1 介绍
本次实验是实现一个简易版本的MapReduce,你需要实现一个工作程序(worker process)和一个调度程序(coordinator process)。工作程序用来调用Map和Reduce函数,并处理文件的读取和写入。调度程序用来协调工作任务并处理失败的任务。你将构建出跟 MapReduce论文 里描述的类似的东西。(注意:本实验中用"coordinator"替代里论文中的"master"。)
实验先决条件:
-
阅读MapReduce论文
-
阅读lab文档
-
理解MapReduce框架
-
理解原框架代码,理清所需完成任务
实验代码实现仓库:https://github.com/unique-pure/MIT6.5840/tree/main/src/mr,实验代码已通过实验测试,并在以下清单中列出了实现的功能及待办事项。
- Complete the basic requirements for MapReduce
- Handling worker failures
- No data competition, a big lock ensures safety
- Pass lab test
- Communicate over TCP/IP and read/write files using a shared file system
2 原框架解析
-
src/mrapps/wc.go这是一个用于 MapReduce 的字数统计(Word Count)插件。该插件包含 Map 和 Reduce 函数,用于统计输入文本中的单词频率。
func Map(filename string, contents string) []mr.KeyValue {// function to detect word separators.ff := func(r rune) bool { return !unicode.IsLetter(r) }// split contents into an array of words.words := strings.FieldsFunc(contents, ff)kva := []mr.KeyValue{}for _, w := range words {kv := mr.KeyValue{w, "1"}kva = append(kva, kv)}return kva }func Reduce(key string, values []string) string {// return the number of occurrences of this word.return strconv.Itoa(len(values)) } -
src/main/mrcoordinator.gomrcoordinator.go定义了调度器(Coordinator)的主要逻辑。调度器通过MakeCoordinator启动一个Coordinator实例c,并在c.server()中通过协程go http.Serve(l, nil)启动一个 HTTP 服务器来接收和处理 RPC 调用。func (c *Coordinator) server() {rpc.Register(c)rpc.HandleHTTP()//l, e := net.Listen("tcp", ":1234")sockname := coordinatorSock()os.Remove(sockname)l, e := net.Listen("unix", sockname)if e != nil {log.Fatal("listen error:", e)}go http.Serve(l, nil) }func MakeCoordinator(files []string, nReduce int) *Coordinator {c := Coordinator{}c.server()return &c }注意:在 Go 的
net/http包中,使用http.Serve(l, nil)启动 HTTP 服务器时,服务器会为每个传入的请求自动启动一个新的协程。这意味着每个 RPC 调用都是在独立的协程中处理的,从而允许并发处理多个请求。因此,在设计时可能需要使用锁等同步原语来保护共享资源。此外,Coordinator 不会主动与 Worker 通信(除非额外实现),只能通过 Worker 的 RPC 通信来完成任务。同时,当所有任务完成时,Done方法将返回false,从而关闭 Coordinator。 -
src/main/mrworker.gomrworker.go通过Worker函数运行。因此,Worker函数需要完成请求任务、执行任务、报告任务状态等多个任务。可以推测,Worker需要在这个函数中不断地轮询 Coordinator,并根据 Coordinator 的不同回复来驱动当前 Worker 完成各种任务。 -
