xhci 数据结构
xhci 数据结构主要在手册上有详细的定义,本文根据手册进行归纳总结:
中断关注的包括:
- device context
- trb ring
- trb
device context设备上下文
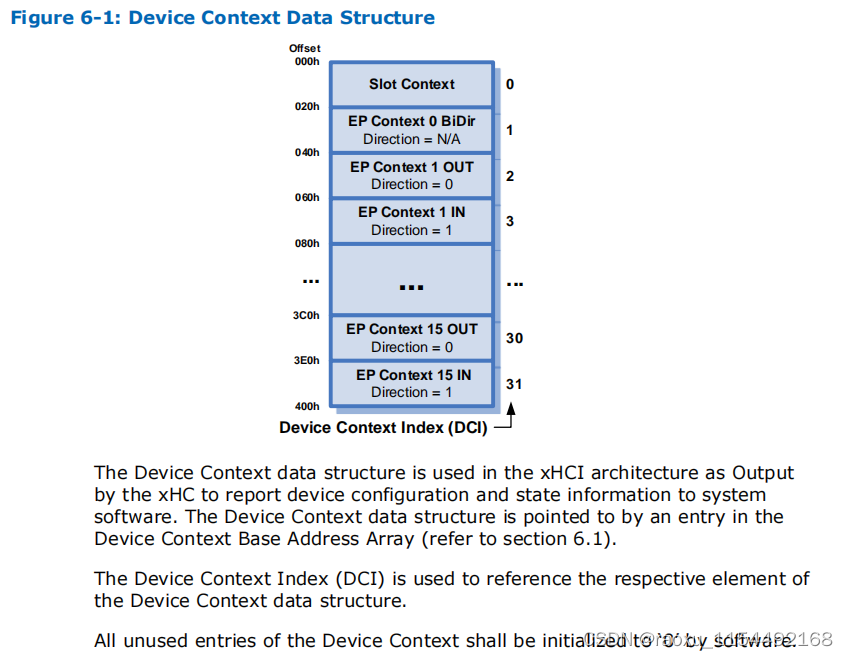
设备上下文数据结构由xHC管理,用于向系统软件报告设备配置和状态信息。设备上下文数据结构由32个数据结构的数组组成。第一个上下文数据结构(索引=“0”)是Slot Context数据结构。其余上下文数据结构是“端点上下文”数据结构
在枚举USB设备的过程中,系统软件会在主机内存中为该设备分配设备上下文数据结构,并将其初始化为“0”。然后,使用地址设备命令将数据结构的所有权传递给xHC。xHC保留对设备上下文的所有权,直到使用“禁用插槽命令”禁用了设备插槽为止。设备上下文数据结构由xHC拥有时,应被系统软件视为只读
其中主要分为slot 上下文 , 和 endpoint 上下文,在host xhci 中有定义
616 struct xhci_slot_ctx {617 __le32 dev_info;618 __le32 dev_info2;619 __le32 tt_info;620 __le32 dev_state;621 /* offset 0x10 to 0x1f reserved for HC internal use */622 __le32 reserved[4];623 }; 700 struct xhci_ep_ctx {701 __le32 ep_info;702 __le32 ep_info2;703 __le64 deq;704 __le32 tx_info;705 /* offset 0x14 - 0x1f reserved for HC internal use */706 __le32 reserved[3];707 };slot 上下文

这个比较抽象,Slot主要是有关 包含与整个设备有关的信息,或影响USB设备的所有端点的信息。Slot Context提供的信息包括: 控制,状态,寻址和电源管理。
作为设备上下文成员,xHC使用插槽上下文数据结构将设备参数的当前值报告给系统软件。
xHC报告的插槽状态标识设备的当前状态,并与USB规范中描述的USB设备状态紧密对应。
设备上下文的Slot Context数据结构也称为“Output Slot Context”。 作为输入上下文成员,系统软件使用Slot
Context数据结构将命令参数传递给主机控制器。 输入上下文的Slot Context数据结构也称为“Input Slot Context”。
如果针对设备插槽的命令成功执行,则xHC将在生成Command Completion Event 之前更新输出插槽上下文,以反映其正在主动使用的参数值来管理设备。
插槽上下文的xHCI保留区域可用作xHC实现定义的暂存器。
插槽上下文中的所有保留字段仅供xHC使用,除非插槽处于“禁用”状态,否则不得由系统软件修改。
enpoint 上下文
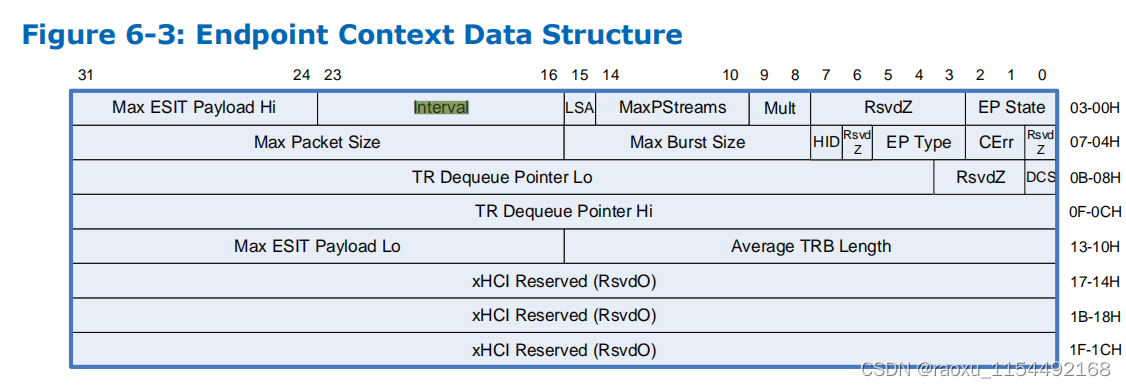
重点参数:


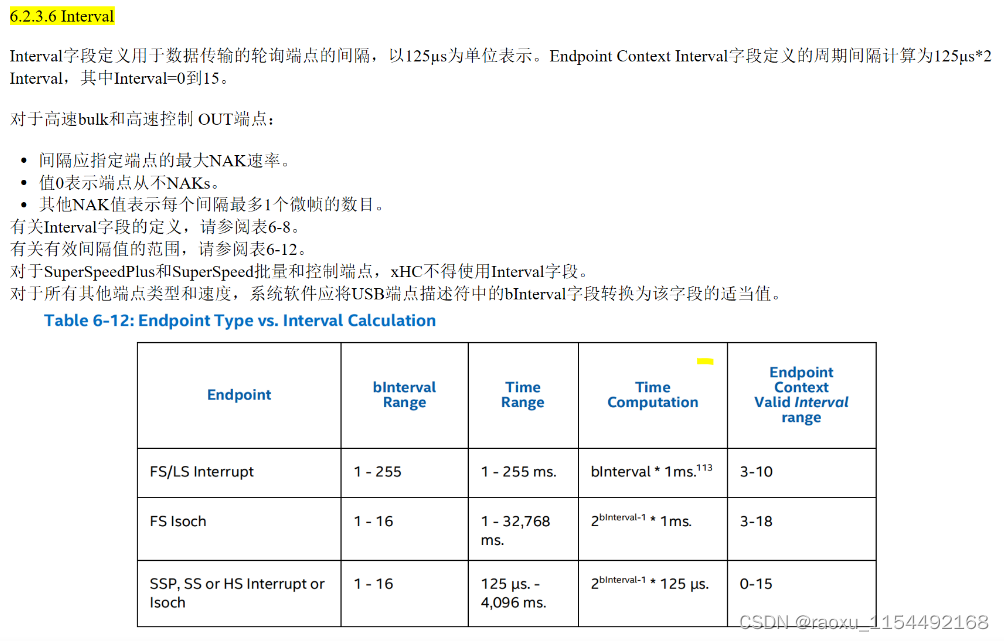

针对iso通信:

在xhci.c 中进行了初始化:
1418 /* Set up an endpoint with one ring segment. Do not allocate stream rings.
1419 * Drivers will have to call usb_alloc_streams() to do that.
1420 */
1421 int xhci_endpoint_init(struct xhci_hcd *xhci,
1422 struct xhci_virt_device *virt_dev,
1423 struct usb_device *udev,
1424 struct usb_host_endpoint *ep,
1425 gfp_t mem_flags)
1426 {
...1494 /* Set up the endpoint ring */
1495 virt_dev->eps[ep_index].new_ring =
1496 xhci_ring_alloc(xhci, 2, 1, ring_type, max_packet, mem_flags);
1497 if (!virt_dev->eps[ep_index].new_ring)
1498 return -ENOMEM;
...
1503 /* Fill the endpoint context */
1504 ep_ctx->ep_info = cpu_to_le32(EP_MAX_ESIT_PAYLOAD_HI(max_esit_payload) |
1505 EP_INTERVAL(interval) |
1506 EP_MULT(mult));
1507 ep_ctx->ep_info2 = cpu_to_le32(EP_TYPE(endpoint_type) |
1508 MAX_PACKET(max_packet) |
1509 MAX_BURST(max_burst) |
1510 ERROR_COUNT(err_count));
1511 ep_ctx->deq = cpu_to_le64(ep_ring->first_seg->dma |
1512 ep_ring->cycle_state);
1513
1514 ep_ctx->tx_info = cpu_to_le32(EP_MAX_ESIT_PAYLOAD_LO(max_esit_payload) |
1515 EP_AVG_TRB_LENGTH(avg_trb_len));...