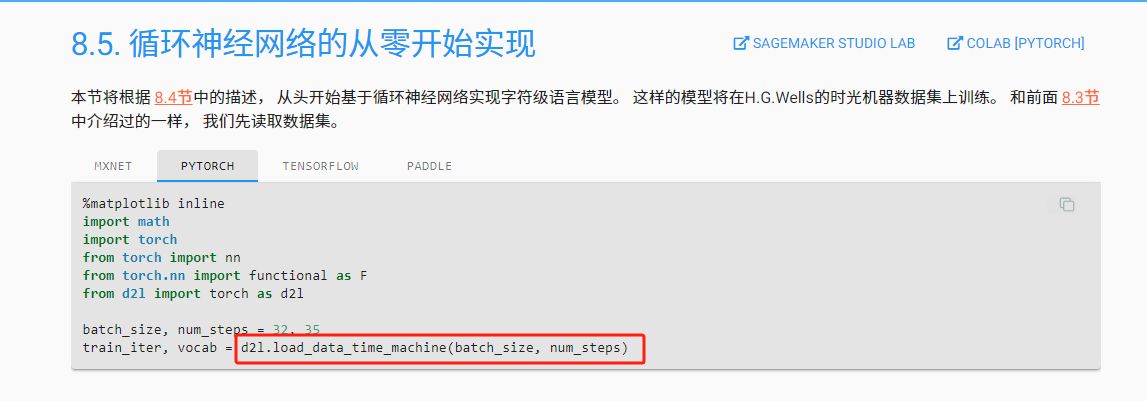
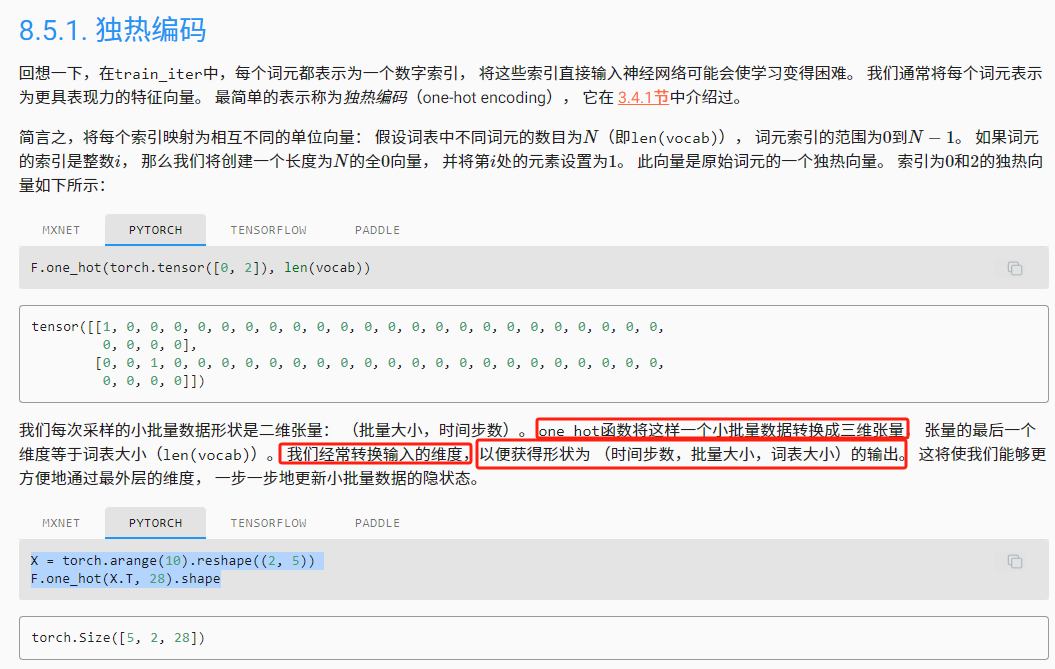
转换输入的维度, 以获得形状为(时间步数,批量大小,词表大小)的输出,这将使我们能够更方便地通过最外层的维度, 一步一步地更新小批量数据的隐状态。
