前言
单链表作为顺序表的一种,了解并且熟悉它的结构对于我们学习更加复杂的数据结构是有一定意义的。虽然单链表有一定的缺陷,但是单链表也有它存在的价值, 它也是作为其他数据结构的一部分出现的,比如在图,哈希表中。
目录
1.链表节点的结构
2.头插头删
3.尾插尾删
4.任意位置的插入和删除
5.查找链表的值和修改链表节点的值
6.销毁链表
7.测试代码
8.全部代码
9.总结
1.链表节点的结构
单链表有节点的值和节点的next指针组成,如图:

typedef int SListDatatype;
typedef struct SListNode
{SListDatatype _data;//存储节点的数据struct SListNode* _next;
}SListNode;2.头插头删
头插分为两种情况,第一种是没有节点的情况,第二种是 有节点的情况。如图:

头删也分为两种情况,如果只有一个节点的时候,直接删除就行了,然后将头结点置空。如果有多个节点,需要先记录头结点,然后再进行删除就可以了。
void SListPushFront(SListNode** ppHead, SListDatatype data)//头插
{SListNode* newNode = SlistBuyNode(data);//申请一个新的节点if (*ppHead == NULL){//链表为空*ppHead = newNode;return;}newNode->_next = (*ppHead);*ppHead = newNode;//对头结点进行链接
}
void SListPopFront(SListNode** ppHead)//头删
{assert(*ppHead);//确保指针的有效性if ((*ppHead)->_next == NULL){//链表只有一个节点free(*ppHead);*ppHead = NULL;return;}//删除头结点,然后更新头结点SListNode* newHead = (*ppHead)->_next;free(*ppHead);*ppHead = newHead;return;
}3.尾插尾删
尾插也分为链表为空和指针不为空的情况,如果链表为空,申请节点,让链表的头结点指向申请的节点,然后将这个节点的_next置空,如果链表不为空,首先需要找到尾结点,然后将尾结点与这个节点链接起来,再将这个新申请的节点的_next置空。如图:
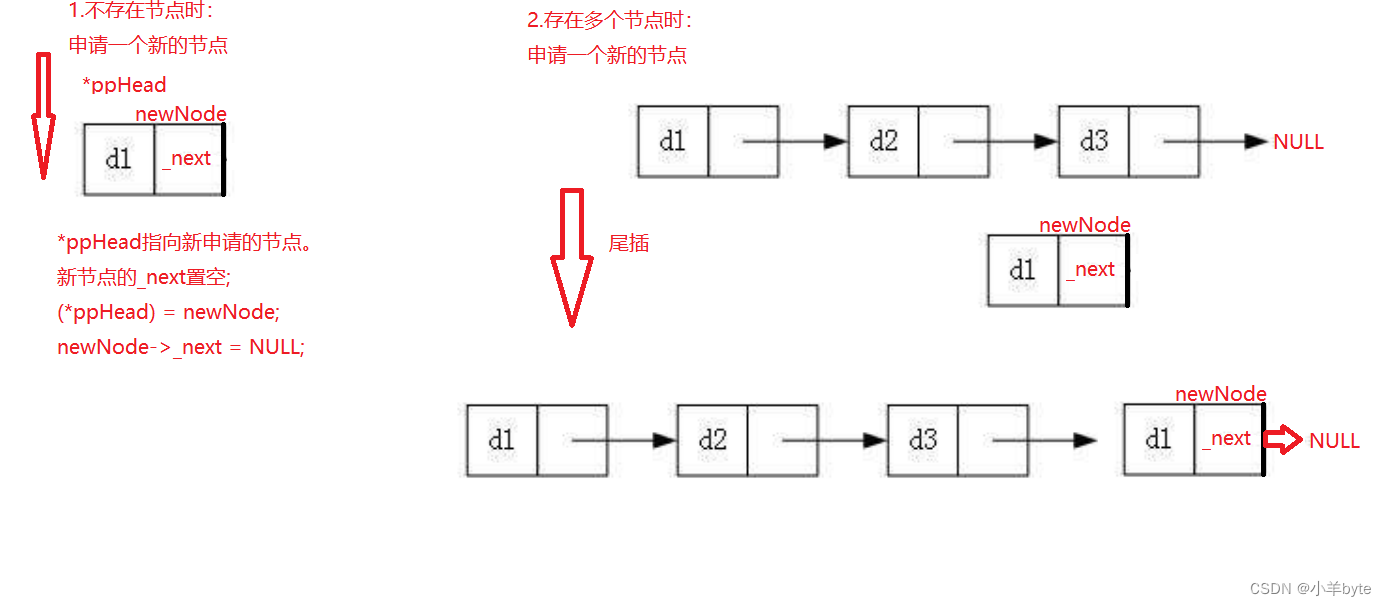
尾删也分为两种情况:1只有一个节点和2存在多个节点
如果只有一个节点,删除以后需要将头结点置空,防止出现野指针的问题。
如果有多个节点,删除尾结点以后需要将新的尾结点置空。
如图: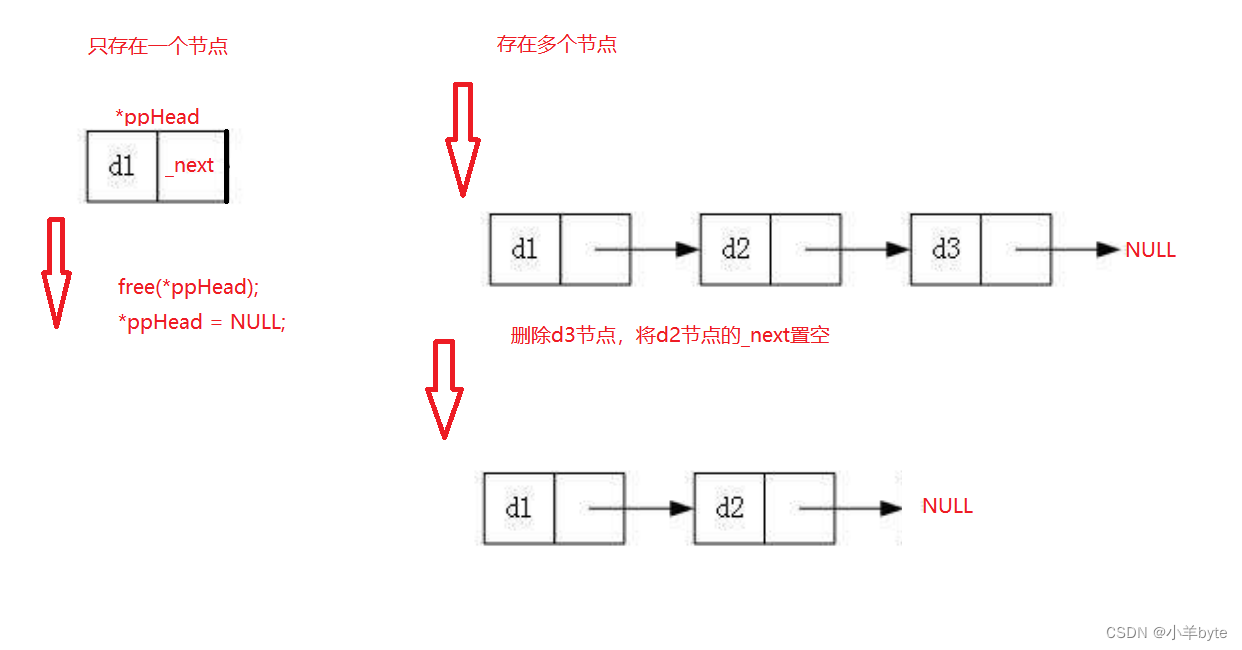
void SListPushBack(SListNode** ppHead, SListDatatype data)//尾插
{SListNode*newNode = SlistBuyNode(data);//申请一个新的节点if (*ppHead == NULL)//链表为空{*ppHead = newNode;return;}if ((*ppHead)->_next == NULL)//链表只存在一个节点{(*ppHead)->_next = newNode;return;}SListNode* cur = *ppHead;while (cur->_next)//找到尾节点{cur = cur->_next;}cur->_next = newNode;//进行链接return;
}
void SListPopBack(SListNode** ppHead)//尾删
{assert(*ppHead);if (*ppHead == NULL)//链表为空不需要删除{return;}if ((*ppHead)->_next == NULL){free(*ppHead);//链表只有一个节点(*ppHead) = NULL;return;}SListNode* cur = *ppHead;SListNode* prev = NULL;while (cur->_next)//找到尾结点{prev = cur;//保存上一个节点cur = cur->_next;}free(cur);//释放尾结点所在的空间prev->_next = NULL;//将上一个节点的_next置空return;