src/main/mrsequential.gomrsequential.go实现了一个简单的顺序 MapReduce 应用程序。该程序读取输入文件,执行 Map 和 Reduce 操作,并将结果写入输出文件。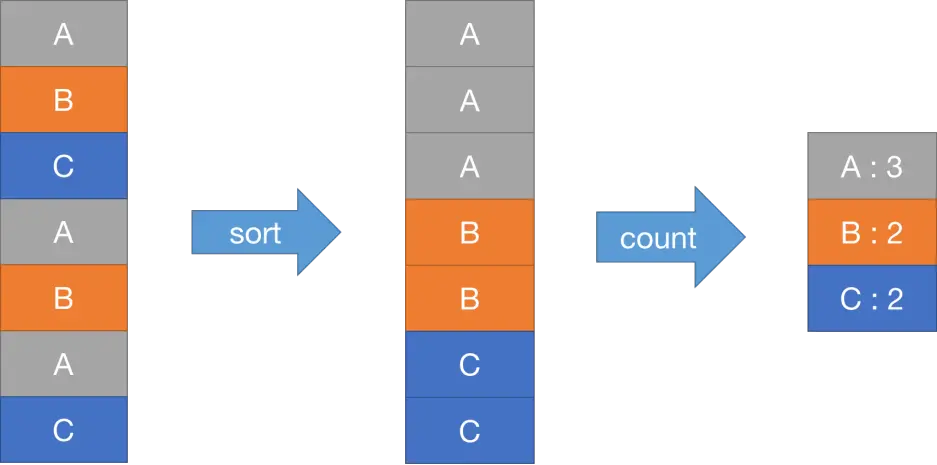
3 设计实现
3.1 任务分析
总体而言,Worker通过RPC轮询Coordinator请求任务,例如Map或者Reduce任务,Coordinator将剩余任务分配给Worker处理(先处理完Map任务才能处理Reduce任务)。
其中,在此实验中Map任务数量就是输入文件数量,每个
Map Task的任务就是处理一个.txt文件;Reduce任务的数量是nReduce。由于Map任务会将文件的内容分割为指定的
nReduce份,每一份应当由序号标明,拥有这样的序号的多个Map任务的输出汇总起来就是对应的Reduce任务的输入。
请求完任务后,Worker需要根据任务类型进行处理,这段处理过程跟mrsequential.go基本一致,但需要注意的就是论文中提到的,如果同一个任务被多个Worker执行,针对同一个最终的输出文件将有多个重命名操作执行。我们这就依赖底层文件系统提供的重命名操作的原子性来保证最终的文件系统状态仅仅包含一个任务产生的数据。即通过os.Rename()。
处理完任务后,Worker通过RPC告知Coordinator任务结果。
所以,我们可以知道Coordinator管理着任务状态和任务分配,而无需记录Worker的信息,Worker实现任务处理。
整个任务流程如下图所示:
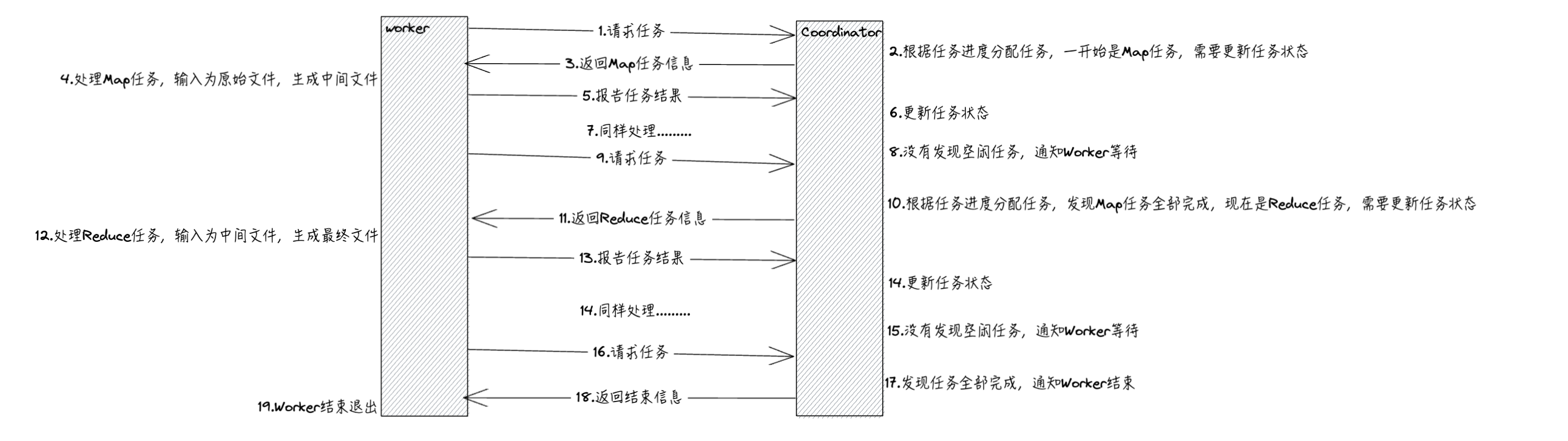
MapReduce处理WordCount程序的流程如下图所示:
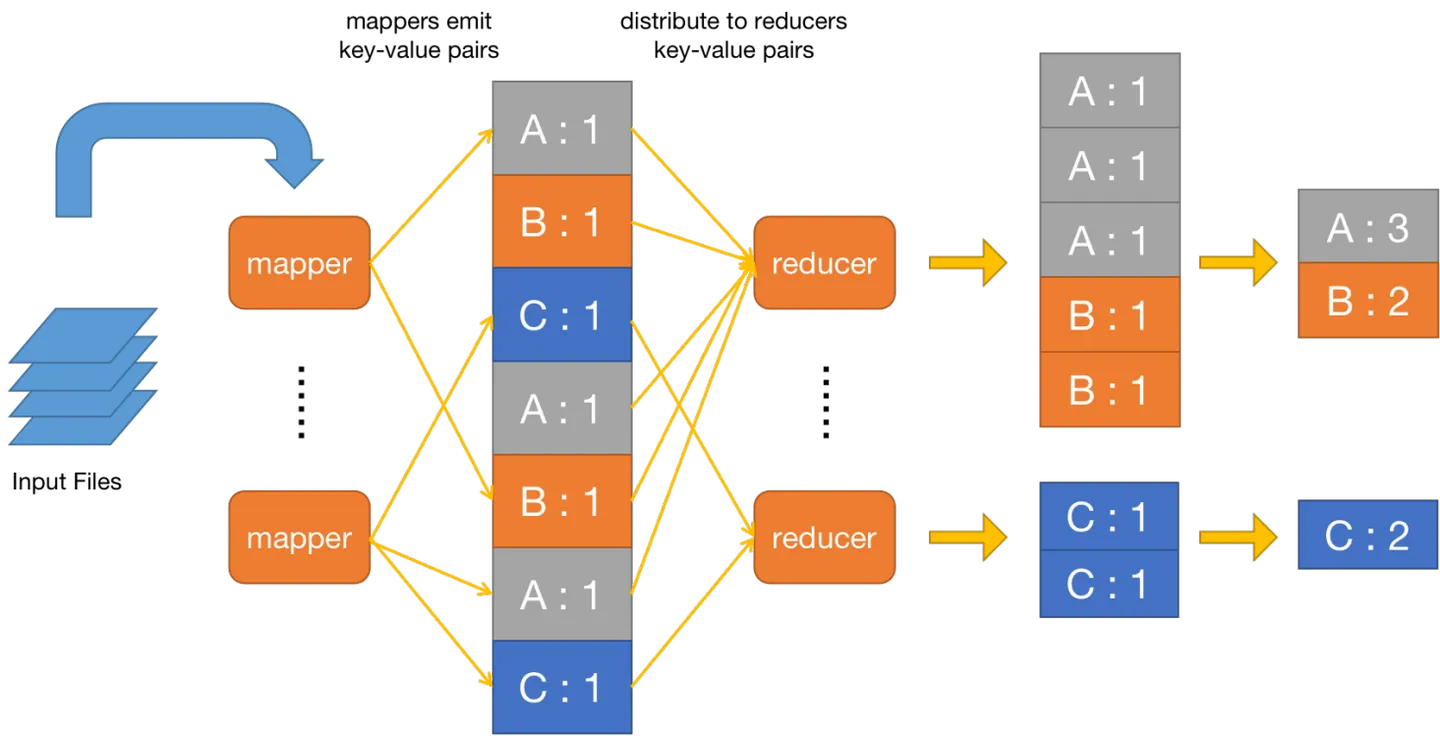
3.2 RPC
通信时首先需要确定这个消息是什么类型, 通过前述分析可知:
-
对于
Worker发送消息,Worker需要跟Coordinator报告Map或Reduce任务的执行情况(成功或失败)type TaskCompletedStatus int const (MapTaskCompleted = iotaMapTaskFailedReduceTaskCompletedReduceTaskFailed )
-
对于
Coordinator回复消息,Coordinator需要分配Reduce或Map任务,告知任务的类型,或者告知Worker休眠(暂时没有任务需要执行)、Worker退出(所有任务执行成功)type TaskType int const (MapTask = iotaReduceTaskWaitExit )
同时,消息还需要附带额外的信息,我这里的设计是发送消息包含任务ID,以便Coordinator更新任务状态,结构如下:
type MessageSend struct {TaskID int // task idTaskCompletedStatus TaskCompletedStatus // task completed status
}
回复消息结构如下:
type MessageReply struct {TaskID int // task idTaskType TaskType // task type, map or reduce or wait or exitTaskFile string // task file nameNReduce int // reduce number, indicate the number of reduce tasksNMap int // map number, indicate the number of map tasks
}
这些字段都是为了辅助Worker进行任务处理,如NMap是为了提供Map任务的数量,以便生成中间文件名,TaskFile是保存Map任务需要处理的输入文件。
对于通信,原框架已提供Unix套接字通信,如果有想法,我们可以将 RPC 设置为通过 TCP/IP 而不是 Unix 套接字进行通信(请参阅 Coordinator.server() 中注释掉的行),并使用共享文件系统读/写文件。
3.2 Coordinator
3.2.1 结构
如前所述,Coordinator需要管理任务的状态信息,对于一个任务而言,我们这里定义它的状态为:未分配、已分配、完成、失败。
type TaskStatus int
const (Unassigned = iotaAssignedCompletedFailed
)
那么,任务结构应该包括任务状态,同时,如论文中提到的,可能有Worker成为落伍者,所以我们还需要考虑一个任务是否执行了很长时间还没结束,故这里需要记录任务分配时的时间戳,以便计算运行时间。另外,我们还需要一个字段来存储需要处理的任务文件名。故任务信息结构如下:
type TaskInfo struct {TaskStatus TaskStatus // task statusTaskFile string // task fileTimeStamp time.Time // time stamp, indicating the running time of the task
}
对于Coordinator结构,首先肯定是需要两个数据结构来存储所有的Map任务状态和Reduce任务状态,我这里使用的列表;然后由于是并发执行,更新共享任务状态数据,需要一把大锁保平安;最后需要一些额外变量存储任务数量(也可以直接len(list))以及标志某阶段任务是否完成(如在Reduce任务进行之前Map任务是否已经完成)。
type Coordinator struct {NMap int // number of map tasksNReduce int // number of reduce tasksMapTasks []TaskInfo // map taskReduceTasks []TaskInfo // reduce taskAllMapTaskCompleted bool // whether all map tasks have been completedAllReduceTaskCompleted bool // whether all reduce tasks have been completedMutex sync.Mutex // mutex, used to protect the shared data
}
3.2.2 初始化
我们需要对Coordinator初始化,其中最重要的是更新任务初始状态,一开始都是未分配,
func (c *Coordinator) InitTask(file []string) {for idx := range file {c.MapTasks[idx] = TaskInfo{TaskFile: file[idx],TaskStatus: Unassigned,TimeStamp: time.Now(),}}for idx := range c.ReduceTasks {c.ReduceTasks[idx] = TaskInfo{TaskStatus: Unassigned,}}
}
func MakeCoordinator(files []string, nReduce int) *Coordinator {c := Coordinator{NReduce: nReduce,NMap: len(files),MapTasks: make([]TaskInfo, len(files)),ReduceTasks: make([]TaskInfo, nReduce),AllMapTaskCompleted: false,AllReduceTaskCompleted: false,Mutex: sync.Mutex{},}c.InitTask(files)c.server()return &c
}
3.2.3 RequestTask函数
这部分比较复杂,根据我们之前的分析,处理逻辑如下:
- 如果有未分配的任务、之前执行失败、已分配但已经超时(10s)的
Map任务,则选择这个任务进行分配; - 如果以上的
Map任务均不存在,但Map又没有全部执行完成,告知Worker先等待; Map任务全部执行完成的情况下,按照1和2相同的逻辑进行Reduce任务的分配;- 所有的任务都执行完成了, 告知
Worker退出。
因此,处理代码如下:
func (c *Coordinator) RequestTask(args *MessageSend, reply *MessageReply) error {// lockc.Mutex.Lock()defer c.Mutex.Unlock()// assign map taskif !c.AllMapTaskCompleted {// count the number of completed map tasksNMapTaskCompleted := 0for idx, taskInfo := range c.MapTasks {if taskInfo.TaskStatus == Unassigned || taskInfo.TaskStatus == Failed ||(taskInfo.TaskStatus == Assigned && time.Since(taskInfo.TimeStamp) > 10*time.Second) {reply.TaskFile = taskInfo.TaskFilereply.TaskID = idxreply.TaskType = MapTaskreply.NReduce = c.NReducereply.NMap = c.NMapc.MapTasks[idx].TaskStatus = Assigned // mark the task as assignedc.MapTasks[idx].TimeStamp = time.Now() // update