- 代码随想录:代码随想录
- 力扣:力扣 (LeetCode) 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台
- 代码随想录-力扣刷题-总结笔记01
- 代码随想录-力扣刷题-总结笔记02
目录
01、代码随想录
00、其他
ArrayList转数组
07、二叉树
7.0、递归法
7.1、二叉树的层序遍历模板
7.2、判断两棵树是否相同
7.3、求二叉树高度
7.4、二叉树路径和相关题目
7.5、深度优先搜索(DFS)广度优先搜索(BFS)
7.6、统计最高出现频率元素集合的技巧
7.7、删除二叉搜索树中的节点
08、回溯
8.1、回溯函数遍历过程
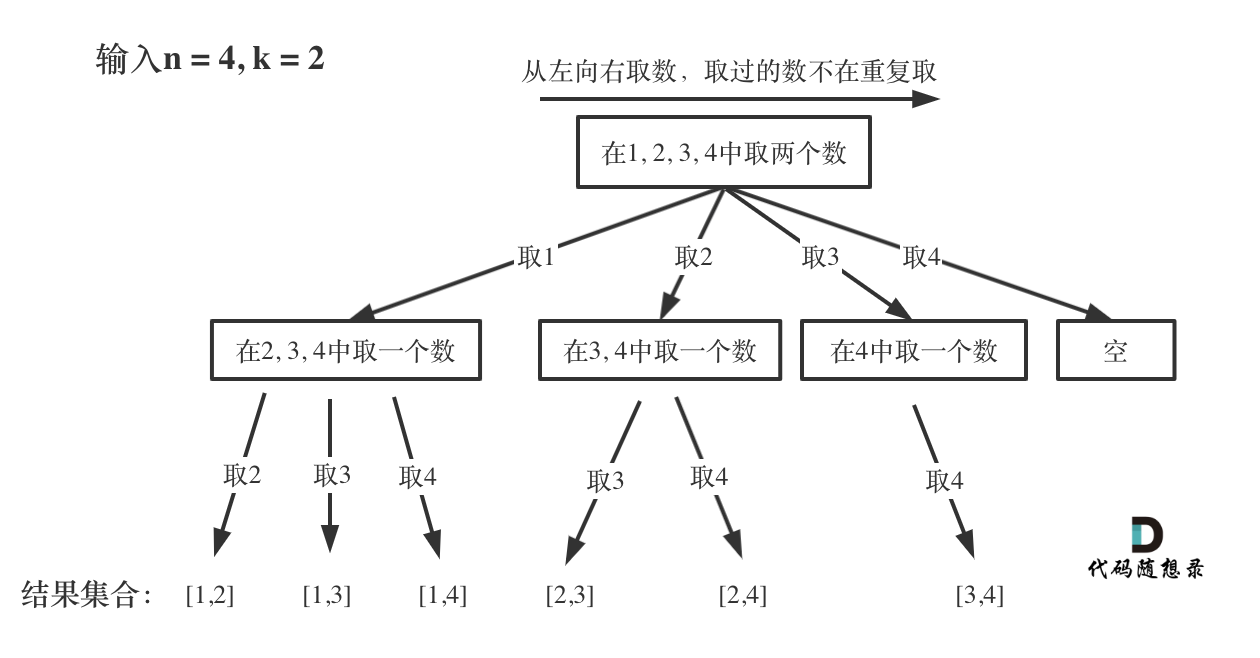
8.2、回溯函数模板1-组合
8.3、回溯函数模板2-组合总和
8.4、回溯函数模板3-全排列
8.5、回溯总结
09、贪心算法
9.1、将数组按照绝对值大小从大到小排序
9.2、二维数组排序
9.3、重叠区间问题
10、动态规划
11、单调栈
12、图论
12.1、dfs回溯模板
12.2、岛屿问题模板-dfs/bfs
01、代码随想录
00、其他
ArrayList转数组
ArrayList<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
//将 ArrayList 转换为 int数组
int[] intArray = list.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();ArrayList<String> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
//将 ArrayList 转换为 String数组
String[] stringArray = arrayList.toArray(new String[0]);07、二叉树
7.0、递归法
解决二叉树题目,应该优先使用递归法。
- 确定递归函数的参数和返回值;
- 确定终止条件;
- 确定单层递归的逻辑。
代码随想录,二叉树:总结篇!