4.任意位置的插入和删除
由于单链表结构的限制,这里只实现了在pos位置之后的插入和删除,如果删除pos的后一个节点就需要确保pos的后一个节点是存在的,否则就会出现问题。
void SListInsertAfter(SListNode*pos, SListDatatype data)//任意位置的插入,在pos之后插入
{assert(pos);//确保指针不为空SListNode* newNode = SlistBuyNode(data);SListNode* next = pos->_next;pos->_next = newNode;newNode->_next = next;
}
void SListErase(SListNode*pos)//任意位置的删除,pox位置之后的删除
{assert(pos);//确保节点的有效性//如果只有一个节点if (pos->_next )//pos节点的下一个节点存在{SListNode* next = pos->_next;SListNode* nextNext = next->_next;free(next);//删除节点,重新链接pos->_next = nextNext;}
}5.查找链表的值和修改链表节点的值
遍历链表就可以对链表中的数据进行查找,找到查找的值,就可以对节点的值进行修改。
SListNode* SListFind(SListNode* pHead, SListDatatype data)//查找
{SListNode* cur = pHead;while (cur){if (cur->_data == data)return cur;cur = cur->_next;//迭代向后走}return NULL;//找不到
}
void testSList()
{//查找和修改的测试SListNode* pHead = NULL;SListPushFront(&pHead, 1);SListPushFront(&pHead, 2);SListPushFront(&pHead, 3);SListPushFront(&pHead, 4);SListPushFront(&pHead, 5);SListPushFront(&pHead, 6);SListPrint(pHead);SListNode* node = SListFind(pHead, 5);//查找if (node){//节点的数据node->_data = 50;}SListPrint(pHead);
}6.销毁链表
void SListDestory(SListNode** ppHead)//销毁
{assert(*ppHead);//确保指针有效性SListNode* cur = *ppHead;while (cur){SListNode* freeNode = cur;cur = cur->_next;free(freeNode);}*ppHead = NULL;
}
7.测试代码
void testSListBack()
{//尾插尾删的测试代码SListNode* pHead = NULL;SListPushBack(&pHead, 1);SListPushBack(&pHead, 2);SListPushBack(&pHead, 3);SListPushBack(&pHead, 4);SListPushBack(&pHead, 5);SListPushBack(&pHead, 6);SListPrint(pHead);SListPopBack(&pHead);SListPopBack(&pHead);SListPopBack(&pHead);SListPopBack(&pHead);SListPopBack(&pHead);SListPopBack(&pHead);}
void testSListFront()
{//头插头删的测试代码SListNode* pHead = NULL;SListPushFront(&pHead, 1);SListPushFront(&pHead, 2);SListPushFront(&pHead, 3);SListPushFront(&pHead, 4);SListPushFront(&pHead, 5);SListPushFront(&pHead, 6);SListPrint(pHead);SListPopFront(&pHead);SListPopFront(&pHead);SListPopFront(&pHead);SListPopFront(&pHead);SListPopFront(&pHead);SListPopFront(&pHead);