the time stampreturn nil} else if taskInfo.TaskStatus == Completed {NMapTaskCompleted++}}// check if all map tasks have been completedif NMapTaskCompleted == len(c.MapTasks) {c.AllMapTaskCompleted = true} else {reply.TaskType = Waitreturn nil}}// assign reduce taskif !c.AllReduceTaskCompleted {// count the number of completed reduce tasksNReduceTaskCompleted := 0for idx, taskInfo := range c.ReduceTasks {if taskInfo.TaskStatus == Unassigned || taskInfo.TaskStatus == Failed ||(taskInfo.TaskStatus == Assigned && time.Since(taskInfo.TimeStamp) > 10*time.Second) {reply.TaskID = idxreply.TaskType = ReduceTaskreply.NReduce = c.NReducereply.NMap = c.NMapc.ReduceTasks[idx].TaskStatus = Assigned // mark the task as assignedc.ReduceTasks[idx].TimeStamp = time.Now() // update the time stampreturn nil} else if taskInfo.TaskStatus == Completed {NReduceTaskCompleted++}}// check if all reduce tasks have been completedif NReduceTaskCompleted == len(c.ReduceTasks) {c.AllReduceTaskCompleted = true} else {reply.TaskType = Waitreturn nil}}// all tasks have been completedreply.TaskType = Exitreturn nil
}
3.2.4 ReportTask函数
这个函数则是根据Worker发送的消息任务完成状态来更新任务状态信息即可,记住,一把大锁保平安。
func (c *Coordinator) ReportTask(args *MessageSend, reply *MessageReply) error {c.Mutex.Lock()defer c.Mutex.Unlock()if args.TaskCompletedStatus == MapTaskCompleted {c.MapTasks[args.TaskID].TaskStatus = Completedreturn nil} else if args.TaskCompletedStatus == MapTaskFailed {c.MapTasks[args.TaskID].TaskStatus = Failedreturn nil} else if args.TaskCompletedStatus == ReduceTaskCompleted {c.ReduceTasks[args.TaskID].TaskStatus = Completedreturn nil} else if args.TaskCompletedStatus == ReduceTaskFailed {c.ReduceTasks[args.TaskID].TaskStatus = Failedreturn nil}return nil
}
3.3 Worker
3.3.1 Worker轮询
Worker需要通过RPC轮询Coordinator请求任务,然后根据返回的任务类型进行处理(即调用相应函数):
func Worker(mapf func(string, string) []KeyValue,reducef func(string, []string) string) {for {args := MessageSend{}reply := MessageReply{}call("Coordinator.RequestTask", &args, &reply)switch reply.TaskType {case MapTask:HandleMapTask(&reply, mapf)case ReduceTask:HandleReduceTask(&reply, reducef)case Wait:time.Sleep(1 * time.Second)case Exit:os.Exit(0)default:time.Sleep(1 * time.Second)}}
