简介
最近遇到求两个椭圆交点的的问题,一番搜索发现利用线性代数的二次型(Quadratic form)相关知识可解决,于是决定编程实践。
圆锥曲线的齐次式与二次型
椭圆是圆锥曲线(conic section)的一种,圆锥曲线又是特定条件下的二次曲线(quadratic curve)。
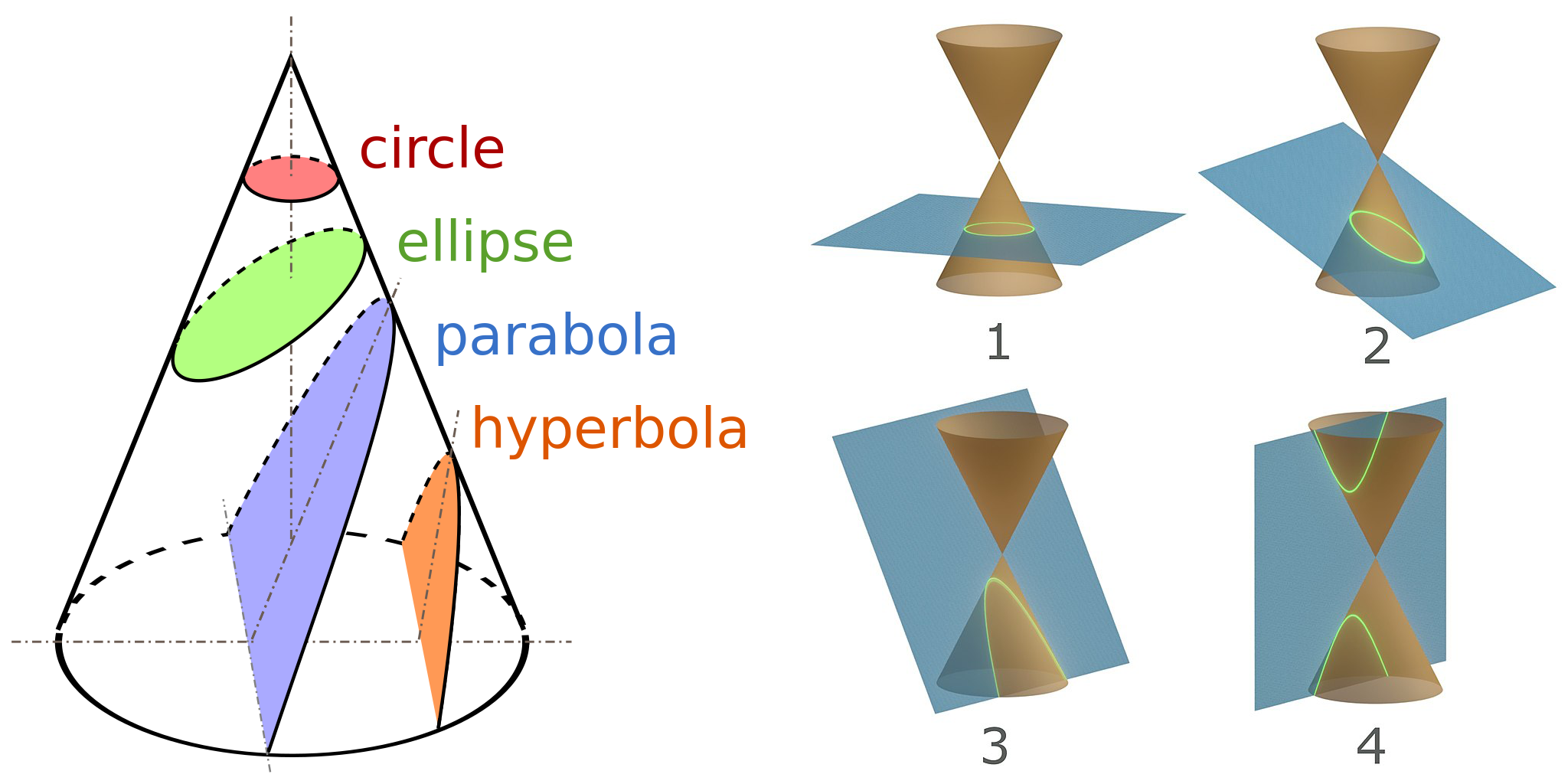
二次曲线的齐次式(homogeneous form)是。也可以按二次型定义写成
,其中
,
。
另外与其余子式
一起能够判定二次曲线什么时候是圆锥曲线以及退化情况,引用一下Wikipedia上的原文:
If
, the conic is degenerate.
