list使用
list常用函数及使用(1)
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <algorithm>int main() {// 创建liststd::list<int> myList = {5, 2, 9, 1, 5, 6};// 打印liststd::cout << "Original list: ";for(auto i = myList.begin(); i != myList.end(); ++i) {std::cout << *i << ' ';}std::cout << '\n';// 检查list是否为空,然后获取大小if (!myList.empty()) {std::cout << "List is not empty and has size: " << myList.size() << '\n';}// 访问第一个和最后一个元素std::cout << "First element: " << myList.front() << '\n';std::cout << "Last element: " << myList.back() << '\n';// 向list前后插入元素myList.push_front(0);myList.push_back(10);// 删除第一个和最后一个元素myList.pop_front();myList.pop_back();// 在list中插入元素auto it = std::find(myList.begin(), myList.end(), 5);if (it != myList.end()) {myList.insert(it, 4); // 在第一个5之前插入4}// 删除一个特定的元素myList.remove(2); // 删除所有的2// 对list进行排序myList.sort();// 删除所有连续重复的元素myList.unique();// 打印修改后的liststd::cout << "Modified list: ";for(const auto& elem : myList) {std::cout << elem << ' ';}std::cout << '\n';return 0;
}
list常用函数及使用(2)
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <algorithm>int main() {// 初始化两个liststd::list<int> list1 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};std::list<int> list2 = {6, 7, 8, 9, 10};// 使用splice将list2的元素转移到list1的末尾list1.splice(list1.end(), list2);// 使用remove删除所有的'3'list1.remove(3);// 使用remove_if删除所有偶数list1.remove_if([](const int& value) { return value % 2 == 0; });// 创建第三个list用于merge操作std::list<int> list3 = {11, 12, 13};list1.sort(); // 确保merge前list1是排序的list3.sort(); // 确保merge前list3是排序的list1.merge(list3);// 使用reverse反转list1list1.reverse();// 使用swap交换list1和list2的元素list1.swap(list2);// 使用resize调整list1的大小list1.resize(3);// 使用clear清空list2list2.clear();// 使用rbegin和rend进行反向迭代std::cout << "List1 in reverse: ";for (auto rit = list1.rbegin(); rit != list1.rend(); ++rit) {std::cout << *rit << " ";}std::cout << "\n";// 使用cbegin和cend进行const迭代std::cout << "List1: ";for (auto cit = list1.cbegin(); cit != list1.cend(); ++cit) {std::cout << *cit << " ";}std::cout << "\n";return 0;
}
splice: 将一个list中的元素转移到另一个list中,不进行元素的复制或移动,而是改变节点的链接。remove: 删除list中所有与给定值匹配的元素。remove_if: 根据给定的条件删除元素。merge: 合并两个已排序的list,并清空被合并的list。sort: 对list中的元素进行排序。reverse: 反转list中元素的顺序。swap: 交换两个list的内容。resize: 调整list的大小,可以增加或减少元素数量。clear: 清空list中的所有元素。rbegin,rend: 提供反向迭代器,用于从list的末尾向开始进行遍历。cbegin,cend: 提供常量正向迭代器,用于从list的开始到末尾的遍历,不允许修改元素。crbegin,crend: 提供常量反向迭代器,用于从list的末尾到开始的遍历,不允许修改元素。
list的数据结构
STL中list是使用环状双向链表实现的。它的结点结构定义如下:
template <class T>
struct __list_node {typedef void* void_pointer;void_pointer next;void_pointer prev;T data;
};可以看出list节点是一个双向链表,next指向下一个节点,prev指向前一个节点。

链表最后使用一个指针指向环形链表的空白节点,空白节点指向头节点,这样就形成了一个环了。
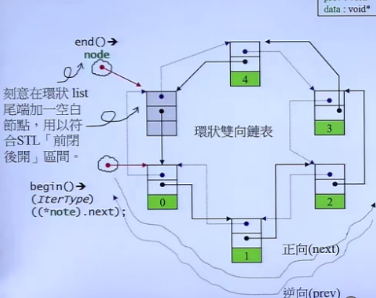
template<class T,class Alloc = alloc> //缺省使用alloc为配置器class list{ protected : typedef __list_node<T> list_node ; public : typedef list_node* link_type ; protected : link_type node ; //只要一个指针,便可以表示整个环状双向链表 ...};node是指向list节点的一个指针,可以使用这个指针表示整个环状双向链表。
如果指针node指向置于尾端的一个空白节点,node就能符合stl对于前闭后开区间的要求,这样以下函数便能轻易完成。