在每一道二叉树的题目中,我都使用了递归三部曲来分析题目,相信大家以后看到二叉树,看到递归,都会想:返回值、参数是什么?终止条件是什么?单层逻辑是什么?
7.1、二叉树的层序遍历模板
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* public class TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode left;* TreeNode right;* TreeNode() {}* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {* this.val = val;* this.left = left;* this.right = right;* }* }*/class Solution0102 {//力扣102.二叉树的层序遍历public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {Deque<TreeNode> deque = new LinkedList<>();if (root != null) {deque.push(root);}List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();while (!deque.isEmpty()) {int size = deque.size();ArrayList<Integer> tempList = new ArrayList<Integer>();while (size-- > 0) {//for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {//fori操作空间更大,513题-找树左下角的值TreeNode treeNode = deque.poll();tempList.add(treeNode.val);if (treeNode.left != null) {deque.offer(treeNode.left);}if (treeNode.right != null) {deque.offer(treeNode.right);}}res.add(tempList);}return res;}
}import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Stack;class Solution0617_1 {public TreeNode mergeTrees(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {if (root1 == null) {return root2;} else if (root2 == null) {return root1;} else if (root1 == null && root2 == null) {return null;}Deque<TreeNode> deque = new LinkedList<>();deque.offer(root1);deque.offer(root2);while (!deque.isEmpty()) {TreeNode poll1 = deque.poll();TreeNode poll2 = deque.poll();poll1.val += poll2.val;if (poll1.left != null && poll2.left != null) {deque.offer(poll1.left);deque.offer(poll2.left);}if (poll1.right != null && poll2.right != null) {deque.offer(poll1.right);deque.offer(poll2.right);}if (poll1.left == null && poll2.left != null) {poll1.left = poll2.left;}if (poll1.right == null && poll2.right != null) {poll1.right = poll2.right;}}return root1;}
}7.2、判断两棵树是否相同
/*** 判断两棵树是否相同*/
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode s, TreeNode t) {if (s == null && t == null) {return true;}if (s == null || t == null) {return false;}if (s.val != t.val) {return false;}return isSameTree(s.left, t.left) && isSameTree(s.right, t.right);
}7.3、求二叉树高度
public int getHeight(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) {return 0;} else {int leftHeight = maxDepth(root.left);int rightHeight = maxDepth(root.right);return Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1;}
}7.4、二叉树路径和相关题目
- 257.二叉树的所有路径
- 112.路径总和
- 113.路径总和II
7.5、深度优先搜索(DFS)广度优先搜索(BFS)
package com.question.solve.leetcode.programmerCarl._07binaryTrees;import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;public class BinaryTreeSearch {public static void main(String[] args) {//构建一个二叉树TreeNode root = new TreeNode(1);root.left = new TreeNode(2);root.right = new TreeNode(3);root.left.left = new TreeNode(4);root.left.right = new TreeNode(5);root.right.left = new TreeNode(6);root.right.right = new TreeNode(7);BinaryTreeSearch searcher = new BinaryTreeSearch();System.out.println("深度优先搜索结果:");searcher.dfs(root);System.out.println("\n广度优先搜索结果:");searcher.bfs(root);}public void dfs(TreeNode root) {//深度优先搜索(DFS)if (root == null) {return;}System.out.print(root.val + " ");//先访问当前节点dfs(root.left);//递归遍历左子树dfs(root.right);//递归遍历右子树}public void bfs(TreeNode root) {//广度优先搜索(BFS)if (root == null) {return;}Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(root);while (!queue.isEmpty()) {TreeNode node = queue.poll();System.out.print(node.val + " ");if (node.left != null) {queue.offer(node.left);}if (node.right != null) {queue.offer(node.right);}}}