If
so that Q is not degenerate, we can see what type of conic section it is by computing the minor,
:
- Q is a hyperbola if and only if
,
- Q is a parabola if and only if
, and
- Q is an ellipse if and only if
.
In the case of an ellipse, we can distinguish the special case of a circle by comparing the last two diagonal elements corresponding to the coefficients of
and
:
- If A = C and B = 0, then Q is a circle.
Moreover, in the case of a non-degenerate ellipse (with
and
), we have a real ellipse if
but an imaginary ellipse if
. An example of the latter is
, which has no real-valued solutions.
If the conic section is degenerate (
),
still allows us to distinguish its form:
- Two intersecting lines (a hyperbola degenerated to its two asymptotes) if and only if
.
- Two parallel straight lines (a degenerate parabola) if and only if
. These lines are distinct and real if
, coincident if
, and non-existent in the real plane if
.
- A single point (a degenerate ellipse) if and only if
.
The case of coincident lines occurs if and only if the rank of the 3 × 3 matrix
is 1; in all other degenerate cases its rank is 2.
求两个二次曲线交点的理论
其实Wikipedia说的退化情况正好就是用于求两个二次曲线交点的后半部分理论,Wikipedia也给出了前半部分理论:
The solutions to a system of two second degree equations in two variables may be viewed as the coordinates of the points of intersection of two generic conic sections. In particular two conics may possess none, two or four possibly coincident intersection points. An efficient method of locating these solutions exploits the homogeneous matrix representation of conic sections, i.e. a 3 × 3 symmetric matrix which depends on six parameters.
The procedure to locate the intersection points follows these steps, where the conics are represented by matrices:
- given the two conics
and
, consider the pencil of conics given by their linear combination
.
- identify the homogeneous parameters
which correspond to the degenerate conic of the pencil. This can be done by imposing the condition that
and solving for
and
. These turn out to be the solutions of a third degree equation.
- given the degenerate conic
, identify the two, possibly coincident, lines constituting it.
- intersect each identified line with either one of the two original conics; this step can be done efficiently using the dual conic representation of
.
- the points of intersection will represent the solutions to the initial equation system.
编程实践
0、计算二次型矩阵参数
对要求交点的两个二次曲线的参数进行转化,得到二次型矩阵需要的形式,即将二次曲线表示成
(1)
(1)式按为主元可整理成
(2)
有关圆锥曲线一般式和齐次式之间的参数转换计算请参见我另外的一篇博文:
1、解三次方程计算参数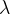
根据方程计算参数
,这其实是一个三次方程:
其中表示方阵
的协因数阵(cofactor matrix),
表示方阵Q的迹(trace)。这里细说一下Wikipedia用了
两个参数,但其实可以取
变成一个参数
(可以根据矩阵行列式的性质推一下)并且求三次方程的根时只需要找到任意一个实根赋给
即可而不需要求出所有实根。
2、将 代入,分类计算出实际直线,回代到二次曲线方程求出交点
代入,分类计算出实际直线,回代到二次曲线方程求出交点
将代入,得到一个二次型方阵
,此时
,即
(3)
根据Wikipedia的理论分类计算出两个二次曲线相交形成的交点直线系,回代到任意一个原二次曲线得到最终交点。编程实践中,考虑浮点运算的精度误差,不适合直接与0比较进行分类,而需要引入eps(实践中通常eps取1e-12到1e-10之间),实际的分类要更细致:
2.1、时,
,可知
,因此(2)式可以变换成
(4)
由(3)式可得,因此有
(5)
由于与
同号,可见
此时唯一的交点是,编程实践中最好将此点回代到两个二次曲线做检验(同样地,不能严格与0比较,而是要按
作为标准)
2.2、时,
,
可能为0,但与(5)式相似,下式成立:
(6)
因此得出两条直线为,两直线和其中一个二次曲线求交点,回代到另外一个二次曲线做检验,最后对点去重,就能得到答案。
2.3、时,按
的情况细分:
2.3.1、时,看成
,因此
或
(其实是
或
)
假设但
,结合(3)式分析一下,此时
必有,因此可以按如下方式处理:
2.3.1.1、且
,则求直线
与一个二次曲线求交点,回代到另外一个二次曲线做检验;
2.3.1.2、仅,则解二次方程
得到
,回代到一个二次曲线求出对应的
从而得出所有交点,最后回代到另外一个二次曲线做检验;
2.3.1.3、仅,则解二次方程
得到
,回代到一个二次曲线求出对应的
从而得出所有交点,最后回代到另外一个二次曲线做检验。
2.3.2、时,
且
,可见
此时(3)式变成
(7)
不妨设(否则只需要将所有系数成-1即可),可见(7)式当且仅当
且
时才成立。
另一方面,则(1)式可转化成
,即
(这里前两式其实等价)故
时才有解。
这两个结论相结合,得出以下处理方式:
2.3.2.1、或
或
,两二次曲线无实交点(可以有虚交点);
2.3.2.2、,由于经过2.3.2.1排除后
,故按
处理,因此
,所以应该求直线
与一个二次曲线求交点,回代到另外一个二次曲线做检验;
2.3.2.3、,因此
,依次求直线
及
与一个二次曲线求交点,回代到另外一个二次曲线做检验。
Python版
源码可在这里下载conic_sections![]() https://github.com/DarrenCai/math/tree/main/computational_geometry/conic_sections
https://github.com/DarrenCai/math/tree/main/computational_geometry/conic_sections
python版我针对椭圆写了测试数据生成脚本,测试了1200个case,结果都正常,美中不足的是交点坐标的数值解精度不高(通常小数点第3位开始就和解析解不一样了)

C++版
/*** 圆锥曲线相关**/#include <cmath>#define DBL long double
#define eps 1e-12lvoid ellipse_homogeneous(DBL a, DBL b, DBL t, DBL x, DBL y, DBL (&c)[6]) {// 根据椭圆的长短半轴、倾斜角度和中心坐标计算椭圆一般式的系数DBL si = sin(t), co = cos(t);c[0] = si/b*si/b + co/a*co/a; c[1] = 2.*(1./a/a - 1./b/b)*si*co; c[2] = co/b*co/b + si/a*si/a;c[3] = -(2.*c[0]*x + c[1]*y); c[4] = -(2.*c[2]*y + c[1]*x); c[5] = -(c[3]*x + c[4]*y)/2. - 1.;
}void ellipse_params(DBL (&c)[6], DBL &a, DBL &b, DBL &t, DBL &x, DBL &y) {// 根据椭圆一般式的系数计算长短半轴、倾斜角度和中心坐标if (c[0] < 0) for (int i=0; i<6; ++i) c[i] = -c[i];DBL p = 4.*c[0]*c[2] - c[1]*c[1], q = sqrt((c[0]-c[2])*(c[0]-c[2]) + c[1]*c[1]);DBL r = 2.*((c[0]*c[4]*c[4] - c[1]*c[3]*c[4] + c[2]*c[3]*c[3])/p - c[5]);a = sqrt(r / (c[0]+c[2]-q)); b = sqrt(r / (c[0]+c[2]+q)); t = atan2(q - c[0] + c[2], c[1]);x = (c[1]*c[4] - 2.*c[2]*c[3]) / p; y = (c[1]*c[3] - 2.*c[0]*c[4]) / p;
}void parabola_homogeneous(DBL x, DBL y, DBL f, DBL t, DBL (&c)[6]) {// 根据抛物线的顶点坐标、焦距和倾斜角度计算抛物线一般式的系数DBL si = sin(t), co = cos(t);c[0] = si*si; c[1] = -2*si*co; c[2] = co*co; c[3] = -2*c[0]*x-c[1]*y-4*f*co;c[4] = -2*c[2]*y-c[1]*x-4*f*si; c[5] = c[0]*x*x + c[1]*x*y + c[2]*y*y + 4*f*x*co + 4*f*y*si;
