hpp>
#include <vector>
#include <fstream>
typedef CGAL::Exact_predicates_inexact_constructions_kernel K;
typedef K::Point_3 Point_3;
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{const std::string filename = (argc>1) ? argv[1] : CGAL::data_file_path("meshes/star.off");std::vector<Point_3> points;if(!CGAL::IO::read_points(filename, std::back_inserter(points))){std::cerr<< "Cannot open input file." <<std::endl;return 1;}//This will contain the extreme verticesstd::vector<std::size_t> extreme_point_indices;//call the function with the traits adapter for verticesCGAL::extreme_points_3(CGAL::make_range(boost::counting_iterator<std::size_t>(0),boost::counting_iterator<std::size_t>(points.size())),std::back_inserter(extreme_point_indices),CGAL::make_extreme_points_traits_adapter(CGAL::make_property_map(points)));//print the number of extreme verticesstd::cout << "Indices of points on the convex hull are:\n";std::copy(extreme_point_indices.begin(), extreme_point_indices.end(), std::ostream_iterator<std::size_t>(std::cout, " "));std::cout << "\n";return 0;
}
下面的程序从一个OFF文件中读取并构建一个网格,然后收集网格凸包上的顶点。
#include <CGAL/Exact_predicates_inexact_constructions_kernel.h>
#include <CGAL/Surface_mesh.h>
#include <CGAL/Extreme_points_traits_adapter_3.h>
#include <CGAL/convex_hull_3.h>
#include <vector>
#include <fstream>
typedef CGAL::Exact_predicates_inexact_constructions_kernel K;
typedef K::Point_3 Point_3;
typedef CGAL::Surface_mesh<Point_3> Mesh;
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{const std::string filename = (argc>1) ? argv[1] : CGAL::data_file_path("meshes/star.off");Mesh sm;if(!CGAL::IO::read_polygon_mesh(filename, sm)){std::cerr<< "Cannot open input file." <<std::endl;return 1;}//This will contain the extreme verticesstd::vector<Mesh::Vertex_index> extreme_vertices;//call the function with the traits adapter for verticesCGAL::extreme_points_3(vertices(sm), std::back_inserter(extreme_vertices),CGAL::make_extreme_points_traits_adapter(sm.points()));//print the number of extreme verticesstd::cout << "There are " << extreme_vertices.size() << " extreme vertices in this mesh." << std::endl;return 0;
}
3. 半空间相交
函数halfspace_intersection_3()和halfspace_intersection_with_constructions_3()使用凸包算法和对偶性来计算半空间列表的交集。第一个版本没有显式地计算对偶点:traits类会处理这个问题。第二种方法构造了这些点,因此鲁棒性较差,但计算速度较快。
为了计算交点,需要一个内点。它可以由用户给出,也可以用线性规划计算出来。请注意,由于线性规划的分辨率,第二种方法比较慢。
下面的例子计算切平面定义的半空间与球面的交点。
#include <CGAL/Exact_predicates_inexact_constructions_kernel.h>
#include <CGAL/Convex_hull_3/dual/halfspace_intersection_3.h>
#include <CGAL/point_generators_3.h>
#include <CGAL/Surface_mesh.h>
#include <list>
typedef CGAL::Exact_predicates_inexact_constructions_kernel K;
typedef K::Plane_3 Plane;
typedef K::Point_3 Point;
typedef CGAL::Surface_mesh<Point> Surface_mesh;
// compute the tangent plane of a point
template <typename K>
typename K::Plane_3 tangent_plane (typename K::Point_3 const& p) {typename K::Vector_3 v(p.x(), p.y(), p.z());v = v / sqrt(v.squared_length());typename K::Plane_3 plane(v.x(), v.y(), v.z(), -(p - CGAL::ORIGIN) * v);return plane;
