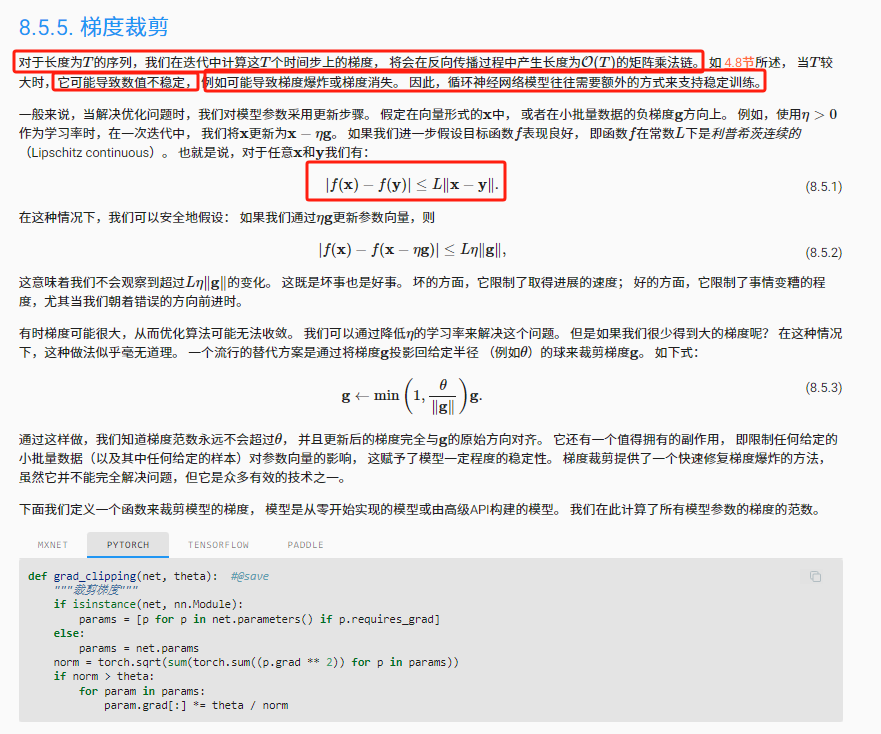
E. Girl Permutation


题意
有一个位置的长度为 n n n 的排列 ,现在给定一个前缀最值下标数组 p p p 和一个后缀最值下标数组 s s s
- 在位置 i i i 的前缀最值下标定义为:以 i i i 为结尾的前缀,最大值恰好在 i i i,也就是 ∀ j < i , a j < a i \forall j < i,a_j < a_i ∀j<i,aj<ai,如果不满足条件,那么 i i i 不出现在 p p p 中
后缀最值下标也是类似
现在求出符合 p p p 和 s s s 的排列个数,对 1 e 9 + 7 1e9 + 7 1e9+7 求模
思路
首先不难观察到:最大值 n n n 所在的下标一定会出现在 p [ m 1 − 1 ] p[m1-1] p[m1−1] 和 s [ 0 ] s[0] s[0],并且 p [ 0 ] = 1 p[0] = 1 p[0]=1, s [ m 2 − 1 ] = n s[m2 - 1] = n s[m2−1]=n,如果不满足这些条件,就不存在任何一个满足条件的排列
否则,我们可以唯一确定 n n n 的位置,就是在 p [ m 1 − 1 ] p[m1 - 1] p[m1−1],那么我们需要从 n − 1 n - 1 n−1(最大值 n n n 已被分配)个数中,选择 p [ m 1 − 1 ] − 1 p[m1 - 1] - 1 p[m1−1]−1 个数到左半部分,剩下的数在右半部分,这里的方案数是 ( n − 1 p m 1 − 1 − 1 ) \binom{n - 1}{p_{m_1-1} - 1} (pm1−1−1n−1),然后我们继续对于 p [ m 1 − 2 ] p[m1-2] p[m1−2] 考虑,可以发现,这个位置是 [ 1 , p m 1 − 1 − 1 ] [1,p_{m_1-1}-1] [1,pm1−1−1] 这个前缀的最大值,也就是我们前面分配过来的那些数的最大值!
想到这里,我们就可以考虑分治来求解方案数了,对于当前的一个左半部份,其最大值在 p [ i ] p[i] p[i],那么表示的是前缀 [ 1 , p [ i + 1 ] − 1 ] [1, p[i + 1] - 1] [1,p[i+1]−1] 这个子状态,我们继续从 p [ i + 1 ] − 2 p[i + 1] - 2 p[i+1]−2 个数(两个数已经在 p [ i ] p[i] p[i] 和 p [ i + 1 ] p[i + 1] p[i+1])中选择 p [ i ] − 1 p[i] - 1 p[i]−1 个数到 p [ i ] p[i] p[i] 的左边,其余留在 [ p [ i ] + 1 , p [ i + 1 ] − 1 ] [p[i] + 1, p[i + 1] - 1] [p[i]+1,p[i+1]−1],这里贡献的方案数是 ( p i + 1 − 2 p i − 1 ) \binom{p_{i + 1} - 2}{p_i - 1} (pi−1pi+1−2),注意这里还要考虑留在 [ p [ i ] + 1 , p [ i + 1 ] − 1 ] [p[i] + 1, p[i + 1] - 1] [p[i]+1,p[i+1]−1] 的部分,这里的数字可以 任意排列 ,因此我们要乘上阶乘 ( p i + 1 − p i − 1 ) ! (p_{i + 1} - p_i - 1)! (pi+1−pi−1)!