}void parabola_params(DBL (&c)[6], DBL &x, DBL &y, DBL &f, DBL &t) {// 根据抛物线一般式的系数计算顶点坐标、焦距和倾斜角度t = atan2(2.*c[0], -c[1]);DBL co = cos(t), si = sin(t), s = (c[0]+c[2])*co, t = (c[0]+c[2])*si;f = (c[1]*c[4]-2.*c[2]*c[3]) / (8.*c[2]*s-4.*c[1]*t);if (f < 0.) t = atan2(-2.*c[0], c[1]), f = -f, si = -si, co = -co, s = -s, t = -t;DBL d1 = c[3] + 4.*f*s, e1 = c[4] + 4.*f*t; s = 4.*f*s - d1/2.; t = 4.*f*t - e1/2.;x = (c[1]*c[5] + d1*t) / (c[1]*s - 2*c[0]*t); y = -(2.*c[0]*x + d1) / c[1];
}void hyperbola_homogeneous(DBL a, DBL b, DBL t, DBL x, DBL y, DBL (&c)[6]) {// 根据双曲线的实半轴、虚半轴、倾斜角度和中心坐标计算双曲线一般式的系数DBL si = sin(t), co = cos(t);c[0] = co/a*co/a - si/b*si/b; c[1] = 2.*(1./a/a + 1./b/b)*si*co; c[2] = si/a*si/a - co/b*co/b;c[3] = -(2.*c[0]*x + c[1]*y); c[4] = -(2.*c[2]*y + c[1]*x); c[5] = -(c[3]*x + c[4]*y)/2. - 1.;
}void hyperbola_params(DBL (&c)[6], DBL &a, DBL &b, DBL &t, DBL &x, DBL &y) {// 根据双曲线一般式的系数计算长短半轴、倾斜角度和中心坐标DBL p = 4.*c[0]*c[2] - c[1]*c[1], q = sqrt((c[0]-c[2])*(c[0]-c[2]) + c[1]*c[1]);DBL r = 2.*((c[0]*c[4]*c[4] - c[1]*c[3]*c[4] + c[2]*c[3]*c[3])/p - c[5]); t = atan2(c[2]-c[0]+q, c[1]);if (r > 0.) a = sqrt(r / (q+c[0]+c[2])), b = sqrt(r / (q-c[0]-c[2]));else a = sqrt(r / (c[0]+c[2]-q)), b = sqrt(-r / (q+c[0]+c[2]));x = (c[1]*c[4] - 2.*c[2]*c[3]) / p; y = (c[1]*c[3] - 2.*c[0]*c[4]) / p;
}void cofactor(const DBL (&a)[3][3], DBL (&c)[3][3]) {// 计算协因数阵(cofactor matrix)// https://byjus.com/maths/cofactor/c[0][0] = a[1][1]*a[2][2] - a[1][2]*a[2][1];c[0][1] = a[1][2]*a[2][0] - a[1][0]*a[2][2];c[0][2] = a[1][0]*a[2][1] - a[1][1]*a[2][0];c[1][0] = a[0][2]*a[2][1] - a[0][1]*a[2][2];c[1][1] = a[0][0]*a[2][2] - a[0][2]*a[2][0];c[1][2] = a[0][1]*a[2][0] - a[0][0]*a[2][1];c[2][0] = a[0][1]*a[1][2] - a[0][2]*a[1][1];c[2][1] = a[0][2]*a[1][0] - a[0][0]*a[1][2];c[2][2] = a[0][0]*a[1][1] - a[0][1]*a[1][0];
}void mul(const DBL (&a)[3][3], const DBL (&b)[3][3], DBL (&c)[3][3]) {c[0][0] = a[0][0]*b[0][0] + a[0][1]*b[1][0] + a[0][2]*b[2][0];c[0][1] = a[0][0]*b[0][1] + a[0][1]*b[1][1] + a[0][2]*b[2][1];c[0][2] = a[0][0]*b[0][2] + a[0][1]*b[1][2] + a[0][2]*b[2][2];c[1][0] = a[1][0]*b[0][0] + a[1][1]*b[1][0] + a[1][2]*b[2][0];c[1][1] = a[1][0]*b[0][1] + a[1][1]*b[1][1] + a[1][2]*b[2][1];c[1][2] = a[1][0]*b[0][2] + a[1][1]*b[1][2] + a[1][2]*b[2][2];c[2][0] = a[2][0]*b[0][0] + a[2][1]*b[1][0] + a[2][2]*b[2][0];c[2][1] = a[2][0]*b[0][1] + a[2][1]*b[1][1] + a[2][2]*b[2][1];c[2][2] = a[2][0]*b[0][2] + a[2][1]*b[1][2] + a[2][2]*b[2][2];
}DBL dot_product(const DBL (&a)[3][3], const DBL (&b)[3][3]) {return a[0][0]*b[0][0] + a[0][1]*b[0][1] + a[0][2]*b[0][2] +a[1][0]*b[1][0] + a[1][1]*b[1][1] + a[1][2]*b[1][2] + a[2][0]*b[2][0] + a[2][1]*b[2][1] + a[2][2]*b[2][2];