}7.6、统计最高出现频率元素集合的技巧
//501. 二叉搜索树中的众数
============================================================
//统计最高出现频率元素集合的技巧
if (count == maxCount) {//如果和最大值相同,放进result中result.push_back(cur->val);
}
if (count > maxCount) { // 如果计数大于最大值频率maxCount = count; // 更新最大频率result.clear(); // 很关键的一步,不要忘记清空result,之前result里的元素都失效了result.push_back(cur->val);
}
============================================================
int maxValue = 0;
ArrayList<Integer> resultList = new ArrayList<>();
for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : map.entrySet()) {//优化,统计最高出现频率元素集合的技巧int count = entry.getValue();int value = entry.getKey();if (count == maxValue) {resultList.add(value);}if (count > maxValue) {maxValue = count;resultList.clear();resultList.add(value);}
}
int[] res = resultList.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();7.7、删除二叉搜索树中的节点
//力扣450.删除二叉搜索树中的节点
TreeNode cur = root.right;
while (cur.left != null) {cur = cur.left;
}
cur.left = root.left;
root = root.right;
return root;//第五种情况:左右孩子节点都不为空,则将删除节点的左子树放到删除节点的右子树的最左面节点的左孩子的位置
//并返回删除节点右孩子为新的根节点。
if(root.left != null && root.right != null) {TreeNode leftNode = root.right;//找右子树最左面的节点while(leftNode.left != null)leftNode = leftNode.left;leftNode.left = root.left;//把要删除的节点(root)左子树放在leftNode的左孩子的位置return root.right;//返回旧root的右孩子作为新root
}08、回溯
回溯算法题分为两大块:组合、排列。
8.1、回溯函数遍历过程
回溯函数遍历过程伪代码如下:
for (选择:本层集合中元素(树中节点孩子的数量就是集合的大小)) {处理节点;backtracking(路径,选择列表); //递归回溯,撤销处理结果;
}
-------------------------------------------------------
void backtracking(参数) {//backtracking(递归)就是纵向遍历if (终止条件) {存放结果;return;}for (选择: 本层集合中元素(树中节点孩子的数量就是集合的大小)) {//for循环可以理解是横向遍历处理节点;backtracking(路径,选择列表);//递归回溯,撤销处理结果;}
}8.2、回溯函数模板1-组合
Java【全排列 算法 模板】_全排列java模板-CSDN博客
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;class Solution0077 {//LeetCode第77题.组合List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();//存放符合条件结果的集合,结果集合LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>(); //存放符合条件的单一结果,路径集合public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) {backtracking(n, k, 1);return result;}public void backtracking(int n, int k, int startIndex) {if (path.size() == k) {//终止条件result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));//复制list中的所有元素到新的ArrayList对象中return;}//for (int i = startIndex; i <= n - (k - path.size()) + 1; i++) {//剪枝for (int i = startIndex; i <= n; i++) {path.add(i);backtracking(n, k, i + 1);path.removeLast();}}
}
/**
在Java中,new ArrayList<>(list)的作用是创建一个新的ArrayList对象,并使用list中的元素来初始化它。
这种语法称为复制构造函数,它会复制list中的所有元素到新的ArrayList对象中。
这样做的好处是,原始列表list和新创建的列表之间没有直接的引用关系,因此对其中一个列表的修改不会影响到另一个列表。
*/import java.util.*;public class Permutations {public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();List<Integer> tempList = new ArrayList<>();backtrack(result, tempList, nums);return result;}private void backtrack(List<List<Integer>> result, List<Integer> tempList, int[] nums) {if (tempList.size() == nums.length) {result.add(new ArrayList<>(tempList));} else {for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {if (tempList.contains(nums[i])) continue; // Skip if element already existstempList.add(nums[i]);backtrack(result, tempList, nums);tempList.remove(tempList.size() - 1);}}}public static void main(String[] args) {Permutations perm = new Permutations();int[] nums = {1, 2, 3};List<List<Integer>> result = perm.permute(nums);System.out.println("Permutations: " + result);}