}
3.3.2 处理Map任务
跟mrsequential.go处理基本一致,处理完成后需要通过RPC告知Coordinator结果。但需要注意的是,我们需要通过os.Rename()原子重命名来保证最终的文件系统状态仅仅包含一个任务产生的数据。
func HandleMapTask(reply *MessageReply, mapf func(string, string) []KeyValue) {// open the filefile, err := os.Open(reply.TaskFile)if err != nil {log.Fatalf("cannot open %v", reply.TaskFile)return}// read the file, get the contentcontent, err := io.ReadAll(file)if err != nil {log.Fatalf("cannot read %v", reply.TaskFile)return}file.Close()// call the map function to get the key-value pairskva := mapf(reply.TaskFile, string(content))// create intermediate filesintermediate := make([][]KeyValue, reply.NReduce)for _, kv := range kva {r := ihash(kv.Key) % reply.NReduceintermediate[r] = append(intermediate[r], kv)}// write the intermediate filesfor r, kva := range intermediate {oname := fmt.Sprintf("mr-%v-%v", reply.TaskID, r)ofile, err := os.CreateTemp("", oname)if err != nil {log.Fatalf("cannot create tempfile %v", oname)}enc := json.NewEncoder(ofile)for _, kv := range kva {// write the key-value pairs to the intermediate fileenc.Encode(kv)}ofile.Close()// Atomic file renaming:rename the tempfile to the final intermediate fileos.Rename(ofile.Name(), oname)}// send the task completion message to the coordinatorargs := MessageSend{TaskID: reply.TaskID,TaskCompletedStatus: MapTaskCompleted,}call("Coordinator.ReportTask", &args, &MessageReply{})
}
3.3.3 处理Reduce任务
这里利用我们生成的中间文件名特点,对于每个Reduce任务,它的输入文件(中间文件)名为mr-MapID-ReduceID,所以我们构造出输入文件数组,将其解码得到键值对,再进行处理。
// generate the intermediate files for reduce tasks
func generateFileName(r int, NMap int) []string {var fileName []stringfor TaskID := 0; TaskID < NMap; TaskID++ {fileName = append(fileName, fmt.Sprintf("mr-%d-%d", TaskID, r))}return fileName
}func HandleReduceTask(reply *MessageReply, reducef func(string, []string) string) {// load the intermediate filesvar intermediate []KeyValue// get the intermediate file namesintermediateFiles := generateFileName(reply.TaskID, reply.NMap)// fmt.Println(intermediateFiles)for _, filename := range intermediateFiles {file, err := os.Open(filename)if err != nil {log.Fatalf("cannot open %v", filename)return}// decode the intermediate filedec := json.NewDecoder(file)for {kv := KeyValue{}if err := dec.Decode(&kv); err == io.EOF {break}intermediate = append(intermediate, kv)}file.Close()}// sort the intermediate key-value pairs by keysort.Slice(intermediate, func(i, j int) bool {return intermediate[i].Key < intermediate[j].Key})// write the key-value pairs to the output fileoname := fmt.Sprintf("mr-out-%v", reply.TaskID)ofile, err := os.Create(oname)if err != nil {log.Fatalf("cannot create %v", oname)return}for i := 0; i < len(intermediate); {j := i + 1for j < len(intermediate) && intermediate[j].Key == intermediate[i].Key {j++}var values []stringfor k := i; k < j; k++ {values = append(values, intermediate[k].Value)}// call the reduce function to get the outputoutput := reducef(intermediate[i].Key, values)// write the key-value pairs to the output filefmt.Fprintf(ofile, "%v %v\n", intermediate[i].Key, output)i = j}ofile.Close()// rename the output file to the final output fileos.Rename(ofile.Name(), oname)// send the task completion message to the coordinatorargs := MessageSend{TaskID: reply.TaskID,TaskCompletedStatus: ReduceTaskCompleted,}call("Coordinator.ReportTask", &args, &MessageReply{})
}
4 测试和常见问题
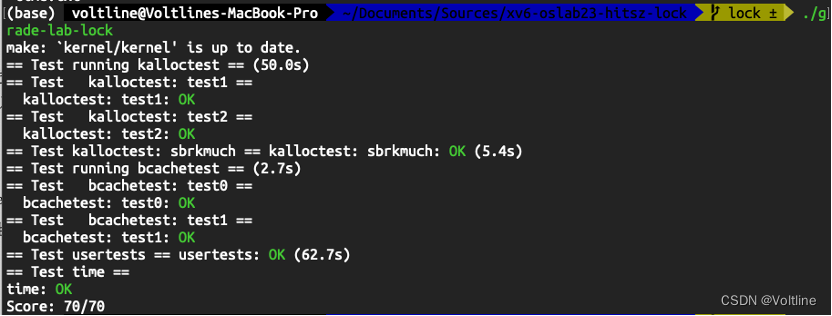
test-mr.sh为测试脚本,也可以通过运行sh test-mr-many.sh n来运行 n n n次测试。
❯ bash test-mr.sh
*** Starting wc test
--- wc test: PASS
*** Starting indexer test.
--- indexer test: PASS
*** Starting map parallelism test.
--- map parallelism test: PASS
*** Starting reduce parallelism test.
--- reduce parallelism test: PASS
*** Starting job count test.
--- job count test: PASS
*** Starting early exit test.
--- early exit test: PASS
*** Starting crash test.
--- crash test: PASS
*** PASSED ALL TESTS
常见的问题如下:
-
不能通过
job-count测试*** Starting job count test. --- map jobs ran incorrect number of times (10 != 8) --- job count test: FAIL因为多次处理同一个任务,且任务没有异常。这是因为在分配任务后没有更新任务的状态,例如标记为已分配和记录当前时间戳。

![[Cesium for Supermap]加载iserver发布的wms服务](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/e1ce7d7be7fe4a519e84a576dd3d36bf.png)