目录
🌼两数之和
暴力
二分
哈希
🌼字母异位词分组
unordered_map + 排序
unordered_map + 计数
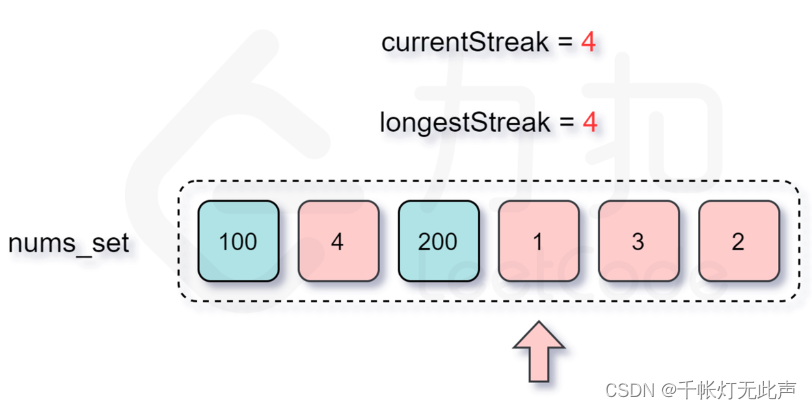
🌼最长连续序列
unordered_set + 跳过前驱
排序 + dp
🌼两数之和
1. 两数之和 - 力扣(LeetCode)
暴力
O(n^2) 两层循环
class Solution {
public:vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) { // 返回vector数组int n = nums.size();for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i)for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) if (nums[i] + nums[j] == target) return {i, j};return {}; // 返回空数组}
};二分
O(nlogn)
O(nlogn) 整数二分 整数二分需要注意边界,防止下取整的坑(死循环)
排序 O(nlogn)
外层for O(n) * for 循环里二分 O(logn) = O(nlogn)
详细解释下第 32 行
if (a[i].x == a[l].x) l++; // 避免同一个元素, 索引++(最关键)
比如 i == 2, l == 4,2 + 4 == 6,而假设此时双方的值都是3,3 + 3 == 6
那么就会输出同一个元素的下标,需要索引 + 1
AC 代码
#include<algorithm> // sort()
using namespace std;struct node {int v, x; // value 和 index
}a[10010];bool cmp(node x, node y)
{return x.v < y.v;
}class Solution {
public:vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {int n = nums.size();for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)a[i].v = nums[i], a[i].x = i; // 先结合sort(a, a + n, cmp); // 再排序(结构体数组)// 遍历for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {int l = 0, r = n - 1;while (l < r) { // 二分int m = (l + r) >> 1;if (a[m].v >= target - a[i].v) // target - a[i].v 为要查找的值r = m;elsel = m + 1;}// 退出 while 后, l == rif (a[i].v + a[l].v == target) {if (a[i].x == a[l].x) l++; // 避免同一个元素, 索引++(最关键)return {a[i].x, a[l].x}; // 返回下标}}return {}; // 返回空数组}
};哈希
O(n)
知识
map<string, int>a; //升序
map<string, int, greater<string> >a; //降序h[key] = val;
//等价于
h.insert(make_pair(key, val));for(map<string, int>::iterator it = a.begin(); it != a.end(); ++it)cout<<it->first<<"\t"<<it->second<<endl;size/empty/clear //元素个数,判空,清空
begin / end //指向开始 / 结束位置的指针
insert(x) //将元素x插入集合(x为二元组)
erase(x) //删除所有等于x的元素(x为二元组)
erase(it) //删除it指向的元素(it为指向二元组的迭代器)
find(k) //查找键为k的二元组的位置, 若不存在, 返回尾指针 .end()C++ map和unordered_map详解-腾讯云开发者社区-腾讯云 (tencent.com)
AC 代码
class Solution {
public:vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) { // 返回vector数组int n = nums.size();unordered_map<int, int> h; // 键 元素大小;值 元素下标for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {auto it = h.find(target - nums[i]); // 查找这个键 -- 元素大小if (it != h.end()) // 找到了该元素return {i, it->second}; // 返回下标//h.insert(make_pair(nums[i], i)); // 插入键值对h[nums[i]] = i; // 插入键值对}return {}; // 返回空数组}
};🌼字母异位词分组
49. 字母异位词分组 - 力扣(LeetCode)
知识
1)emplace_back 与 push_back
一文弄清楚 push_back 和 emplace_back 的区别-emplace_back和push_back有区别吗 (51cto.com)
2)unordered_map 与 map
map和unordered_map区别及其优缺点 - 己平事 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
map、multimap 容器都会自行根据键的大小对存储的键值对进行排序
3)代码中,两个要注意的点
(一)引用传递 比 迭代器 快很多(访问vector<string>时)
// 引用传递 for (string& str : strs) // 迭代器 for (vector<string>::iterator it = strs.begin(); it != strs.end(); ++it)(二)emplace_back 比 push_back 快 20%
unordered_map + 排序
O(n*k*logk) n -- strs中字符串数量 k 单个字符串最大长度 ≈ 5*1e6