}
void testSList()
{//查找和修改的测试SListNode* pHead = NULL;SListPushFront(&pHead, 1);SListPushFront(&pHead, 2);SListPushFront(&pHead, 3);SListPushFront(&pHead, 4);SListPushFront(&pHead, 5);SListPushFront(&pHead, 6);SListPrint(pHead);SListNode* node = SListFind(pHead, 5);//查找if (node){//节点的数据node->_data = 50;}SListPrint(pHead);
}
void TestSList1()
{//对在pos节点之后进行插入和删除的测试SListNode* pHead = NULL;SListPushFront(&pHead, 1);SListPushFront(&pHead, 2);SListPushFront(&pHead, 3);SListPushFront(&pHead, 4);SListPushFront(&pHead, 5);SListPushFront(&pHead, 6);SListPrint(pHead);SListNode* node = SListFind(pHead, 5);//查找if (node){//插入节点SListInsertAfter(node, -2);SListPrint(pHead);SListErase(node);SListPrint(pHead);}SListDestory(&pHead);
}8.全部代码
//SList.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef int SListDatatype;
typedef struct SListNode
{SListDatatype _data;//存储节点的数据struct SListNode* _next;
}SListNode;
SListNode* SlistBuyNode(SListDatatype data);void SListDestory(SListNode** ppHead);//销毁
void SListPushBack(SListNode**ppHead,SListDatatype data);//尾插
void SListPopBack(SListNode** ppHead );//尾删void SListPushFront(SListNode** ppHead, SListDatatype data);//头插
void SListPopFront(SListNode** ppHead);//头删void SListInsertAfter(SListNode* pos, SListDatatype data);//任意位置的插入void SListErase(SListNode*pos);//任意位置的删除SListNode* SListFind(SListNode*pHead, SListDatatype data);//查找
void SListPrint(SListNode* pHead);//显示链表数据
//void SListDestory(SListNode** ppHead);//删除链表//SList.c
#include"SList.h"SListNode* SlistBuyNode(SListDatatype data)
{SListNode*newNode = (SListNode*)malloc(sizeof(SListNode));if (newNode == NULL){//申请节点失败printf("申请节点失败\n");exit(-1);//暴力返回}newNode->_data = data;//给节点赋值newNode->_next = NULL;return newNode;
}void SListDestory(SListNode** ppHead)//销毁