}
int main (void) {// number of generated planesint N = 200;// generates random planes on a spherestd::list<Plane> planes;CGAL::Random_points_on_sphere_3<Point> g;for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {planes.push_back(tangent_plane<K>(*g++));}// define polyhedron to hold the intersectionSurface_mesh chull;// compute the intersection// if no point inside the intersection is provided, one// will be automatically found using linear programmingCGAL::halfspace_intersection_3(planes.begin(),planes.end(),chull );std::cout << "The convex hull contains " << num_vertices(chull) << " vertices" << std::endl;return 0;
}
4. 凸性检验
函数 is_strongly_convex_3() 实现了 Mehlhorn等人[2]的算法,用于判断给定多胞体的顶点是否构成强凸点集。该函数用于对 convex_hull_3() 进行后置条件测试。
三、动态凸包构造
Delaunay_triangulation_3 类可实现凸包的全动态维护。这个类支持插入和删除点(即三角剖分的顶点),凸包边只是无限面的有限边。下面的例子演示了凸包的动态构造。首先从一定半径的球面上随机生成点并插入到三角剖分中;然后通过统计与无限顶点相关的三角剖分顶点数得到凸包的点数;去掉一些点,然后确定船体上剩余的点的数量。请注意,与三角剖分的无限顶点相关的顶点都在凸包上,但可能不是所有的顶点都是凸包的顶点。
下面的例子展示了如何用三角剖分计算凸包。与无限大顶点相关的顶点在凸包上。
函数convex_hull_3_to_face_graph()可用于获得一个多面体曲面,它是MutableFaceGraph概念的模型,例如Polyhedron_3和Surface_mesh。
#include <CGAL/Exact_predicates_inexact_constructions_kernel.h>
#include <CGAL/point_generators_3.h>
#include <CGAL/Delaunay_triangulation_3.h>
#include <CGAL/Surface_mesh.h>
#include <CGAL/algorithm.h>
#include <CGAL/convex_hull_3_to_face_graph.h>
#include <list>
typedef CGAL::Exact_predicates_inexact_constructions_kernel K;
typedef K::Point_3 Point_3;
typedef CGAL::Delaunay_triangulation_3<K> Delaunay;
typedef Delaunay::Vertex_handle Vertex_handle;
typedef CGAL::Surface_mesh<Point_3> Surface_mesh;
int main()
{CGAL::Random_points_in_sphere_3<Point_3> gen(100.0);std::list<Point_3> points;// generate 250 points randomly in a sphere of radius 100.0// and insert them into the triangulationstd::copy_n(gen, 250, std::back_inserter(points));Delaunay T;T.insert(points.begin(), points.end());std::list<Vertex_handle> vertices;T.incident_vertices(T.infinite_vertex(), std::back_inserter(vertices));std::cout << "This convex hull of the 250 points has "<< vertices.size() << " points on it." << std::endl;// remove 25 of the input pointsstd::list<Vertex_handle>::iterator v_set_it = vertices.begin();for (int i = 0; i < 25; i++){T.remove(*v_set_it);v_set_it++;}//copy the convex hull of points into a polyhedron and use it//to get the number of points on the convex hullSurface_mesh chull;CGAL::convex_hull_3_to_face_graph(T, chull);std::cout << "After removal of 25 points, there are "<< num_vertices(chull) << " points on the convex hull." << std::endl;return 0;
}
四、性能
下面,我们比较两种方法计算3D凸包的运行时间。对于静态版本(使用convex_hull_3())和动态版本(使用Delaunay_triangulation_3和convex_hull_3_to_face_graph()),使用的内核是Exact_predicates_inexact_constructions_kernel。
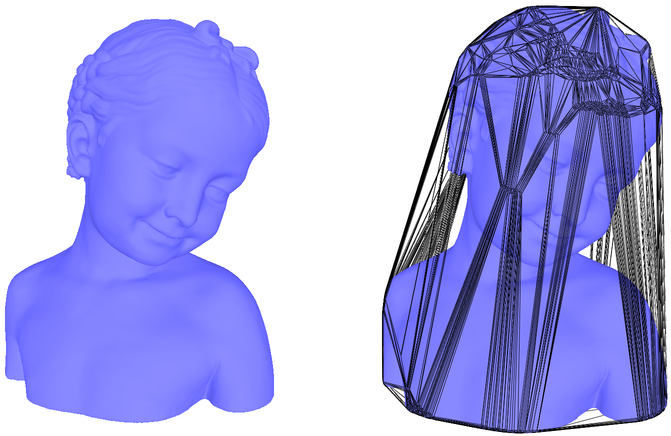
对于计算单位球中一百万个随机点的凸包,静态方法需要1.63s,而动态方法需要9.50s。要计算图13.1中192135个点的模型的凸包,静态方法需要0.18s,而动态方法需要1.90s。
在Linux (Debian发行版)下,使用GNU c++编译器4.3.5版本的CGAL 3.9执行测量,编译选项为-O3 -DCGAL_NDEBUG。使用的计算机配备了64位英特尔Xeon 2.27GHz处理器和12GB RAM。