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<string>> groupAnagrams(vector<string>& strs) {unordered_map<string, vector<string> > s; // 键 string 值 vector<string>vector<vector<string> > ans; // 返回类型// 遍历字符串数组 strsfor (string& str : strs) { // 引用传递 快很多string key = str;sort(key.begin(), key.end());s[key].push_back(str);}// for (vector<string>::iterator it = strs.begin(); it != strs.end(); ++it) {// string key = *it; // 键// sort(key.begin(), key.end()); // 对键排序// s[key].push_back(*it); // 键 -- 排序后的值// }for (auto t : s) ans.push_back(t.second); // 插入vector<string>类型数组// for (auto it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); ++it)// ans.push_back(it->second);return ans;}
};unordered_map + 计数
O(n*k)
排序 --> 计数,变相得到了每个字符串按字典序的排序(隐含的是:int 和 char 之间的
隐式转换
但是有个疑问,如果一个字母出现100次,' ' + 100 == 132,超过了ASCII的127范围,超过范围阶段,可能和前面的冲突才对
可能是样例太少了
注意:& 比 不用&,快很多,避免将元素的值复制到新的变量中
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<string>> groupAnagrams(vector<string>& strs) {// 键--已排序字符串 值--未排序字符串 组成的数组unordered_map<string, vector<string> > s;vector<vector<string> > ans; // 数组元素为 vector<string>for (string& str : strs) { // str 每个字符串// string count = string(26, ' '); string count(26, ' ');for (char& c : str) // c 一个字符count[c - 'a']++;s[count].push_back(str); // 插入键值对}for (auto& t : s) // t--unordered_map<string, vector<string>> 类型ans.push_back(t.second); // 插入 vector<string> 类型return ans;}
};🌼最长连续序列
128. 最长连续序列 - 力扣(LeetCode)
知识
size/empty/clear //元素个数 判空 清空
begin/end //开始和结束位置
inset(x) //元素x插入集合
erase(x) //删除所有值为x的元素
erase(it) //删除it迭代器指向的元素
find(x) //查找x在集合的位置,不存在则返回end
count(x) //统计x元素的个数
lower_bound(x) //返回大于等于x的最小元素位置
upper_bound(x) //返回大于x的最小元素位置思路
set 用于去重
unordered_set,不需要有序,所以用 unordered
存在前驱则跳过
unordered_set + 跳过前驱
O(n)
外层循环 for,因为“存在前驱,则跳过”,数组中每个数,只会进入 内层 while 循环 1 次
所以外层 O(n),内层 O(1)
class Solution {
public:int longestConsecutive(vector<int>& nums) {int ans = 0; // 初始0 有可能空数组unordered_set<int> s; // 去重for (const int& num : nums) // 引用传递s.insert(num);for (auto& num : s) { // 遍历哈希表if (s.count(num - 1)) continue; // 存在前驱 -- 跳过当前int currentNum = num, currentLen = 1; // 当前长度 1while (s.count(currentNum + 1)) {currentLen++; // 长度 +1currentNum++; // 值 +1}ans = max(ans, currentLen);}return ans;}
};排序 + dp
很好奇,为什么 O(nlogn) 的复杂度,要比上面的 O(n) 快得多........
class Solution {
public:int longestConsecutive(vector<int>& nums) {if (!nums.size()) return 0; // 避免空数组sort(nums.begin(), nums.end()); // 先排序vector<int> nums2;nums2.push_back(nums[0]);for (int i = 1; i < nums.size(); ++i) if (nums[i] != nums[i - 1]) // 再去重nums2.push_back(nums[i]); int n = nums2.size(), ans = 1;if (n == 0) return 0; // 避免空数组vector<int> dp(n, 1); // 初始化for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {if (nums2[i] == nums2[i - 1] + 1)dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + 1;ans = max(ans, dp[i]);}return ans;}
};/*
含义:dp[i] 以第 i 个数结尾的最大长度(下标 0 开始)
递推式:if (nums[i] == nums[i - 1] + 1) dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + 1;
初始化:dp[0...n-1] = 1
遍历顺序:nums[] 0...n-1
打表检查
*/