>当训练语言模型时,输入和输出来自相同的词表
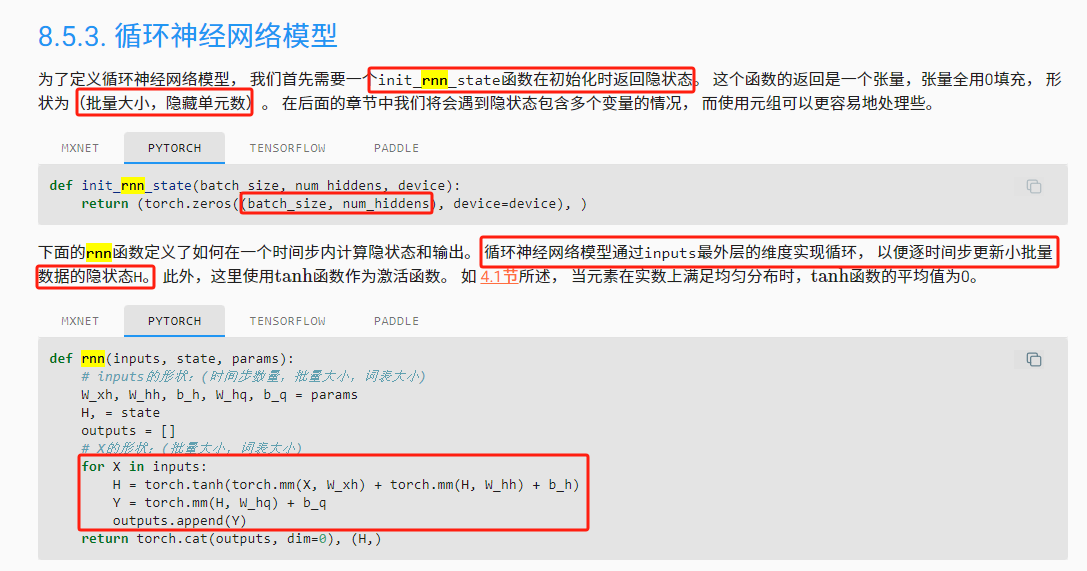
循环神经网络模型通过inputs最外层的维度实现循环, 以便逐时间步更新小批量数据的隐状态H
最外层为时间步,与上面的转置相关
输出 output 和隐状态