}DBL det(const DBL (&a)[3][3], const DBL (&c)[3][3]) {// 已知方阵A和其协因数阵C,计算det|A|return a[0][0]*c[0][0] + a[0][1]*c[0][1] + a[0][2]*c[0][2];
}DBL trace(const DBL (&a)[3][3], const DBL (&b)[3][3]) {// 计算方阵AB的迹// https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trace_(linear_algebra)return a[0][0]*b[0][0] + a[0][1]*b[1][0] + a[0][2]*b[2][0] +a[1][0]*b[0][1] + a[1][1]*b[1][1] + a[1][2]*b[2][1] + a[2][0]*b[0][2] + a[2][1]*b[1][2] + a[2][2]*b[2][2];
}DBL cubic_root(DBL x) {return x<0. ? -pow(-x, 1./3.) : pow(x, 1./3.);
}DBL find_a_root(DBL a, DBL b, DBL c, DBL d) {// 求出一元三次方程的一个实根DBL A = b*b - 3*a*c, B = b*c - 9*a*d, C = c*c - 3*b*d, delta = B*B - 4.*A*C;if (A == 0. && B == 0.) return -c/b;if (delta > 0.) {delta = sqrt(delta);DBL y1 = A*b + 1.5*a*(delta-B), y2 = A*b - 1.5*a*(delta+B);return -(cubic_root(y1) + cubic_root(y2) + b)/3./a;} else if (delta > -eps) return -B/2./A;DBL sA = sqrt(A), t = acos((A*b-1.5*a*B)/A/sA)/3.;return -(b + 2*sA*cos(t)) / 3. / a;
}int solve_quadratic_equation(DBL a, DBL b, DBL c, DBL *x) {// 解一元二次方程(a可以为0)并返回实根数量if (a == 0.) {if (b == 0.) return 0;*x = -c/b;return 1;}DBL delta = b*b - 4.*a*c;if (delta < 0.) {if (delta < -eps) return 0;delta = 0.;}a *= 2; delta = sqrt(delta);if (delta == 0. || delta < a*eps) {*x = -b/a;return 1;}*x = (-b-delta)/a; *(++x) = (delta-b)/a;return 2;
}bool check(const DBL (&q)[3][3], DBL x, DBL y) {// 根据圆锥曲线的矩阵表示,检查点(x,y)是否在圆锥曲线上return abs(q[0][0]*x*x + 2.*q[0][1]*x*y + q[1][1]*y*y + 2.*q[0][2]*x + 2.*q[1][2]*y + q[2][2]) < eps;
}int line_conic_intersection(const DBL (&q)[3][3], DBL a, DBL b, DBL c, DBL *x, DBL *y) {// 根据圆锥曲线的矩阵表示求其与直线ax+by+c=0的交点并返回交点数量(0/1/2)if (a == 0. && b == 0.) return 0;if (abs(a) > abs(b)) {DBL d = q[0][0]*b*b - 2.*q[0][1]*a*b + q[1][1]*a*a, f = q[0][0]*c*c - 2.*q[0][2]*a*c + q[2][2]*a*a;int m = solve_quadratic_equation(d, 2.*(q[1][2]*a*a + q[0][0]*b*c - q[0][1]*a*c - q[0][2]*a*b), f, y);for (int i=0; i<m; ++i) *(x+i) = (-c - b * (*(y+i)))/a;return m;}DBL d = q[0][0]*b*b - 2.*q[0][1]*a*b + q[1][1]*a*a, f = q[1][1]*c*c - 2.*q[1][2]*b*c + q[2][2]*b*b;int m = solve_quadratic_equation(d, 2.*(q[0][2]*b*b + q[1][1]*a*c - q[0][1]*b*c - q[1][2]*a*b), f, x);for (int i=0; i<m; ++i) *(x+i) = (-c - a * (*(x+i)))/b;return m;
}bool check(const DBL (&q)[3][3], DBL (&x)[4], DBL (&y)[4], int m, int &n) {for (int i=n-1; i>=0; --i) {if (!check(q, x[m+i], y[m+i])) {if (i < n-1) x[m] = x[m+1], y[m] = y[m+1];--n; continue;}for (int j=0; j<m; ++j) if (abs(x[j]-x[m+i])<eps && abs(y[j]-y[m+i])<eps) {if (i < n-1) x[m] = x[m+1], y[m] = y[m+1];--n; break;}}