}8.3、回溯函数模板2-组合总和
class Solution0040 {//力扣40.组合总和IIList<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {Arrays.sort(candidates);backtracking(candidates, 0, target, 0);return res;}private void backtracking(int[] candidates, int startIndex, int target, int sum) {if (sum > target) {return;}if (sum == target) {if (!res.contains(new ArrayList<>(path))) {res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));}}for (int i = startIndex; i < candidates.length && sum + candidates[i] <= target; i++) {if (i > startIndex && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1]) {//把所有组合求出来,再用set或者map去重,这么做很容易超时!所以要在搜索的过程中就去掉重复组合。continue;}path.add(candidates[i]);sum += candidates[i];backtracking(candidates, i + 1, target, sum);path.removeLast();sum -= candidates[i];}}
}8.4、回溯函数模板3-全排列
class Solution0046 {//力扣46.全排列List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();//LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList();public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {backtracking(nums, 0);return res;}private void backtracking(int[] nums, int startIndex) {if (startIndex == nums.length) {ArrayList<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {path.add(nums[i]);}if (!res.contains(path)) {res.add(path);return;}//res.add(path);//return;}for (int i = startIndex; i < nums.length; i++) {int temp = nums[i];nums[i] = nums[startIndex];nums[startIndex] = temp;//path.add(nums[i]);backtracking(nums, startIndex + 1);//path.removeLast();temp = nums[i];nums[i] = nums[startIndex];nums[startIndex] = temp;}}
}8.5、回溯总结
回溯一共就三类,分为组合、子集、排列。其中组合与子集又是一个问题,只不过子集还会搜集非叶子节点,但本质都是组合。
这三类又有其他变体,变体主要就是约束条件,共有三类:
①、元素无重,不可重复选。
②、元素可重,不可重复选。
③、元素无重,可重复选。
组合问题是否需要startIndex:组合考虑起始位置的问题,是因为需要避免组合重复,如2,3和3,2,不能走回头路。
- 单集合取组合需要
- 元素无重,不可复选:为i+1,因为不可重复选,每次递归都得从下一个元素开始,避免复选。
- 元素无重,可复选:为了避免组合重复依然不能走回头路,但是单条路径向下递归要求可以复选,也就是向下递归还可以使用上位递归的元素,故为 i 。
- 多集合取组合不需要,各个集合之间互不影响
元素可重,不可复选。结果不可重复是需要树层去重的,否则1,1,1,1就会出现1,1和1,1。
- 数组可以排序:排序后,相同的数挨着 if (i > index && nums[i] == nums[i-1]) continue;
- 数组不可排序:相同的数不挨着,在树层使用set,过滤重复数,递归每进入下一层都是新的set。
对于不能排序的,递增递减子序列问题,含有重复元素,想要去重,自然没法用之前的横向去重的策略(if( i > index && nums[i] == nums[i-1])continue;)。这个去重策略只能是排序后,让重复元素都挨着才能用。那么树层该如何去重?就需要使用一个set数组,每次递归都是一个新的数组,不影响纵向,但横向for循环时会记录靠左的孩子使用的元素,遇到重复元素就跳过去,避免重复使用。
排列问题,和组合问题还不一样,排列问题不需要indexStart,也就是for循环是固定的0到结束,但是纵向需要去重,避免使用重复元素,这时可以使用used数组,标记为true即跳过,只有向下递归才会遇到重复元素跳过,横向是没有重复元素的。一个纵向路径为一个排列,一个排列里一个元素只能使用一次。
含重复元素的排列,nums = [1,1,2]包含重复元素,又是排序,所以,不光要纵向去重,也需要横向去重,纵向去重使用used数组,横向去重需要排序,而且used[i-1]为false,即可起到去重的效果。
09、贪心算法
所以唯一的难点就是如何通过局部最优,推出整体最优。
贪心一般解题步骤,贪心算法一般分为如下四步:
- 将问题分解为若干个子问题
- 找出适合的贪心策略
- 求解每一个子问题的最优解
- 将局部最优解堆叠成全局最优解
9.1、将数组按照绝对值大小从大到小排序
// 声明一个名为array的int数组,大小为10
int[] array = new int[10];// 或者声明并初始化数组
int[] array = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; // 这会创建一个包含5个元素的数组,分别是1,2,3,4,5//力扣1005:K次取反后最大化的数组和
//将数组按照绝对值大小从大到小排序,注意要按照绝对值的大小
nums = IntStream.of(nums).boxed().sorted((o1, o2) -> Math.abs(o2) - Math.abs(o1)).mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();9.2、二维数组排序
/*** 406.根据身高重建队列*/