{assert(*ppHead);//确保指针有效性SListNode* cur = *ppHead;while (cur){SListNode* freeNode = cur;cur = cur->_next;free(freeNode);}*ppHead = NULL;
}
void SListPushBack(SListNode** ppHead, SListDatatype data)//尾插
{SListNode*newNode = SlistBuyNode(data);//申请一个新的节点if (*ppHead == NULL)//链表为空{*ppHead = newNode;return;}if ((*ppHead)->_next == NULL)//链表只存在一个节点{(*ppHead)->_next = newNode;return;}SListNode* cur = *ppHead;while (cur->_next)//找到尾节点{cur = cur->_next;}cur->_next = newNode;//进行链接return;
}
void SListPopBack(SListNode** ppHead)//尾删
{assert(*ppHead);if (*ppHead == NULL)//链表为空不需要删除{return;}if ((*ppHead)->_next == NULL){free(*ppHead);//链表只有一个节点(*ppHead) = NULL;return;}SListNode* cur = *ppHead;SListNode* prev = NULL;while (cur->_next)//找到尾结点{prev = cur;//保存上一个节点cur = cur->_next;}free(cur);//释放尾结点所在的空间prev->_next = NULL;//将上一个节点的_next置空return;
}
void SListPushFront(SListNode** ppHead, SListDatatype data)//头插
{SListNode* newNode = SlistBuyNode(data);//申请一个新的节点if (*ppHead == NULL){//链表为空*ppHead = newNode;return;}newNode->_next = (*ppHead);*ppHead = newNode;//对头结点进行链接
}
void SListPopFront(SListNode** ppHead)//头删
{assert(*ppHead);//确保指针的有效性if ((*ppHead)->_next == NULL){//链表只有一个节点free(*ppHead);*ppHead = NULL;return;}//删除头结点,然后更新头结点SListNode* newHead = (*ppHead)->_next;free(*ppHead);*ppHead = newHead;return;
}
void SListInsertAfter(SListNode*pos, SListDatatype data)//任意位置的插入,在pos之后插入
{assert(pos);//确保指针不为空SListNode* newNode = SlistBuyNode(data);SListNode* next = pos->_next;pos->_next = newNode;newNode->_next = next;
}
void SListErase(SListNode*pos)//任意位置的删除,pox位置之后的删除
{assert(pos);//确保节点的有效性//如果只有一个节点if (pos->_next )//pos节点的下一个节点存在{SListNode* next = pos->_next;SListNode* nextNext = next->_next;free(next);//删除节点,重新链接pos->_next = nextNext;}
}SListNode* SListFind(SListNode* pHead, SListDatatype data)//查找
{SListNode* cur = pHead;while (cur){if (cur->_data == data)return cur;cur = cur->_next;//迭代向后走}return NULL;//找不到