}int conics_intersection(const DBL (&p)[3][3], const DBL (&q)[3][3], DBL (&x)[4], DBL (&y)[4]) {// 根据两圆锥曲线的矩阵表示,计算二者的交点并返回交点数量(0/1/2/3/4)// 即便用了long double,交点坐标的数值解其实精度仍然不高(一般小数点第3位开始就可能和解析解不一样了)// https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Matrix_representation_of_conic_sections// https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conic_section#Intersecting_two_conicsDBL c1[3][3], c2[3][3];cofactor(p, c1); cofactor(q, c2);DBL r = find_a_root(det(p, c1), trace(c1, q), trace(p, c2), det(q, c2));DBL a = r*p[0][0] + q[0][0], b = r*p[0][1] + q[0][1], c = r*p[1][1] + q[1][1],d = r*p[0][2] + q[0][2], e = r*p[1][2] + q[1][2], f = r*p[2][2] + q[2][2], a33 = a*c - b*b;if (a33 > eps) {x[0] = (b*e - c*d) / a33; y[0] = (b*d - a*e) / a33;return check(p, x[0], y[0]) && check(q, x[0], y[0]);} else if (a33 < -eps) {a33 = sqrt(-a33); c = (b*d - a*e) / a33;int m = line_conic_intersection(q, a, b-a33, d-c, x, y);check(p, x, y, 0, m);int n = line_conic_intersection(q, a, b+a33, d+c, x+m, y+m);check(p, x, y, m, n);return m+n;} else if (abs(b) < eps) {if (abs(a) > max(abs(c), eps)) {int t = solve_quadratic_equation(a, 2.*d, f, x), s = x[1];if (!t) return 0;int m = line_conic_intersection(q, -1., 0., x[0], x, y);check(p, x, y, 0, m);int n = t > 1 ? line_conic_intersection(q, -1., 0., s, x+m, y+m) : 0;check(p, x, y, m, n);return m+n;} else if (abs(c) > max(abs(a), eps)) {int t = solve_quadratic_equation(c, 2.*e, f, y), s = y[1];if (!t) return 0;int m = line_conic_intersection(q, 0., -1., y[0], x, y);check(p, x, y, 0, m);int n = t > 1 ? line_conic_intersection(q, 0., -1., s, x+m, y+m) : 0;check(p, x, y, m, n);return m+n;}int m = line_conic_intersection(q, 2.*d, 2.*e, f, x, y);check(p, x, y, 0, m);return m;}if (a < 0) a = -a, b = -b, c = -c, d = -d, e = -e, f = -f;DBL s = d*d - a*f;if (b*d*e < -eps || abs(a*e*e - c*d*d) > eps || s < -eps) return 0;if (s < eps) {int m = line_conic_intersection(q, a, b, d, x, y);check(p, x, y, 0, m);return m;}s = sqrt(s);int m = line_conic_intersection(q, a, b, d-s, x, y);check(p, x, y, 0, m);int n = line_conic_intersection(q, a, b, d+s, x+m, y+m);check(p, x, y, m, n);return m+n;
}展望
其实我之前借助常见级数展开和牛顿迭代法等运算加速技巧基于C++实现过高精度的15种运算,双目运算:add, sub, mul, div, pow, atan2,单目运算:exp, ln, sqrt, asin, acos, atan, sin, cos, tan。
UVa12413 Big Decimal Calculator-CSDN博客文章浏览阅读38次。本人学习icpc算法竞赛时自己对UVa部分题目的解题思路 add 和 sub 的计算结果在精度范围内为0时符号按照加数/减数来,但是 mul 和 div 的结果是+0,不受乘数和除数影响。exp, ln, sqrt, asin, acos, atan, sin, cos, tan。使用泰勒展开时,需要配合一些数值技巧以保证级数快速收敛。add, sub, mul, div, pow, atan2。计算atan(x)时要考虑|x|接近1时确保快速收敛的处理方式。先实现加减乘除运算,作为实现后续运算的基础。https://blog.csdn.net/hlhgzx/article/details/133325844 因此可以将求两个二次曲线交点的C++实现写出高精度版本。