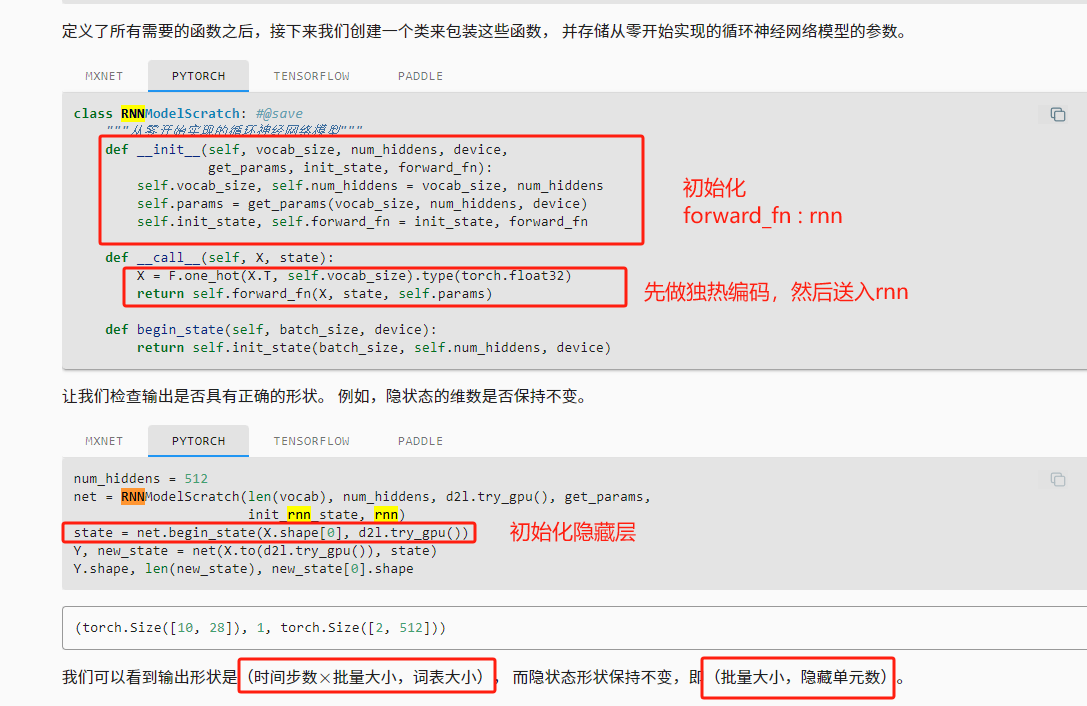
我们可以看到输出形状是(时间步数
批量大小,词表大小), 而隐状态形状保持不变,即(批量大小,隐藏单元数)。
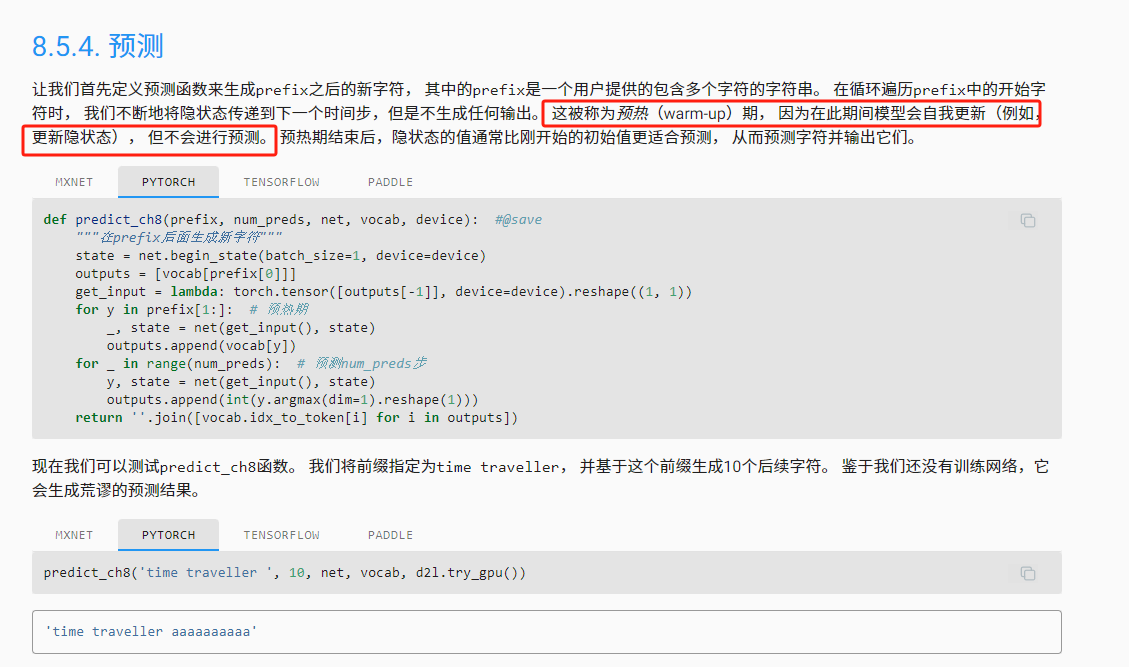
预热(warm-up)期
问题:不用把预测值加到末尾再预测下一个吗?