对于右半部分,也是类似的计算方法
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define fore(i,l,r) for(int i=(int)(l);i<(int)(r);++i)
#define fi first
#define se second
#define endl '\n'
#define ull unsigned long long
#define ALL(v) v.begin(), v.end()
#define Debug(x, ed) std::cerr << #x << " = " << x << ed;const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
const long long INFLL=1e18;typedef long long ll;template<class T>
constexpr T power(T a, ll b){T res = 1;while(b){if(b&1) res = res * a;a = a * a;b >>= 1;}return res;
}constexpr ll mul(ll a,ll b,ll mod){ //快速乘,避免两个long long相乘取模溢出ll res = a * b - ll(1.L * a * b / mod) * mod;res %= mod;if(res < 0) res += mod; //误差return res;
}template<ll P>
struct MLL{ll x;constexpr MLL() = default;constexpr MLL(ll x) : x(norm(x % getMod())) {}static ll Mod;constexpr static ll getMod(){if(P > 0) return P;return Mod;}constexpr static void setMod(int _Mod){Mod = _Mod;}constexpr ll norm(ll x) const{if(x < 0){x += getMod();}if(x >= getMod()){x -= getMod();}return x;}constexpr ll val() const{return x;}explicit constexpr operator ll() const{ return x; //将结构体显示转换为ll类型: ll res = static_cast<ll>(OBJ)}constexpr MLL operator -() const{ //负号,等价于加上ModMLL res;res.x = norm(getMod() - x);return res;}constexpr MLL inv() const{assert(x != 0);return power(*this, getMod() - 2); //用费马小定理求逆}constexpr MLL& operator *= (MLL rhs) & { //& 表示“this”指针不能指向一个临时对象或const对象x = mul(x, rhs.x, getMod()); //该函数只能被一个左值调用return *this;}constexpr MLL& operator += (MLL rhs) & {x = norm(x + rhs.x);return *this;}constexpr MLL& operator -= (MLL rhs) & {x = norm(x - rhs.x);return *this;}constexpr MLL& operator /= (MLL rhs) & {return *this *= rhs.inv();}friend constexpr MLL operator * (MLL lhs, MLL rhs){MLL res = lhs;res *= rhs;return res;}friend constexpr MLL operator + (MLL lhs, MLL rhs){MLL res = lhs;res += rhs;return res;}friend constexpr MLL operator - (MLL lhs, MLL rhs){MLL res = lhs;res -= rhs;return res;}friend constexpr MLL operator / (MLL lhs, MLL rhs){MLL res = lhs;res /= rhs;return res;}friend constexpr std::istream& operator >> (std::istream& is, MLL& a){ll v;is >> v;a = MLL(v);return is;}friend constexpr std::ostream& operator << (std::ostream& os, MLL& a){return os << a.val();}friend constexpr bool operator == (MLL lhs, MLL rhs){return lhs.val() == rhs.val();}friend constexpr bool operator != (MLL lhs, MLL rhs){return lhs.val() != rhs.val();}
};const ll mod = 1e9 + 7;
using Z = MLL<mod>;struct Comb {int n;std::vector<Z> _fac;std::vector<Z> _invfac;std::vector<Z> _inv;Comb() : n{0}, _fac{1}, _invfac{1}, _inv{0} {}Comb(int n) : Comb() {init(n);}void init(int m) {m = std::min(1ll * m, Z::getMod() - 1);if (m <= n) return; //已经处理完了需要的长度_fac.resize(m + 1);_invfac.resize(m + 1);_inv.resize(m + 1);for (int i = n + 1; i <= m; i++) {_fac[i] = _fac[i - 1] * i;}_invfac[m] = _fac[m].inv();for (int i = m; i > n; i--) { //线性递推逆元和阶乘逆元_invfac[i - 1] = _invfac[i] * i;_inv[i] = _invfac[i] * _fac[i - 1];}n = m; //新的长度}Z fac(int m) {if (m > n) init(2 * m);return _fac[m];}Z invfac(int m) {if (m > n) init(2 * m);return _invfac[m];}Z inv(int m) {if (m > n) init(2 * m);return _inv[m];}Z binom(int n, int m) { //二项式系数if (n < m || m < 0) return 0;return fac(n) * invfac(m) * invfac(n - m);}
} comb;int main(){std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);std::cin.tie(nullptr);std::cout.tie(nullptr);int t;std::cin >> t;while(t--) {int n, m1, m2;std::cin >> n >> m1 >> m2;std::vector<int> p(m1), s(m2);fore(i, 0, m1) std::cin >> p[i];fore(i, 0, m2) std::cin >> s[i];if(p[0] != 1 || p[m1 - 1] != s[0] || s[m2 - 1] != n){std::cout << "0\n";continue;}Z ans = comb.binom(n - 1, p[m1 - 1] - 1);for(int i = m1 - 2; i >= 0; --i) ans *= comb.binom(p[i + 1] - 2, p[i] - 1) * comb.fac(p[i + 1] - p[i] - 1);fore(i, 1, m2) ans *= comb.binom(n - s[i - 1] - 1, n - s[i]) * comb.fac(s[i] - s[i - 1] - 1);std::cout << ans << endl;}return 0;
}