iterator begin() { return (link_type)((*node).next); }
iterator end() { return node; }bool empty() const { return node->next == node; }size_type size() const
{size_type result = 0;distance(begin(), end(), result);//SGI里面的distance函数作用就是遍历链表return result;
}reference front() { return *begin(); }
reference back() { return *(--end()); }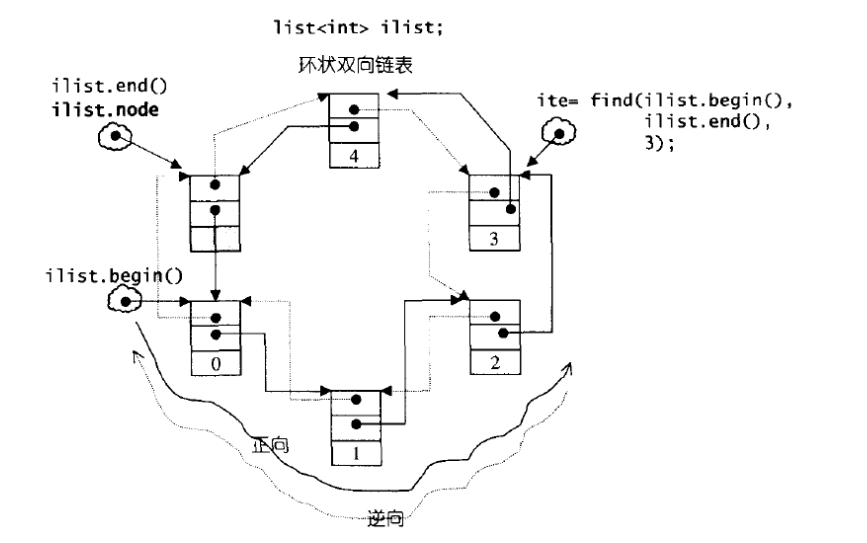
list的迭代器
list是一个双向链表实现的容器,元素在内存中不需要连续存放。vector需要其元素在内存中连续存放,vector可以使用普通指针作为迭代器。
因此,list不能使用普通指针作为迭代器,因为它需要特殊的迭代器。
list提供的迭代器是双向迭代器(Bidirectional Iterators),允许前移和后移操作。
vector插入操作可能会导致容器重新分配内存,这会使所有现有迭代器、引用和指针失效。
list删除操作,只有指向被删除元素的迭代器会失效,其他迭代器仍然有效。插入不会使任何的迭代器失效。
template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr>struct _list_iterator{typedef _list_iterator<T,T&,T*> iterator;typedef _list_iterator<T,T&,T*> iterator;typedef bidirectional_iterator_tag iterator_category;typedef T value_type;typedef Ptr pointer;typedef Ref reference;typedef _list_node<T>* link_type;typedef size_t size_type;typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;link_type node;_list_iterator(link_type x):node(x){}_list_iterator(){}_list_iterator(const iterator& x):node(x.node){}bool operator==(const self& x) const {return node==x.node;}bool operator!=(const self& x) const {return node!=x.node;}reference operator*() const {return (*node).data;}reference operator->() const {return &(operator*());} self& operator++(){node=(link_type)((*node).next);return *this;}self operator++(int){self tmp=*this;++*this;return tmp;}self& operator--(){node=(link_type)((*node).prev);return *this;}self operator--(int){self tmp=*this;--*this;return tmp;}}list节点的构造和释放
template <class T, class Alloc = alloc>
class list {
public://...// 默认构造函数list() { empty_initialize(); }
protected:// 为结点分配内存link_type get_node() { return list_node_allocator::allocate(); }// 回收内存void put_node(link_type p) { list_node_allocator::deallocate(p); }// 构造nodelink_type create_node(const T& x) {link_type p = get_node();construct(&p->data, x);return p;}// 销毁nodevoid destroy_node(link_type p) {destroy(&p->data);put_node(p);}// 初始化void empty_initialize() {node = get_node();node->next = node;node->prev = node;}
// ...
};默认构造函数调用empty_initialize()来初始化链表。这个初始化函数设置了一个哨兵节点(或称为头节点),使得链表的next和prev指针都指向自己,表示一个空的链表。
list操作
insert:类似双向链表的插入。
terator insert(iterator position, const T& x)
{link_type tmp = create_node(x); // 产生一个节点// 调整双向指针,使tmp插入tmp->next = position.node;tmp->prev = position.node->prev;(link_type(position.node->prev))->next = tmp;position.node->prev = tmp;return tmp;
}erase:类似双向链表的删除。
iterator erase(iterator position){ link_type next_node=link_type(position.node->next); link_type prev_node=link_type(position.node->prev_nodext); prev_node->next=next_node; next_node->prev=prev_node; destroy_node(position.node); return iterator(next_node); } push_front(),push_back(),pop_front(), pop_back()在insert和erase的基础上实现。
参考:
《C++ STL 源码剖析》
https://www.cnblogs.com/runnyu/p/5992839.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/LEEYATWAH/p/11707589.html