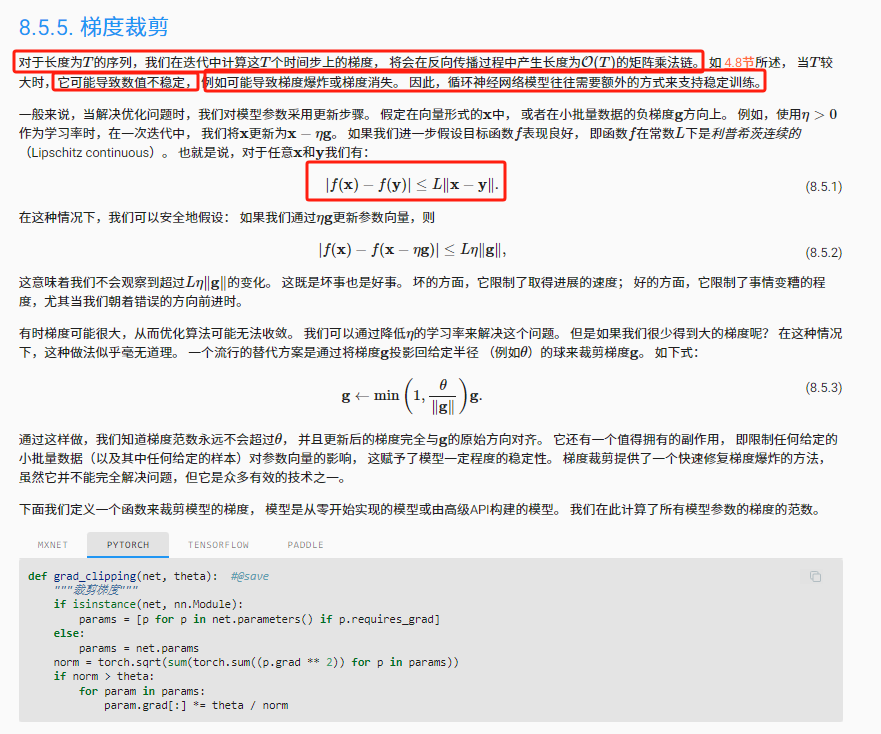
梯度裁剪
为了防止梯度爆炸或者消失,进行梯度剪裁
@save
def train_epoch_ch8(net, train_iter, loss, updater, device, use_random_iter):"""训练网络一个迭代周期(定义见第8章)"""state, timer = None, d2l.Timer()metric = d2l.Accumulator(2) # 训练损失之和,词元数量for X, Y in train_iter:if state is None or use_random_iter:# 在第一次迭代或使用随机抽样时初始化statestate = net.begin_state(batch_size=X.shape[0], device=device)else:if isinstance(net, nn.Module) and not isinstance(state, tuple):# state对于nn.GRU是个张量state.detach_()else:# state对于nn.LSTM或对于我们从零开始实现的模型是个张量for s in state:s.detach_()y = Y.T.reshape(-1)X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device)y_hat, state = net(X, state)l = loss(y_hat, y.long()).mean()if isinstance(updater, torch.optim.Optimizer):updater.zero_grad()l.backward()grad_clipping(net, 1)updater.step()else:l.backward()grad_clipping(net, 1)# 因为已经调用了mean函数updater(batch_size=1)metric.add(l * y.numel(), y.numel())return math.exp(metric[0] / metric[1]), metric[1] / timer.stop()
#@save
def train_ch8(net, train_iter, vocab, lr, num_epochs, device,use_random_iter=False):"""训练模型(定义见第8章)"""loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()animator = d2l.Animator(xlabel='epoch', ylabel='perplexity',legend=['train'], xlim=[10, num_epochs])# 初始化if isinstance(net, nn.Module):updater = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr)else:updater = lambda batch_size: d2l.sgd(net.params, lr, batch_size)predict = lambda prefix: predict_ch8(prefix, 50, net, vocab, device)# 训练和预测for epoch in range(num_epochs):ppl, speed = train_epoch_ch8(net, train_iter, loss, updater, device, use_random_iter)if (epoch + 1) % 10 == 0:print(predict('time traveller'))animator.add(epoch + 1, [ppl])print(f'困惑度 {ppl:.1f}, {speed:.1f} 词元/秒 {str(device)}')print(predict('time traveller'))print(predict('traveller'))
num_epochs, lr = 500, 1
train_ch8(net, train_iter, vocab, lr, num_epochs, d2l.try_gpu())
小结
-
我们可以训练一个基于循环神经网络的字符级语言模型,根据用户提供的文本的前缀生成后续文本。
-
一个简单的循环神经网络语言模型包括输入编码、循环神经网络模型和输出生成。
-
循环神经网络模型在训练以前需要初始化状态,不过随机抽样和顺序划分使用初始化方法不同。
-
当使用顺序划分时,我们需要分离梯度以减少计算量。
-
在进行任何预测之前,模型通过预热期进行自我更新(例如,获得比初始值更好的隐状态)。
-
梯度裁剪可以防止梯度爆炸,但不能应对梯度消失。