class Solution0406 {public int[][] reconstructQueue(int[][] people) {//身高从大到小排(身高相同,k小的站前面)Arrays.sort(people, (a, b) -> {if (a[0] == b[0]) {return a[1] - b[1];//a - b 是升序排列,故在a[0] == b[0]的狀況下,会根据k值升序排列}return b[0] - a[0];//b - a 是降序排列,在a[0] != b[0]的情况会根据h值降序排列});LinkedList<int[]> que = new LinkedList<>();for (int[] p : people) {que.add(p[1], p);//Linkedlist.add(index, value),會將value插入到指定index裡。}return que.toArray(new int[people.length][]);}
}package com.question.solve.test;import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;public class _004_TwoDArray {public static void main(String[] args) {int[][] arr1 = {{3, 5}, {1, 2}, {4, 6}};//使用Comparator定义排序规则Arrays.sort(arr1, new Comparator<int[]>() {@Overridepublic int compare(int[] a, int[] b) {// 按第一个元素升序排序if (a[0] != b[0]) {return a[0] - b[0];} else { // 如果第一个元素相同,则按第二个元素升序排序return a[1] - b[1];}}});//输出排序后的数组for (int i = 0; i < arr1.length; i++) {System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr1[i]));}//------------------------------------------------------------------------int[][] arr2 = {{3, 5}, {9, 8}, {4, 6}};//升序排序Arrays.sort(arr2, (a, b) -> {if (a[0] != b[0]) {return a[0] - b[0];} else {return a[1] - b[1];}});//降序排序Arrays.sort(arr2, (a, b) -> {if (a[0] != b[0]) {return b[0] - a[0];} else {return b[1] - a[1];}});//输出排序后的数组for (int i = 0; i < arr2.length; i++) {System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr2[i]));}}
}二维int数组不溢出排序:
- Arrays.sort(points, (a, b) -> Integer.compare(a[0], b[0])); // 使用Integer内置比较方法,不会溢出
- Arrays.sort(points, Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[0])); // import java.util.Comparator;
/*** 时间复杂度 : O(NlogN) 排序需要O(NlogN)的复杂度* 空间复杂度 : O(logN) java所使用的内置函数用的是快速排序需要 logN 的空间*/
class Solution0452 {public int findMinArrowShots(int[][] points) {
// Arrays.sort(points, (a, b) -> {//代码本身并没有提供对数组越界的保护措施
// if (a[0] != b[0]) {
// return a[0] - b[0];//比较了两个整数值 a[0] 和 b[0],如果这些值的差超出了整数的范围,就会产生溢出
// }
// return a[1] - b[1];
// });Arrays.sort(points, (a, b) -> {if (a[0] != b[0]) {return Long.compare(a[0], b[0]);}return Long.compare(a[1], b[1]);});//根据气球直径的开始坐标从小到大排序,使用Integer内置比较方法,不会溢出
// Arrays.sort(points, (a, b) -> Integer.compare(a[0], b[0]));//二维数组不溢出排序
// Arrays.sort(points, Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[0]));//二维数组不溢出排序int count = 1;for (int i = 1; i < points.length; i++) {
// for (int j = 0; j < points[i].length; j++) {
// System.out.print(points[i][j] + "、");
// }
// System.out.println();if (points[i][0] > points[i - 1][1]) {count++;} else {points[i][1] = Math.min(points[i - 1][1], points[i][1]);}}System.out.println(count);return count;}
}9.3、重叠区间问题
相似题目
0452. 用最少数量的箭引爆气球
0435. 无重叠区间
0763. 划分字母区间
0056. 合并区间
//0452. 用最少数量的箭引爆气球
for (int i = 1; i < points.length; i++) {if (points[i][0] > points[i - 1][1]) {count++;} else {points[i][1] = Math.min(points[i - 1][1], points[i][1]);}
}//0435. 无重叠区间
for (int i = 1; i < intervals.length; i++) {if (intervals[i][0] < intervals[i - 1][1]) {intervals[i][1] = Math.min(intervals[i - 1][1], intervals[i][1]);continue;} else {count++;}
}//0763. 划分字母区间
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {idx = Math.max(idx, edge[chars[i] - 'a']);if (i == idx) {list.add(i - last);last = i;}
}//0056. 合并区间
for (int i = 1; i < intervals.length; i++) {if (intervals[i][0] <= res.getLast()[1]) {int start = res.getLast()[0];int end = Math.max(intervals[i][1], res.getLast()[1]);res.removeLast();res.add(new int[]{start, end});} else {res.add(intervals[i]);}
}10、动态规划
略
11、单调栈
如果求一个元素右边第一个更大元素,单调栈就是递增的;栈头到栈底的顺序,要从小到大。