}
void SListPrint(SListNode* pHead)//显示链表数据
{assert(pHead);//确保指针的有效性SListNode* cur = pHead;while (cur){printf("%d ", cur->_data);printf("->");cur = cur->_next;}printf("NULL\n");
}
//test.c
#include"SList.h"
void testSListBack()
{//尾插尾删的测试代码SListNode* pHead = NULL;SListPushBack(&pHead, 1);SListPushBack(&pHead, 2);SListPushBack(&pHead, 3);SListPushBack(&pHead, 4);SListPushBack(&pHead, 5);SListPushBack(&pHead, 6);SListPrint(pHead);SListPopBack(&pHead);SListPopBack(&pHead);SListPopBack(&pHead);SListPopBack(&pHead);SListPopBack(&pHead);SListPopBack(&pHead);}
void testSListFront()
{//头插头删的测试代码SListNode* pHead = NULL;SListPushFront(&pHead, 1);SListPushFront(&pHead, 2);SListPushFront(&pHead, 3);SListPushFront(&pHead, 4);SListPushFront(&pHead, 5);SListPushFront(&pHead, 6);SListPrint(pHead);SListPopFront(&pHead);SListPopFront(&pHead);SListPopFront(&pHead);SListPopFront(&pHead);SListPopFront(&pHead);SListPopFront(&pHead);
}
void testSList()
{//查找和修改的测试SListNode* pHead = NULL;SListPushFront(&pHead, 1);SListPushFront(&pHead, 2);SListPushFront(&pHead, 3);SListPushFront(&pHead, 4);SListPushFront(&pHead, 5);SListPushFront(&pHead, 6);SListPrint(pHead);SListNode* node = SListFind(pHead, 5);//查找if (node){//节点的数据node->_data = 50;}SListPrint(pHead);
}
void TestSList1()
{//对在pos节点之后进行插入和删除的测试SListNode* pHead = NULL;SListPushFront(&pHead, 1);SListPushFront(&pHead, 2);SListPushFront(&pHead, 3);SListPushFront(&pHead, 4);SListPushFront(&pHead, 5);SListPushFront(&pHead, 6);SListPrint(pHead);SListNode* node = SListFind(pHead, 5);//查找if (node){//插入节点SListInsertAfter(node, -2);SListPrint(pHead);SListErase(node);SListPrint(pHead);}SListDestory(&pHead);
}
int main()
{TestSList1();return 0;
}
9.总结
链表与顺序表区别和联系。顺序表是在数组的基础上实现增删查改的。并且插入时可以动态增长。顺序表的缺陷:可能存在空间的浪费,增容有一定的效率损失,中间或者头部数据的删除,时间复杂度是O(n),因为要挪动数据。这些问题都是由链表来解决的,但是链表也有自己的缺陷,不能随机访问,存在内存碎片等问题。 其实没有哪一种数据结构是完美的,它们都有各自的缺陷,实际中的使用都是相辅相成的。