如果求一个元素右边第一个更小元素,单调栈就是递减的。
import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.LinkedList;/*** 739.每日温度*/
class Solution0739_2 {//版本1public int[] dailyTemperatures(int[] temperatures) {int lens = temperatures.length;int[] res = new int[lens];/**如果当前遍历的元素 大于栈顶元素,表示 栈顶元素的右边的最大的元素就是 当前遍历的元素,所以弹出 栈顶元素,并记录。如果栈不空的话,还要考虑新的栈顶与当前元素的大小关系。否则的话,可以直接入栈。注意,单调栈里 加入的元素是 下标。*/Deque<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<>();stack.push(0);for (int i = 1; i < lens; i++) {if (temperatures[i] <= temperatures[stack.peek()]) {//当前遍历元素小于等于栈顶元素,入栈stack.push(i);} else {//当前遍历元素大于栈顶元素,出栈while (!stack.isEmpty() && temperatures[i] > temperatures[stack.peek()]) {res[stack.peek()] = i - stack.peek();stack.pop();}stack.push(i);}}return res;}//版本2public int[] dailyTemperatures2(int[] temperatures) {int lens = temperatures.length;int[] res = new int[lens];Deque<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<>();for (int i = 0; i < lens; i++) {while (!stack.isEmpty() && temperatures[i] > temperatures[stack.peek()]) {res[stack.peek()] = i - stack.peek();stack.pop();}stack.push(i);}return res;}
}12、图论
12.1、dfs回溯模板
class Solution0797 {//深度优先遍历List<List<Integer>> ans;//用来存放满足条件的路径List<Integer> cnt;//用来保存dfs过程中的节点值public List<List<Integer>> allPathsSourceTarget(int[][] graph) {ans = new ArrayList<>();cnt = new ArrayList<>();cnt.add(0);//注意,0 号节点要加入 cnt 数组中dfs(graph, 0);return ans;}public void dfs(int[][] graph, int node) {if (node == graph.length - 1) {//如果当前节点是 n - 1,那么就保存这条路径ans.add(new ArrayList<>(cnt));return;}for (int index = 0; index < graph[node].length; index++) {int nextNode = graph[node][index];cnt.add(nextNode);dfs(graph, nextNode);cnt.remove(cnt.size() - 1);//回溯}}
}12.2、岛屿问题模板-dfs/bfs
广搜的搜索方式就适合于解决两个点之间的最短路径问题。
因为广搜是从起点出发,以起始点为中心一圈一圈进行搜索,一旦遇到终点,记录之前走过的节点就是一条最短路。
在 LeetCode 中,「岛屿问题」是一个系列系列问题,比如:
- 200. 岛屿数量 (Easy)
- 463. 岛屿的周长 (Easy)
- 695. 岛屿的最大面积 (Medium) 更改代码模板,条件判断应该是:grid[i][j] == 1,而不是 grid[i][j] == '1',不要再写错了!
- 827. 最大人工岛 (Hard)
/**
0:海洋
1:陆地
*/
class Solution0200_4 {//dfspublic int numIslands(char[][] grid) {int count = 0;//记录找到的岛屿数量for (int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++) {if (grid[i][j] == '1') {//找到“1”,count+1,同时淹没这个岛屿dfs(grid, i, j);//深搜//bfs(grid, i, j);//广搜count++;}}}return count;}//使用DFS“淹没”岛屿private void dfs(char[][] grid, int i, int j) {//搜索边界:索引越界或遍历到了"0"则终止if (i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= grid.length || j >= grid[0].length || grid[i][j] == '0') return;//根据"每座岛屿只能由水平方向或竖直方向上相邻的陆地连接形成",对上下左右的相邻顶点进行dfsgrid[i][j] = '0';//将这块土地标记为“0”int res = 1;//可选,计算面积dfs(grid, i + 1, j); //res += dfs(grid, i + 1, j); //可选,计算面积dfs(grid, i - 1, j); //res += dfs(grid, i - 1, j); //可选,计算面积dfs(grid, i, j + 1); //res += dfs(grid, i, j + 1); //可选,计算面积dfs(grid, i, j - 1); //res += dfs(grid, i, j - 1); //可选,计算面积}private void bfs(char[][] grid, int i, int j) {int area = 0;//可选,计算面积Queue<int[]> list = new LinkedList<>();list.add(new int[]{i, j});while (!list.isEmpty()) {int[] cur = list.remove();i = cur[0];j = cur[1];if (0 <= i && i < grid.length && 0 <= j && j < grid[0].length && grid[i][j] == '1') {area++;//可选,计算面积grid[i][j] = '0';list.add(new int[]{i + 1, j});list.add(new int[]{i - 1, j});list.add(new int[]{i, j + 1});list.add(new int[]{i, j - 1});}}}
}
上面的代码使用的是深度优先搜索DFS的做法。为了统计岛屿数量同时不重复记录,每当我们搜索到一个岛后,
就将这个岛 “淹没” —— 将这个岛所占的地方从 “1” 改为 “0”,这样就不用担心后续会重复记录这个岛屿了。
而DFS的过程就体现在 “淹没” 这一步中,详见代码:dfs。😘加油~